Delete the given node in the linked list
leetcode: delete the given node in the linked list
Idea:
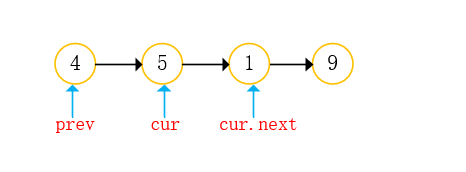
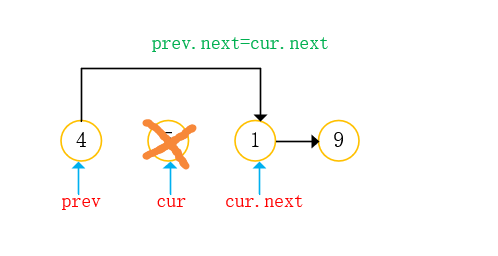
- Find the node to delete;
- Change the reference of the node to delete the node (note the difference between the deletion of the head node and the deletion of the non head node);
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
//When the node is empty
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode prev=null; //prev marks the previous node of cur
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==val){
//Delete Vertex
//If it is a header node
if(prev==null){
head=cur.next;
cur=head;
}else{
//Not a header node
prev.next=cur.next;
cur=prev;
}
}else{
prev=cur;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
Reverse of linked list (reverse linked list)
leetcode: reverse linked list
Idea:
With three references: cur prev next;
Traverse the linked list, and modify the point of the current node to the previous reference to it; Because a node does not reference its previous node, its previous node must be saved in advance. Before changing the reference, it is also necessary to save its next node;
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//When the linked list is empty
if(head==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode prev=null; //Point to the previous node of the current node
ListNode next=null; //Points to the next node of the current node
while(cur!=null){
//Indicates that the node exists
//Save the next node before modifying
next=cur.next;
//Modify reference
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
}
return prev;
}
}
Find the middle node of the linked list
leetcode: intermediate node of linked list

Idea:
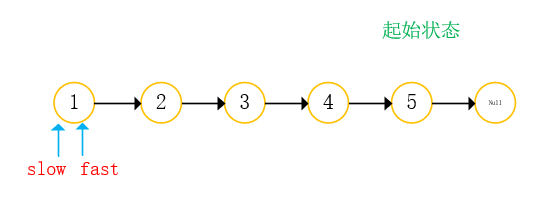
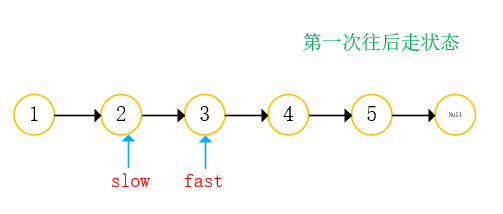
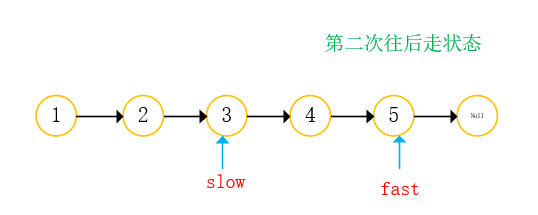
With two references: fast slow;
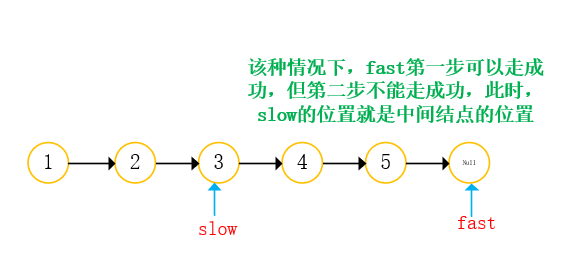
- Both references go back from the starting position. Fast references take two steps at a time and slow references take one step at a time;
- When the fast reference is empty, return the slow reference;
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
//With fast and slow references
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
//Make sure you can succeed in both steps
fast=fast.next.next; //fast takes two steps at a time
slow=slow.next; //slow one step at a time
}
return slow;
}
}
reflection:
In this topic, when the number of nodes is even, the next node is returned. What should I do if I want to return to the previous node?
