On the JDBC operation of Mysql database
The general way of JAVA operating database
1. Loading drive
The purpose of loading driver is to make Java have the ability to link the specified database.
Java load driver only needs one line of code
//1. Loading drive Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
2. Create a connection
Create a connection between memory and database
//Package to import import java.sql.Connection; //Code to create a connection Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/user?useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&user=root&password=261630"); //jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306 / connect Mysql database software, no need to change //user? user is the name of the database that needs to be connected. The database I use is user, so it is "user?", which changes with the database name you use. //If the database name used is dbem, it is "dbem?" //Usessl = true & characterencoding = UTF-8 connection mode and encoding mode, no need to change //&User = root & password = 261630 user is the account used for database connection. Generally, the default is "root", and password is the password used for connection. //It is set when Mysql is installed. It changes with the setting when Mysql software is installed.
3. Write sql statement
String sql="select * from userInfo";
4. Get the statement object
statement object can be used to execute sql statements
PreparedStatement statement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
5. Execute sql to get result set
7. Close resources
//This is a encapsulated method for closing resources, which can be modified according to resource usage. public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement statement, Connection connection){ try { if(connection!=null){ connection.close(); } if(statement!=null){ statement.close(); } if(rs!=null){ rs.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
Sample code (display all data in the table)
Database name used: user
There is only one table in the database: userInfo
There are three elements in the table: ID,userName,userPassWord
ID int(10);
userName varchar(50);
userPassWord varchar(50);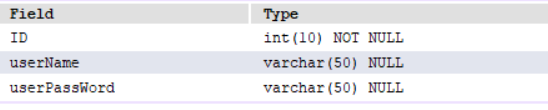
import java.sql.*; public class findAll { public static void main(String[] args) { ResultSet rs=null; PreparedStatement statement=null; Connection connection=null; try { //1. Loading drive Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2. Create a connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection ("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/user?useSSL=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&user=root&password=261630"); System.out.println("Connection created successfully"); //3. write sql String sql="select * from userinfo"; //4. Get the statement object statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //5. Execute sql to get result set rs = statement.executeQuery(); //6. Processing result set - output display while (rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)); System.out.println(rs.getString(2)); System.out.println(rs.getString(3)); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //7. Close resources if(rs!=null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(statement!=null){ try { statement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(connection!=null){ try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }