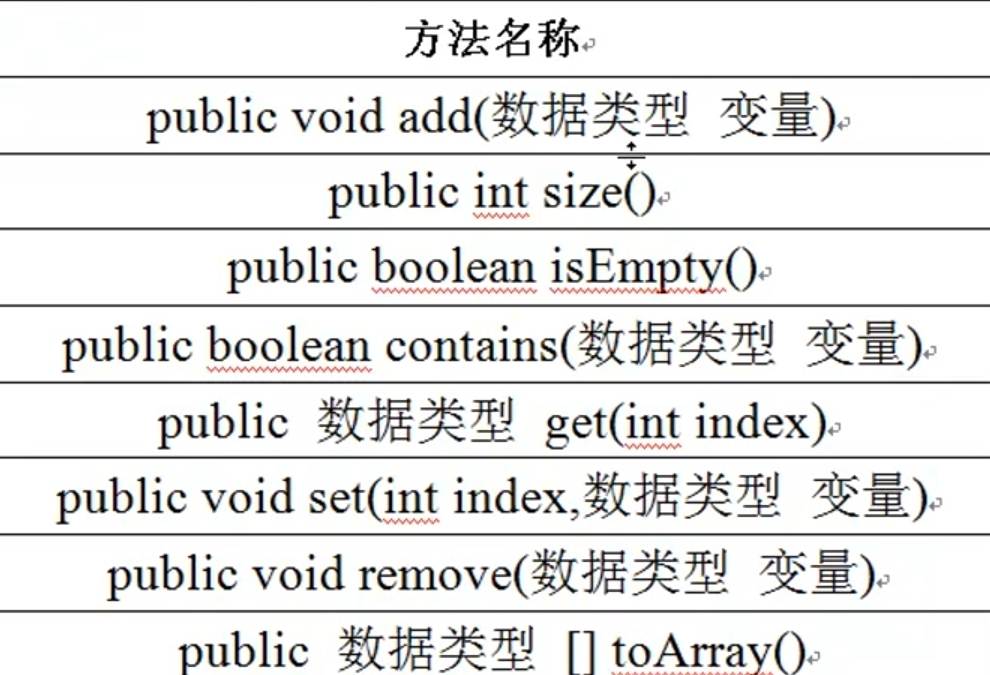
catalogue
1: Only realize the addition and access of linked list
Internal class access properties
2: The content stored in the linked list is the object of the class
1: Only realize the addition and access of linked list
class Link{
private class Node{//Internal class Node
private String data;
private Node next;
public Node(String data) {
this.data=data;
}
public void addNode(Node newNode) {//Add node
if(this.next==null) {
this.next=newNode;
}
else {
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
/*Handle array data in Node class*/
public void toArrayNode() {
/*
1:First call: Link class this=Link.root
2:The second call: Node class this=Link.root.next
*/
//Add Link. Reason: the internal class uses the flag of the external class attribute
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot++]=this.data;
if(this.next!=null) {
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
}//End of Node class
private Node root;//Root node
private int count=0;
private int foot;//Node index subscript
private String[] retArray;//Returned array
public void add(String data) {
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if(this.root==null) {
this.root=newNode;
}
else {
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
count++;
}
/*toArray()Method to return an array*/
public String[] toArray() {
if(this.root==null) return null;//Judge whether the linked list has data
this.foot=0;//Traverse from the head of the linked list every time
/*Open up the array according to the saved content*/
this.retArray=new String[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retArray;
}
}
public class transfer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Link all=new Link();
all.add("aaa");
all.add("bbb");
all.add("ccc");
all.add("ddd");
String []data=all.toArray();
for(int x=0;x<data.length;x++) {
System.out.println(data[x]);
}
}
}The following only analyzes the conversion of linked list to dynamic array access
class Link{
private class Node {/ / internal class Node
private String data;
private Node next;
public Node(String data) {
this.data=data;
}
public void toArrayNode() {
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot++]=this.data;
if(this.next!=null) {
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
}// End of Node class
private Node root;// Root node
private int count=0;
private int foot;// Node index subscript
private String[] retArray;// Returned array
public String[] toArray() {
if(this.root==null) return null;
this.foot=0;
this.retArray=new String[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retArray;
}
}
Analysis: first, define an array in the Link class: string[] retArray; Pass function: String [] toArray() to convert linked list into dynamic array. This function first determines the existence of the root node, and then ensures ab initio traversal by setting the index foot to 0. this.retArray=new String[this.count]; Open up space for existing linked list data.
The specific data processing is implemented through toArrayNode() of Node class
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot++]=this.data;
Since both retArray and foot are private attributes of the external class Link, the class name should be added to the internal class
this.retArray[this.foot + +] is the current object operation.
Finally, you want to access the output: the main program needs to
String []data=all.toArray();
for(int x=0;x<data.length;x++) {
System.out.println(data[x]); }
Assign the returned array retArray directly to the allocated data
Internal class access properties

2: The content stored in the linked list is the object of the class
class Book{
private String title;
private double price;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.price=price;
this.title=title;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "Book name:"+this.title+";"+"Book price:"+this.price;
}
//Because the linked list has the functions of contains() and remove(), there should be object comparison operations in the class
public boolean compare(Book book) {
if(book==null) {
return false;
}
if(this==book) {
return true;
}
if(this.price==book.price&&this.title.equals(book.title)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}This is a Book class. The attributes are price and book name. The methods include construction method and getInfo() method to access private attribute information. Because the linked list has delete and query operations, a compare function is added to judge whether an object is found. Two judgments of the same object: 1: this==book, the memory address is the same, and the pointer points to the same area. 2: The values of private properties are exactly the same.