Method: save the prev of the previous node of slow. When there are even nodes and you want to return the previous one, you only need to return prev;
if(fast)=null,return prev; // Even node
if(fast)!=null,return slow; // Odd node
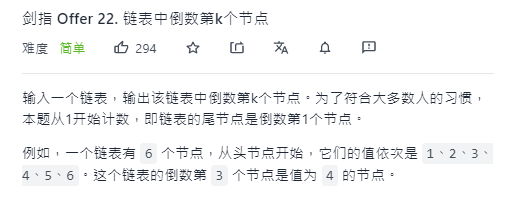
The penultimate node of the linked list
leetcode: the penultimate node of the linked list

Idea:
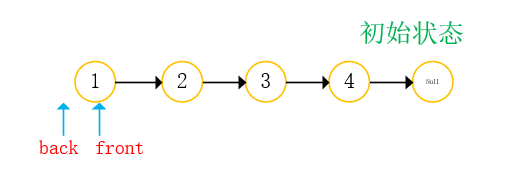
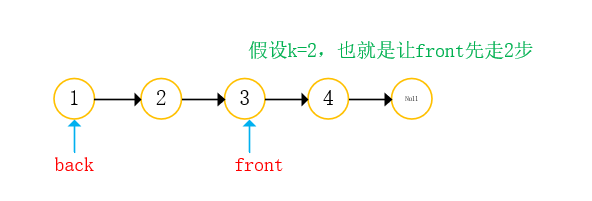
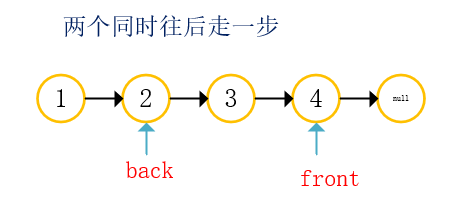
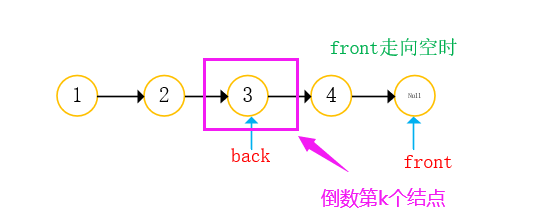
With two references: front back;
- front take step K from the starting position;
- Front and back go back at the same time, and end when front is empty;
- The position of back is just the position of the penultimate K node;
Illustration:
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
//With two references
ListNode front=head;
ListNode back=head;
//Let front go back K steps first
while(0!=k){
if(front==null){
return null;
}
front=front.next;
k--;
}
//Let two references go at the same time
while(front!=null){
front=front.next; //Take a step
back=back.next; //Take a step
}
return back;
}
}
The first public node of the linked list
leetcode: the first public node of the linked list
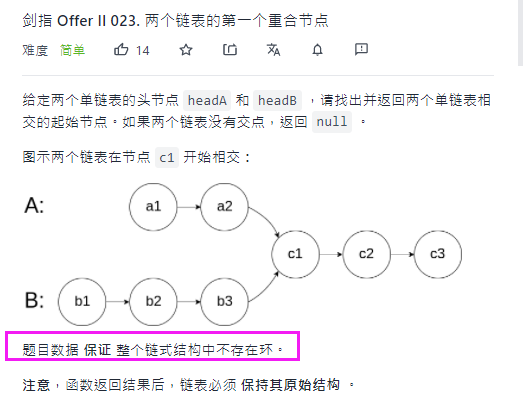
Idea:
- Judge whether they intersect (find the last node - > traverse the linked list to see whether they are equal);
- Find the intersection;
It is known from the title that there are three situations where the linked list does not have a ring and the linked list without a ring intersects as follows:

Code implementation:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
//When any linked list is empty, it is impossible to intersect
if(headA==null ||headB==null){
return null;
}
//Traverse the linked list to find the intersection point
//Traverse linked list A
ListNode curA=headA;
int sizeA=1;
while(curA.next!=null){
sizeA++; //Traverse a node and increase sizeA by one
curA=curA.next;
}
//Traverse linked list B
ListNode curB=headB;
int sizeB=1;
while(curB.next!=null){
sizeB++;//Traverse a node and sizeB adds one
curB=curB.next;
}
if(curA!=curB){
return null;
}
//After the above implementation, it will certainly intersect
