linux basic learning [8]
Keywords:
Linux
snapshot
network
RHEL
vim
Virtual Machine Management
I. Installing Virtual Machines with Local Mirrors
1. Graphic Interface Installation
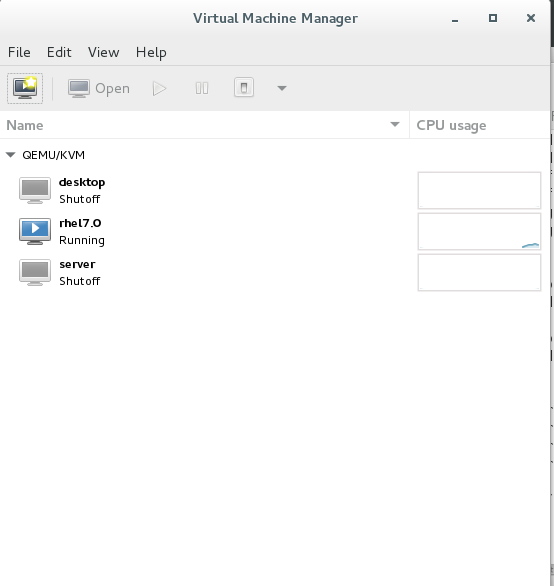
virt-manager ##Open Virtual Machine Manager
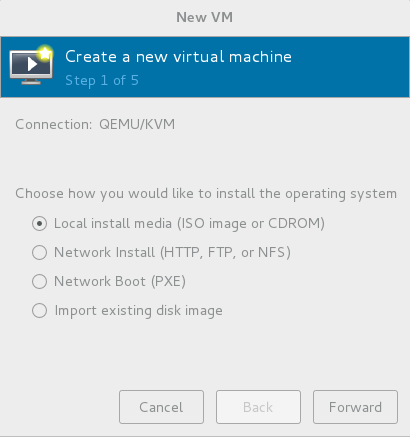
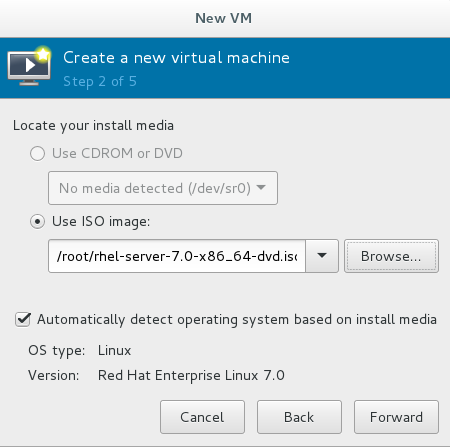
File - > New Virtual Machine, select the local image
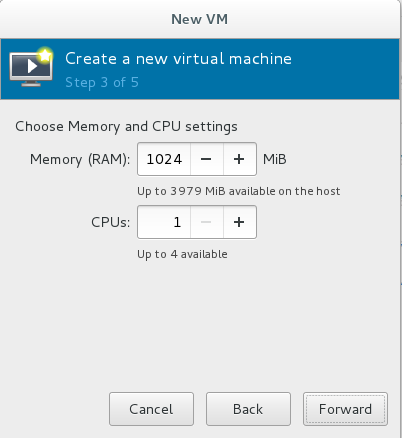
Select the size of the immediate storage space and CPU
Select allocated storage capacity
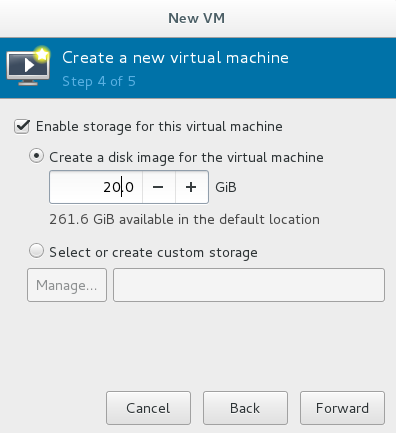
Enter Virtual Machine Name into Installation
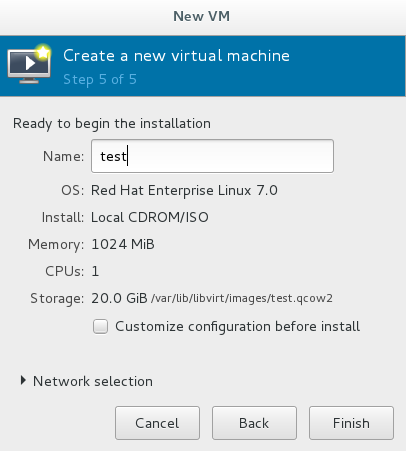
Enter the installation interface and select the installation

