system log
I. Management of System Log
cat /var/log/messages ##View the default saved logs
1. Management of log collection service rsyslog
/var/log/messages ##Service Information Log
/var/lgo/secure ##System login log
/var/log/cron ##Timing Task Log
/var/log/maillog ##Mail log
/var/log/boot.log ##System Startup Log
/var/log/file ##Log Acquisition Rules
Log Category:
auth ##Log generated by pam
authpriv ##Authentication messages for login information such as ssh, ftp, etc.
cron ##Time Task Relevance
kern ##kernel
lpr ##Printing
mail ##mail
mark(syslog)-rsyslog ##Information within services, time identification
news ##Newsgroup
user ##Relevant information generated by user programs
uucp ##unix to unix copy, related communication between unix hosts
local 1~7 ##Custom Logging Device
Log level:
debug ##With debugging information, log information is the most.
info ##Logs of general information, most commonly used
notice ##Information on the most important general conditions
warning ##Warning level
err ##Error level, typing information that a function or module is not working properly
crit ##Seriousness level, information that prevents the whole system or software from working properly
alert ##Information requiring immediate modification
emerg ##Serious information such as kernel crash
none ##Nothing is recorded
Note: From top to bottom, from low to high, less and less information is recorded.
2. Realizing Log Remote Synchronization
Log sender:
vim /etc/rsyslog.conf ##Change the sender rsyslog service configuration file
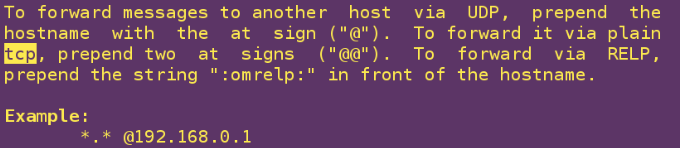
*.* ##The former * denotes all categories and the latter * denotes all levels
*.* @172.25.254.212 ##All logs at all levels are sent to ip using udp protocol
systemctl restart rsyslog ##Restart after configuration changes

man 5 rsyslog View Writing
@ means tcp protocol and @ means udp protocol.
Adding Statements to the Configuration File

Log recipients:
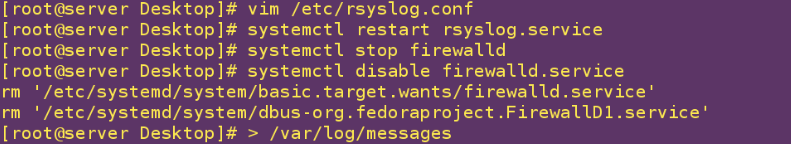
vim /etc/rsyslog.conf ##Change the recipient rsyslog service configuration file
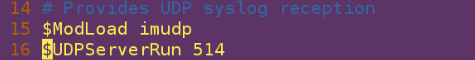
15 $ModLoad imudp ##Open the receiving module
16 $UDPServerRun 514 ##Open the acceptance port
systemctl restart rsyslog ##Restart after configuration changes
systemctl stop firewalld ##Close the firewall
systemctl disabled firewalld ##Set up boot-up not to start
> /var/log/messages ##Clear log
Log sender:
logger test1 # Send message test1 for testing
Cat/var/log/messages ## View sender log
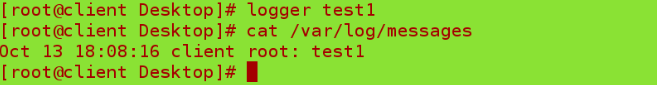
Log recipients:
Cat/var/log/messages ## View recipient logs

3. Setting the format of log collection
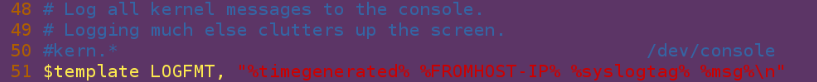
vim /etc/rsyslog.conf ##Change the recipient rsyslog service configuration file
$template LOGFMT, "%timegenerated% %FROMHOST-IP% %syslogtag% %msg%\n"
##Format, LOGFMT as the format variable, followed by time, ip, label, log information
4. Time Synchronization Service
Server:
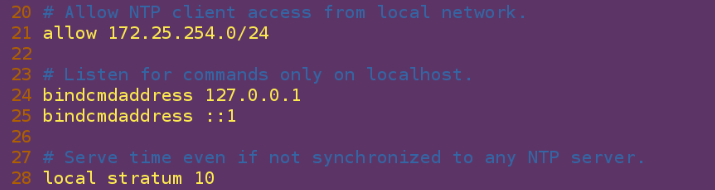
vim /etc/chronyd.conf ##Change Time Synchronization Profile
23 allow 172.25.254.0/24 ##Allowing User Synchronization Time for Corresponding Network Segments
30 local stratum 10 ##As a server time source, not synchronized by others
systemctl restart chronyd ##Restart after configuration
Restart after configuration