//Find intersection
int gap=sizeA-sizeB;
curA=headA;
curB=headB;
if(gap>=0){
//A is longer than B
while(0!=gap--){
curA=curA.next;
}
}else{
while(0!=gap++){
curB=curB.next;
}
}
while(curA!=curB){
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
}
return curA;
}
}
Split linked list
leetcode: split linked list
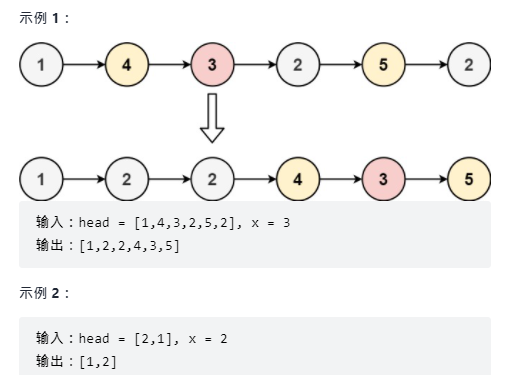
Idea:
- Construct an empty linked list of two leading nodes: lessHead greatHead;
- lessHead is used to store nodes less than the given value, and greatHead is used to store nodes greater than the given value;
- Specify the tail node of lessHead as the head node of greatHead (note that it is the leading node);
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
//When the linked list is empty
if(head==null){
return null;
}
//Give lessHead and greatHead to the linked list of the leading node
ListNode lessHead =new ListNode(0); //Save nodes less than a specific value
ListNode tailL= lessHead;
ListNode greatHead =new ListNode(0); //Save nodes greater than a specific value
ListNode tailG =greatHead;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val<x){
tailL.next=cur;
tailL=cur;
}else{
tailG.next=cur;
tailG=cur;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
//Link up
//Both take the lead node, so point to greatHead.next
tailL.next=greatHead.next;
tailG.next=null;
return lessHead.next;
}
}
Palindrome linked list
leetcode: palindrome linked list
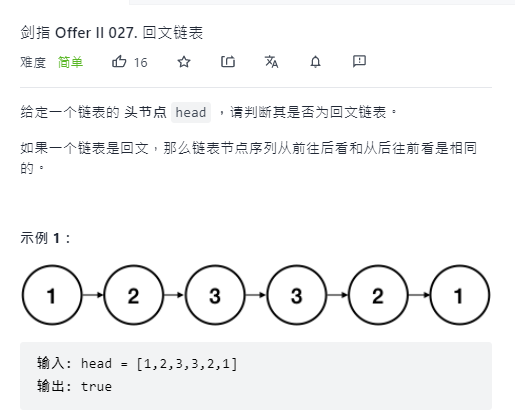
Idea:
- Find the middle node of the linked list, and divide the linked list into head1 and head2 with the middle node;
- Reverse the last linked list;
- Compare whether the node values of the two linked lists are equal in turn;
- Link the linked list;
Code implementation:
class Solution {
//Method of finding intermediate node
public ListNode getMiddleNode(ListNode head){
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode prev=null;
//Make sure fast can succeed twice
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
prev=slow;
slow=slow.next;
}
if(fast==null){
return prev;
}
return slow;
}
//Reverse linked list
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode next=null;