Modification of main contents:
private class Node{
private Book data;// The data is: the object name of the class
private Node next;
public Node(Book data) {
this.data=data;
}}
private Node root;
private Book[] retArray;// The contents stored in the array become object names
Link class: public void add(Book data)
Main program: all.add(new Book("java",17.9))// Note that objects are instantiated
Increase only:
class Book{
private String title;
private double price;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.price=price;
this.title=title;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "Book name:"+this.title+";"+"Book price:"+this.price;
}
//Because the linked list has the functions of contains() and remove(), there should be object comparison operations in the class
public boolean compare(Book book) {
if(book==null) {
return false;
}
if(this==book) {
return true;
}
if(this.price==book.price&&this.title.equals(book.title)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}//end Book
class Link{
private class Node{
private Book data;
private Node next;
public Node(Book data) {
this.data=data;
}
public void addNode(Node newNode) {//Internal class: add
if(this.next==null) {
this.next=newNode;
}
else {
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public void toArrayNode() {//Internal class: the node saves data and becomes an object array
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot++]=this.data;
if(this.next!=null) {
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
}//end Node
private Node root;
private int count=0;
private int foot;
private Book[] retArray;
public void add(Book data) {/*increase*/
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if(this.root==null) {
this.root=newNode;
}
else {
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
public Book[] toArray() {/*Link:Return array*/
if(this.root==null) return null;
this.foot=0;
this.retArray=new Book[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();//Assign values to each element of retArray from the root node
return this.retArray;
}
}
public class transfer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Link all=new Link();
all.add(new Book("java",17.9));
all.add(new Book("jsp",33.3));
Book[] data=all.toArray();
for(int x=0;x<data.length;x++) {
System.out.println(data[x].getInfo());
}
}
}All implemented: add, delete, modify and query
class Book{
private String title;
private double price;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.price=price;
this.title=title;
}
public String getInfo() {
return "name:"+this.title+";"+"price:"+this.price;
}
//Because the linked list has the functions of contains() and remove(), there should be object comparison operations in the class
public boolean compare(Book book) {
if(book==null) {
return false;
}
if(this==book) {
return true;
}
if(this.price==book.price&&this.title.equals(book.title)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
}//end Book
class Link{
private class Node{
private Book data;
private Node next;
public Node(Book data) {
this.data=data;
}
public void addNode(Node newNode) {//Internal class: add
if(this.next==null) {
this.next=newNode;
}
else {
this.next.addNode(newNode);
}
}
public Book getNode(int index) {//Internal class: query
if(Link.this.foot++==index) {
return this.data;
}
return this.next.getNode(index);
}
public boolean containsNode(Book data) {//Internal class: Judgment
if(data.compare(this.data)) {
return true;
}
else {
if(this.next!=null)
return this.next.containsNode(data);
else
return false;
}
}
public void setNode(Book data,int index) {//Internal classes: modifying
if(Link.this.foot++==index) {
this.data=data;
}
else {
this.next.setNode(data, index);
}
}
public void removeNode(Node pre,Book data) {//Delete (save previous node)
if(data.compare(this.data)) {//Comparison of data
pre.next=this.next;
}
else {
this.next.removeNode(this, data);
}
}
public void toArrayNode() {//Internal class: the node saves data and becomes an object array
Link.this.retArray[Link.this.foot++]=this.data;
if(this.next!=null) {
this.next.toArrayNode();
}
}
}//end Node
private Node root;
private int count=0;
private int foot;
private Book[] retArray;
public void add(Book data) {/*increase*/
Node newNode=new Node(data);
if(this.root==null) {
this.root=newNode;
}
else {
this.root.addNode(newNode);
}
this.count++;
}
public Book get(int index) {//Query a specific node
if(index>this.count) return null;
this.foot=0;
return this.root.getNode(index);
}
public boolean contains(Book data) {//Judge the inclusion relationship (check whether there is data before judging)
if(this.root==null||data==null) return false;
this.foot=0;
return this.root.containsNode(data);
}
public void set(Book data,int index) {//change
if(index>this.count) return;
this.foot=0;
this.root.setNode(data,index);
}
public int size() {//Get the length of the linked list
return this.count;
}
public void remove(Book data) {//Delete
if(this.contains(data)) {
if(data.equals(this.root.data)) {
this.root=this.root.next;
}
else {
this.root.next.removeNode(this.root,data);//Next node
}
this.count--;
}
}
public Book[] toArray() {/*Link:Return array*/
if(this.root==null) return null;
this.foot=0;
this.retArray=new Book[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();//Assign values to each element of retArray from the root node
return this.retArray;
}
}
public class transfer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Link all=new Link();
all.add(new Book("aaa",111));
all.add(new Book("bbb",222));
all.add(new Book("ccc",333));
all.add(new Book("ddd",444));
all.add(new Book("eee",555));
all.remove(new Book("ddd",444));
all.remove(new Book("ccc",333));
Book[] data=all.toArray();
for(int x=0;x<data.length;x++) {
System.out.println(data[x].getInfo());
}
}
}This program description: the linked list is a dynamic object array
private Book retArray[ ]=private Book[ ] retArray;