Client:
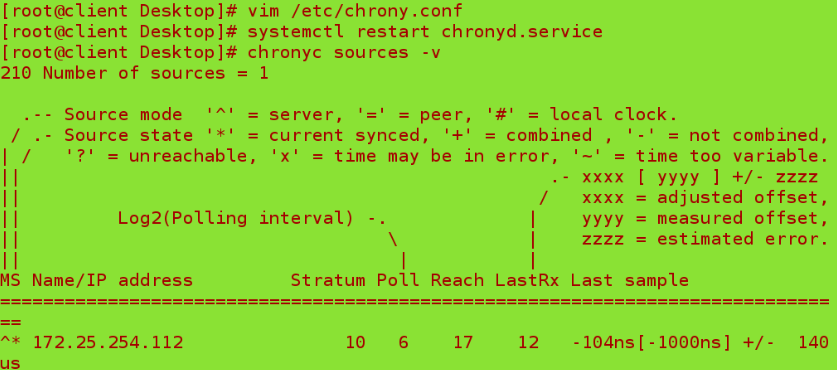
vim /etc/chronyd.conf ##Change client configuration file
server 172.25.254.112 iburst ##Add this statement to the configuration file, and the local machine immediately synchronizes the time of 112 hosts
systemctl restart chronyd ##Restart after configuration
chronyc sources -v ##Test synchronization
Adding Statements to the Configuration File