ListNode prev=null;
while(cur!=null){
//Save the location of next before modifying
next=cur.next;
//Modify reference
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
}
return prev;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
//1. Find the middle node of the linked list
ListNode mid=getMiddleNode(head);
ListNode B=mid.next;
//2. Reverse the last linked list
B= reverseList(B);
//3. Compare the value fields of the two linked lists in turn
ListNode curA=head;
ListNode curB=B;
boolean ret=true;
while(curA!=null && curB!=null){
if(curA.val!=curB.val){
ret=false;
break;
}
curA=curA.next;
curB=curB.next;
}
//4. Link the linked list
B=reverseList(B);
mid.next=B;
return ret;
}
}
Replication of complex linked list
leetcode: copy of complex linked list
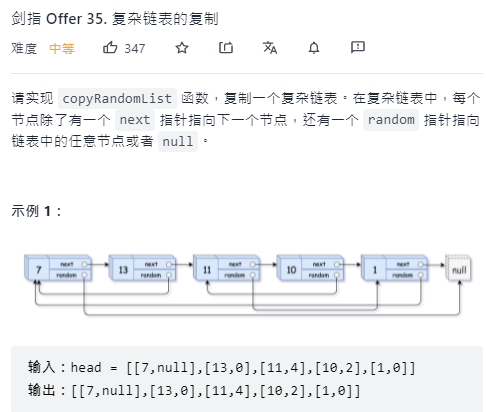
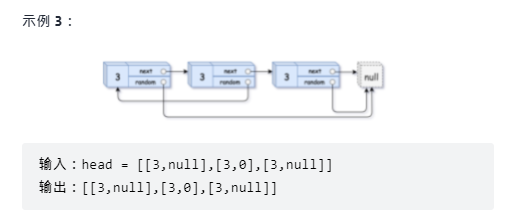
Idea:
- Insert a new node with the same value as the original node after each node of the original linked list;
- Assign a value to the random reference of the newly inserted node;
- Disconnect the newly inserted node;
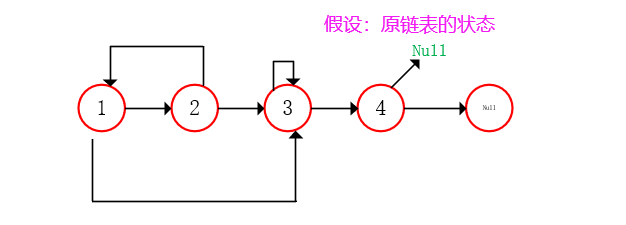
Insert a new linked list of the same node
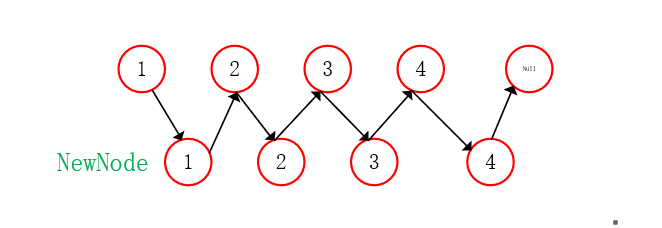
Assign a value to each random reference
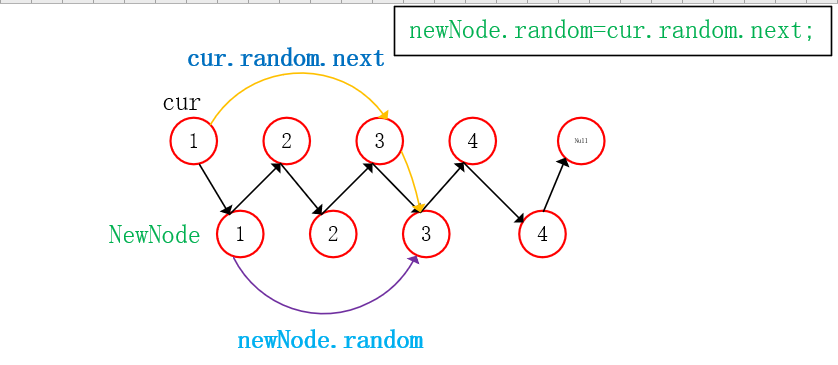
cur at the first node:
The inserted node is broken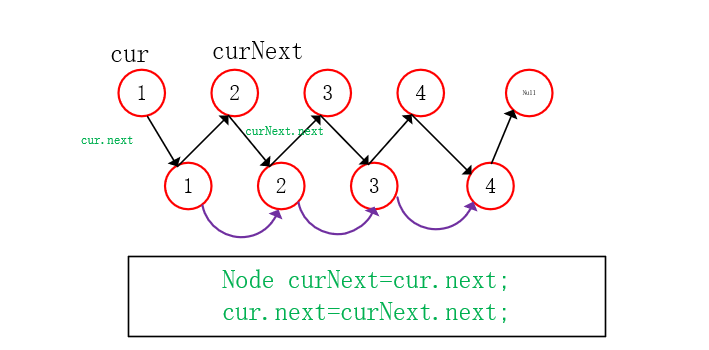
Code implementation:
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
//When the linked list is empty
if(head==null){
return null;
}
//1. Insert nodes with equal values after each node of the original linked list
Node cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
//new a node with the same value range as the original node
Node newNode=new Node(cur.val);
newNode.next=cur.next;
cur.next=newNode;
cur=newNode.next;
}
//2. Assign a value to the random reference of the newly inserted node
cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
Node newNode =cur.next;
if(cur.random!=null){
newNode.random=cur.random.next;
}
cur=newNode.next;
}
//Disconnect the inserted node
Node newHead=head.next;
cur=head;
while(cur.next!=null){
Node curNext=cur.next;
cur.next=curNext.next;
cur=curNext;
}
return newHead;
}
}