Choose the language in the installation process
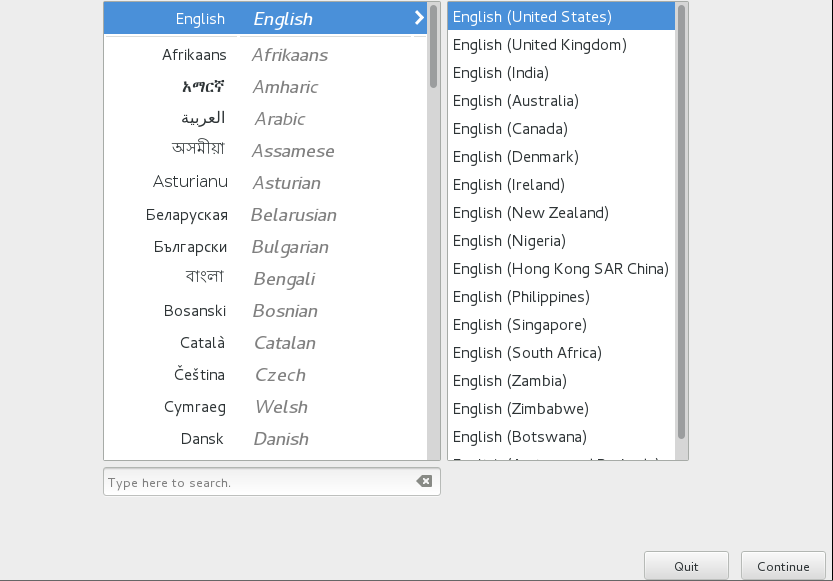
Select time zone/language/install software/mirror source/partition
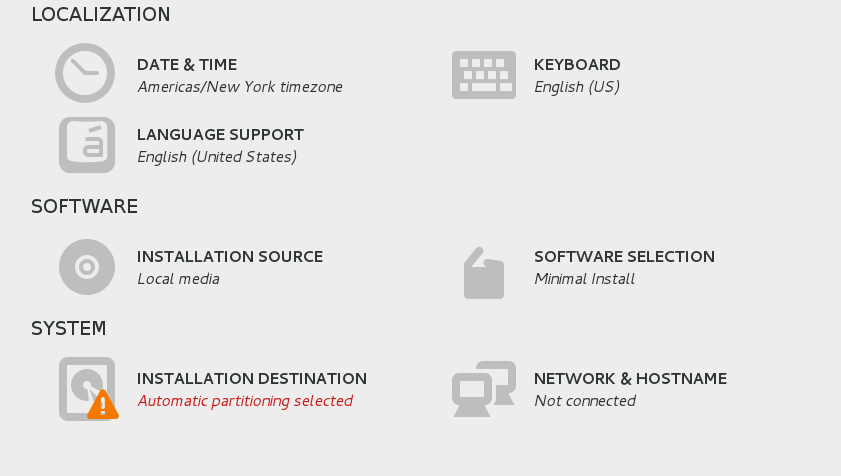
Set the root password and default login user information, and restart after completion.
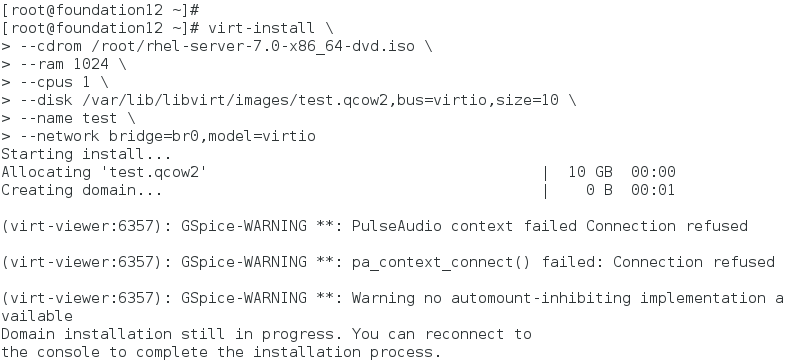
2. Command Installation (\ Represents command line feed, actually a command)
virt-install \ #Installation of Virtual Machines
--cdrom /root/rhel-server-7.0-x86_64-dvd.iso \ #Selection Source
--ram 1024 \ #Select immediate storage
--cpus 1 \ #Choose cpu
--disk /var/lib/libvirt/images/test.qcow2,bus=virtio,size=10 \ #Select partition
--name test \ #Virtual Machine Naming
--network bridge=br0,model=virtio #Select Network Configuration
Command mode execution
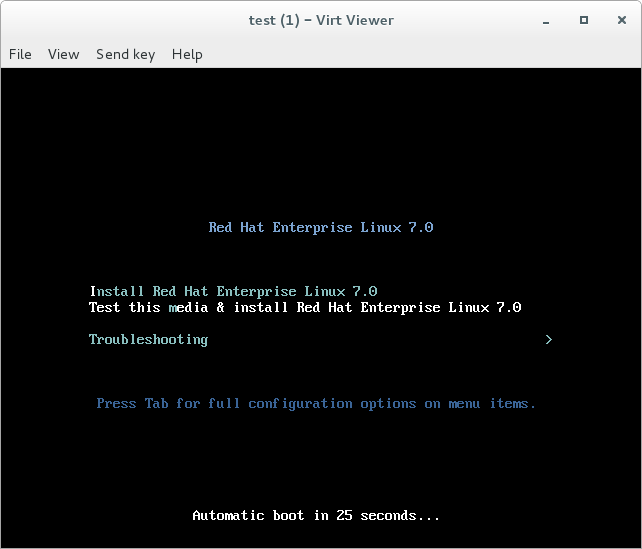
Enter the graphical installation interface after execution
3. Batch Installation of Executing Scripts
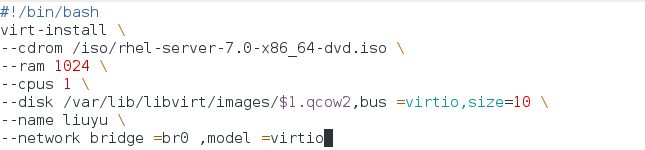
vim create_vm.sh ##Editing scripts
#!/bin/bash ##First line selection shell
virt-install \ #Installation of Virtual Machines
--cdrom /root/rhel-server-7.0-x86_64-dvd.iso \ #Selection Source
--ram 1024 \ #Select immediate storage
--cpus 1 \ #Choose cpu
--disk /var/lib/libvirt/images/test.qcow2,bus=virtio,size=10 \ #Select partition
--name test \ #Virtual Machine Naming
--network bridge=br0,model=virtio #Select Network Configuration
chmod +x create_vm.sh ##Add Execution Permissions
./create_vm.sh ##Execution script
Editing configuration files
Add Execution Permissions and Execute Press

