Main idea of the title:
Given a non-negative integer numRows, the first numRows row of Yang Hui triangle is generated.
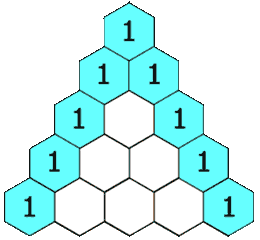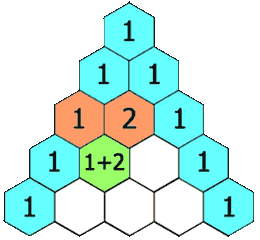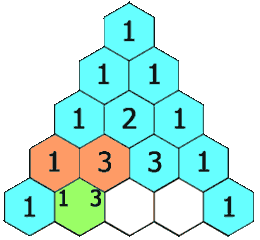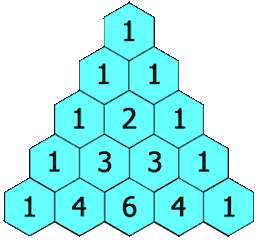
In Yang Hui triangle, each number is the sum of its upper left and upper right.
Example:
Input: 5
Output:
[
[1],
[1,1],
[1,2,1],
[1,3,3,1],
[1,4,6,4,1]
]
Train of thought:
- The first step is to initialize the corresponding two-dimensional array according to the given numRows
- In the second part, according to the rules of Yang Hui triangle, the corresponding number is filled. For each inner list, the element of res[i][j] is equal to the value of res[i-1][j-1] plus the value of res[i-1][j].
class Solution(object):
def generate(self, numRows):
"""
:type numRows: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res=[]
for i in range(numRows):#One row per cycle
temp=[1]*(i+1)#Initialized to 1
res.append(temp)
for j in range(1,i):#column
res[i][j]=res[i-1][j-1]+res[i-1][j]
return resThe following is the Java version:
1. public static List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows){
2. List<List<Integer>> s = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
3. if(numRows == 0) return s;
4. ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>();
5. a.add(1);
6. s.add(a); //Note that the two-dimensional assignment problem cannot be directly added 1
7. for(int i = 1; i < numRows; i++){
8. List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<Integer>();
9. t.add(1);
10. for(int j = 1; j <= i - 1 ; j++){
11. t.add(s.get(i - 1).get(j - 1) + s.get(i - 1).get(j));
12. }
13. t.add(1);
14. s.add(t);
15. }
16. return s;
17. }
Test:
1. public static void main(String[] args){
2.
3. System.out.println(generate(5));
4. }