Where ^* indicates successful synchronization
5. Time Setting
Time datectl # # view time setting
Time calculation method, UTC (Greenwich Time + Time Zone)
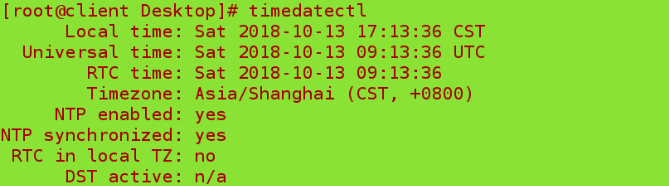
timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Shanghai ##Setting Time Zone
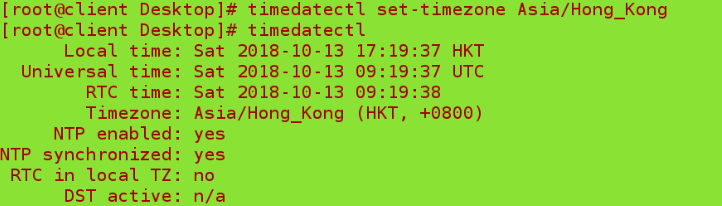
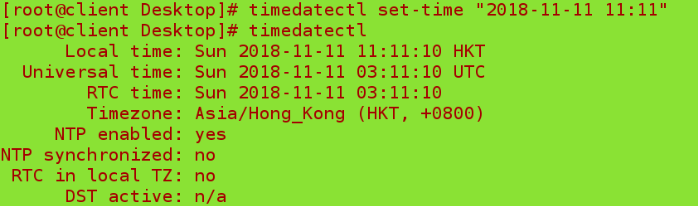
timedatectl set-time "2018-11-13 11:11" ##Set time
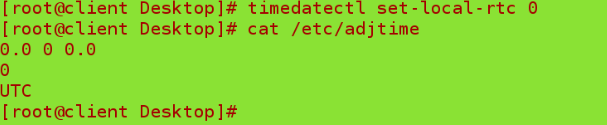
timedatectl set-local-rtc 0 ##Set whether UTC time 0 is 1 or not
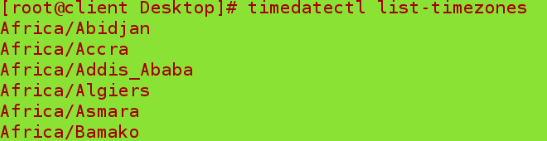
timedatectl list-timezone ##List time zones
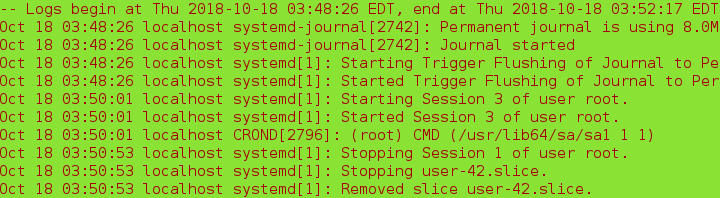
6. View logs
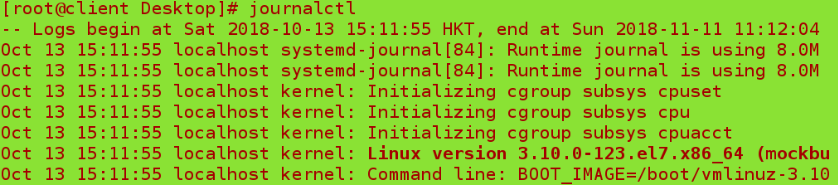
journalctl ##Log Viewing Tool
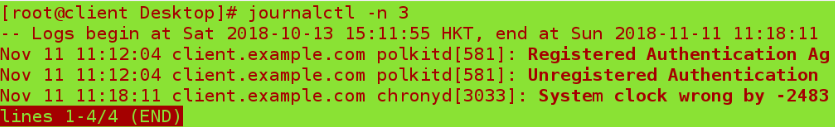
journalctl -n 3 ##View the last three logs
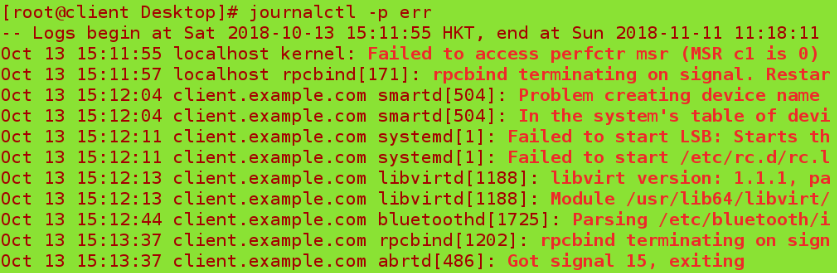
journalctl -p err ##View the error log
journalctl --since ##View logs from a specific time
journalctl --until ##View the log at a specific time
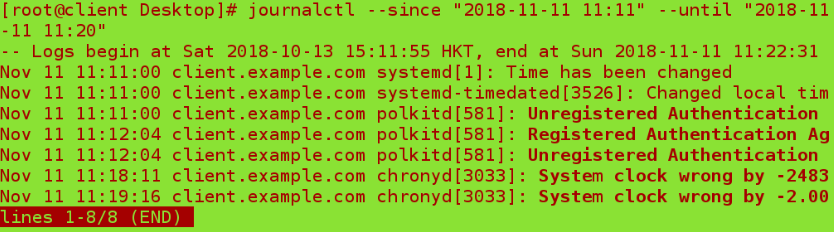
7. Save system logs
mkdir /var/log/journal ##Create a directory for saving
chgrp systemd-journal /var/log/journal ##Change group
chmod g+s /var/log/journal ##Adding coercive bits
ps aux | grep systemmd-journal ##Screening process
killall -1 systemd-journald ##Reload all related processes
ls /var/log/journal ##Display saved log file directories
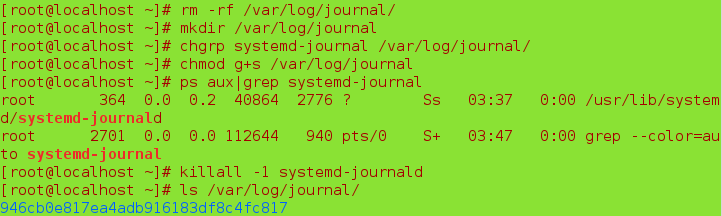
You can still view pre-restart logs through journalctl after restart