What is AOP
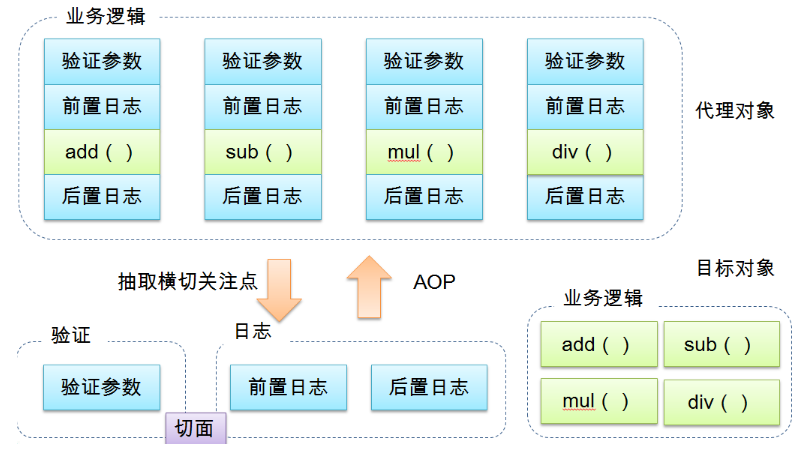
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming) means: Aspect Oriented Programming, which realizes the unified maintenance of program functions through precompiled mode and runtime dynamic agent. AOP is the continuation of OOP, a hot spot in software development, an important content in Spring framework, and a derivative paradigm of functional programming. AOP can isolate each part of business logic, reduce the coupling between each part of business logic, improve the reusability of program, and improve the efficiency of development.
The role of AOP in Spring
Provide declarative transactions; Allows you to customize the cut plane
-
Crosscutting concerns: methods or functions that span multiple modules of an application. That is, the part that has nothing to do with our business logic, but we need to focus on is crosscutting concerns. Such as logging, security, caching, transactions, etc
-
ASPECT: a special object whose crosscutting concerns are modularized. That is, it is a class.
-
Advice: work that must be completed in all aspects. That is, it is a method in a class.
-
Target: the notified object.
-
Proxy: an object created after notification is applied to the target object.
-
PointCut: the definition of the "place" where the aspect notification is executed.
-
Join point: the execution point that matches the pointcut.
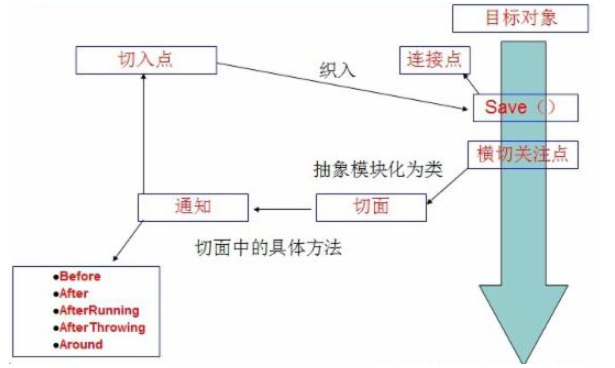
In spring AOP, crosscutting logic is defined through Advice. Spring supports five types of Advice:

That is, Aop adds new functions without changing the original code
Implementing AOP through Spring
To use AOP weaving, you need to import a dependency package
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version>
</dependency>
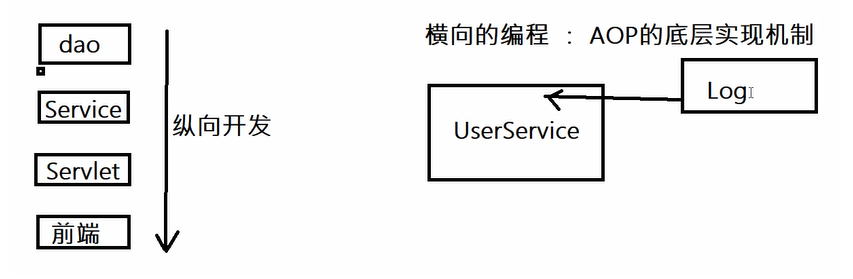
Spring's Aop combines public business (log, security, etc.) with domain business. When executing domain business, it will add public business to realize the reuse of public business. Domain business is more pure. Programs focus on domain business. Its essence is dynamic agent
Implemented through Spring API
Interface class:
package com.pag.service;
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void query();
}
Implementation class:
package com.pag.service;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void add() {
System.out.println("Add user");
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("delete user");
}
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("Update user");
}
@Override
public void query() {
System.out.println("Query user");
}
}
Enhancement class:
Pre enhancement:
package com.pag.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass()+"of"+method.getName()+"Method was executed");
}
}
Post enhancement:
package com.pag.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Yes" + target.getClass().getName()
+"of"+method.getName()+"method,"
+"Return value:"+returnValue);
}
}
spring configuration file:
<!--register bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.pag.log.Log"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.pag.log.AfterLog"/>
<!--aop Configuration of-->
<aop:config>
<!--breakthrough point expression:The expression matches the method to execute-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--Perform wrap; advice-ref Execution method . pointcut-ref breakthrough point-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
Test:
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.query();
}
Implemented through custom classes
Cut in class:
package com.pag.config;
public class DiyPointcut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("---------Before method execution---------");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("---------After method execution---------");
}
}
spring configuration file:
<!--The second way is to customize the implementation-->
<!--register bean-->
<bean id="diy" class="com.pag.config.DiyPointcut"/>
<!--aop Configuration of-->
<aop:config>
<!--The second way: use AOP Label Implementation of-->
<aop:aspect ref="diy">
<aop:pointcut id="diyPonitcut" expression="execution(* com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="diyPonitcut" method="before"/>
<aop:after pointcut-ref="diyPonitcut" method="after"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
Test:
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
Implemented through annotations
Enhanced classes for annotation entities:
package com.pag.config;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class AnnotationPointcut {
@Before("execution(* com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("---------Before method execution---------");
}
@After("execution(* com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("---------After method execution---------");
}
@Around("execution(* com.pag.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Surround front");
System.out.println("autograph:"+jp.getSignature());
//Execute target method
Object proceed = jp.proceed();
System.out.println("After surround");
System.out.println(proceed);
}
}
spring configuration file:
<!--The third way:Annotation implementation-->
<bean id="annotationPointcut" class="com.pag.config.AnnotationPointcut"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
aop:aspectj-autoproxy:
- Through the < aop: aspectJ AutoProxy / > declaration of the aop namespace, automatically create a proxy for those bean s configured with the @ aspectJ aspect in the spring container and weave the aspect in. Of course, spring still uses AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator internally to create automatic proxy, but the specific implementation details have been hidden by < aop: aspectJ AutoProxy / >
- < AOP: AspectJ AutoProxy / > has a proxy target class attribute, which is false by default, indicating that jdk dynamic proxy is used for weaving enhancement. When it is configured as < AOP: AspectJ AutoProxy poxy target class = "true" / /, it indicates that CGLib dynamic proxy technology is used for weaving enhancement. However, even if proxy target class is set to false, if the target class does not declare an interface, spring will automatically use CGLib dynamic proxy.