First, thinking
class Child : public Parent{ };In the code, the colon represents the inheritance relationship, and the Parent represents the inherited class. What is the meaning of public?
Programming experiment:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Parent
{
};
class Child_A : public Parent
{
};
class Child_B : protected Parent
{
};
class Child_C : private Parent
{
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}2, Different ways of inheritance
Three different inheritance methods are supported in C + +
-
public inheritance
- The parent class members keep the original access principle in the child class
-
private inheritance
- Parent member becomes private in child
-
protected inheritance
- The public member in the parent class becomes a protected member and the other members remain unchanged
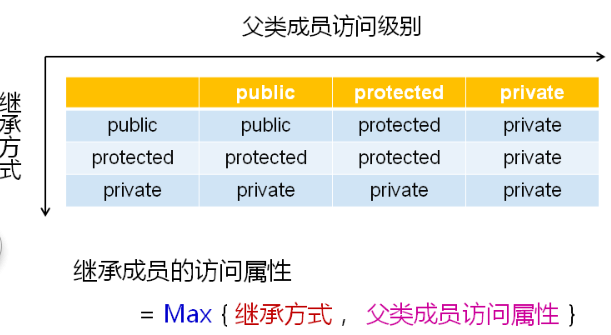
The default inheritance method in C + + is private
Programming experiment -- Inheritance and access level deep practice
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Parent{
protected:
int m_a;
protected:
int m_b;
public:
int m_c;
void set(int a,int b,int c){
m_a = a;
m_b = b;
m_c = c;
}
};
class Child_A : public Parent{
public:
void print(){
cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl;
cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl;
cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl;
}
};
class Child_B : protected Parent{
public:
void print(){
cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl;
cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl;
cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl;
}
};
class Child_C :private Parent{
public:
void print(){
cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl;
cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl;
cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl;
}
};
int main(){
Child_A a;
Child_B b;
Child_C c;
a.m_c = 100;
// b. M ﹣ C = 100; / / child ﹣ B protection inherits from Parent, so all public members become protected members, so the outside world cannot access them
// c. M ﹣ C = 100; / / child ﹣ C inherits from the Parent, so all members become private members, so the outside world cannot access them
a.set(1,1,1);
// b.set(2,2,2);
// c.set(3,3,3);
a.print();
b.print();
c.print();
return 0;
} Print results:
m_a1 m_b1 m_c1 m_a0 m_b0 m_c28 m_a1 m_b0 m_c4254425
Regrettable facts:
- Generally speaking, only public inheritance is used in C + + project
- C + + only supports one inheritance method (public inheritance)
- The complexity of protected and private inheritance is far greater than the utility
3, On C + + derived language
D language:
module D_Demo;
import std.stdio;
import std.string;
class Obj
{
protected:
string mName;
string mInfo;
public:
this()
{
mName = "Object";
mInfo = "";
}
string name()
{
return mName;
}
string info()
{
return mInfo;
}
}
class Point : Obj
{
private:
int mX;
int mY;
public:
this(int x, int y)
{
mX = x;
mY = y;
mName = "Point";
mInfo = format("P(%d, %d)", mX, mY);
}
int x()
{
return mX;
}
int y()
{
return mY;
}
}
void main(string[] args)
{
writefln("D Demo"); // D Demo
Point p = new Point(1, 2);
writefln(p.name()); // Point
writefln(p.info()); // P(1, 2)
}C# language:
class Obj
{
protected string mName;
protected string mInfo;
public Obj()
{
mName = "Object";
mInfo = "";
}
public string name()
{
return mName;
}
public string info()
{
return mInfo;
}
}
class Point : Obj
{
private int mX;
private int mY;
public Point(int x, int y)
{
mX = x;
mY = y;
mName = "Point";
mInfo = "P(" + mX + ", " + mY + ")";
}
public int x()
{
return mX;
}
public int y()
{
return mY;
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
System.Console.WriteLine("C# Demo"); // C# Demo
Point p = new Point(1, 2);
System.Console.WriteLine(p.name()); // Point
System.Console.WriteLine(p.info()); // P(1, 2)
}
}Java language:
class Obj
{
protected String mName;
protected String mInfo;
public Obj()
{
mName = "Object";
mInfo = "";
}
public String name()
{
return mName;
}
public String info()
{
return mInfo;
}
}
class Point extends Obj //Use keywords to indicate inheritance
{
private int mX;
private int mY;
public Point(int x, int y)
{
mX = x;
mY = y;
mName = "Point";
mInfo = "P(" + mX + ", " + mY + ")";
}
public int x()
{
return mX;
}
public int y()
{
return mY;
}
}
class Program {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Java Demo"); // Java Demo
Point p = new Point(1, 2);
System.out.println(p.name()); // Point
System.out.println(p.info()); // P(1, 2)
}
}Four, summary
- Three different inheritance methods are supported in C + +
- Inheritance directly affects the access properties of the parent class members in the child class
- Generally speaking, only public inheritance is used in the project
- Only public inheritance is supported in C + + derived languages