2. Virtual Machine Management Command
virt-manager ##Open Virtual Machine Manager
virsh list ##Display the virtual machine being opened
virsh list --all ##View all virtual machines
virsh start vmname ##Open virtual machine vmname
virsh shutdown vmname ##Turn off virtual machine vmname (after entering the system)
virsh destory vmname ##Forced shutdown of virtual machine vmname (equivalent to power off)
virsh undefine vmname ##Delete virtual machine vmname
virsh-viewer vmname ##Display virtual machine vmname
virsh list shows the virtual machine being opened
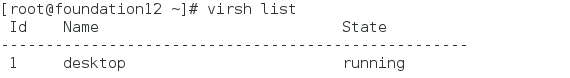
virsh list --all view all virtual machines

virsh destroy forces virtual machine shutdown

virsh undefine deletes virtual machines

3. Restoring Virtual Machines Using Configuration Files and Mirrors
Permanent recovery
mv /mnt/ /var/lib/libvirt/images/.qcow2 ##Mobile Mirror File
/etc/libvirt/qemu/.xml ##Hardware Profile Directory
virsh create .xml ##Using Hardware Information File to Start Virtual Machine
virsh define .xml ##Permanent recovery virtual machine vmname
3. Make snapshots
vim snapshot.sh ##Editing scripts
#!/bin/bash
qemu-img create -f qcow2 -b /var/lib/libvirt/images/$1.qcow2 /var/lib/libvirt/images/$2.qcow2
##Create a snapshot named $2 with $1 as the mirror
virt-install \ ##Installation of Virtual Machines
--name $2 \ ##Name it the second variable
--ram 1024 \ ##Set the size of the immediate storage space
--cpus 1 \ ##Setting up cpu
--disk /var/lib/libvirt/images/$2.qcow2,bus=virtio \ ##Set the storage file to $2.qcow2
--network bridge=br0,model=virtio \ ##Setting up Virtual Machine Network Settings
--import & ##Background output
./snapshot.sh rhel7.0 test ##Create a test snapshot with rhel as the mirror
Where $1/$2 represents the first/second input variable
IV. Reset Virtual Machine Script
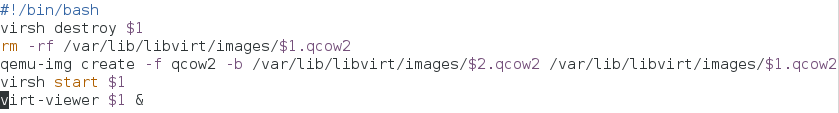
vim reset.sh ##Editing scripts
#!/bin/bash
virsh destroy $1 ##Force virtual machine shutdown $1
rm -rf /var/lib/libvirt/images/$1.qcow2 ##Delete the corresponding snapshot
qemu-img create -f qcow2 -b /var/lib/libvirt/images/$2.qcow2 /var/lib/libvirt/images/$1.qcow2
##Create a snapshot named $1 with $2 as the mirror
virsh start $1 ##Open virtual machine $1
virt-viewer $1 & ##Background Display Virtual Machine $1
Posted by ahmad03 on Fri, 25 Jan 2019 10:42:14 -0800


















