Based on the previously deployed multi Master cluster architecture, deploy two scheduler servers (nginx is used here) to achieve load balancing: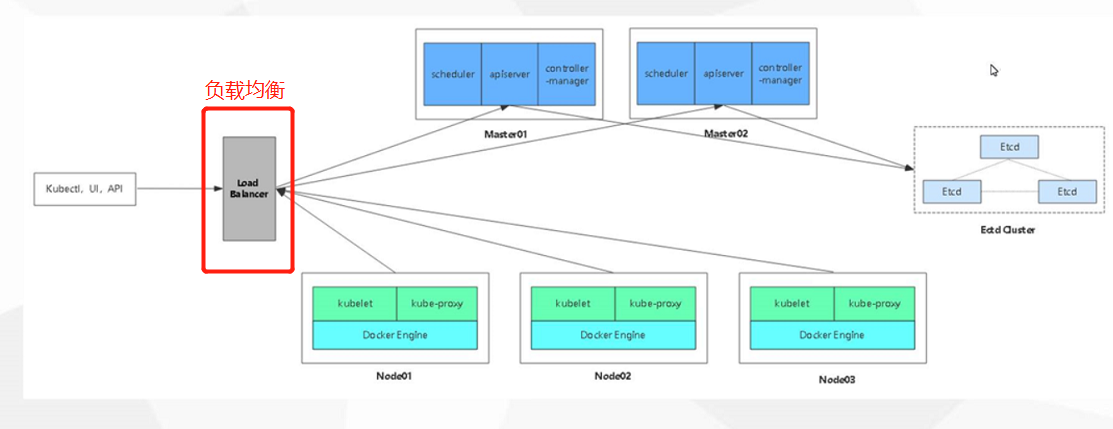
Again, the environment:
| role | IP address |
|---|---|
| master01 | 192.168.100.110 |
| master02 | 192.168.100.109 |
| Scheduler 1 (nginx01) | 192.168.100.113 |
| Scheduler 2 (nginx02) | 192.168. 100.233 |
| node01 node | 192.168.100.111 |
| node02 node | 192.168.100.112 |
| Virtual ip | 192.168.100.100 |
Prepare two of the following scripts:
First: keepalived.conf ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { # Receiving email address notification_email { acassen@firewall.loc failover@firewall.loc sysadmin@firewall.loc } # Mailing address notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc smtp_server 127.0.0.1 smtp_connect_timeout 30 router_id NGINX_MASTER } vrrp_script check_nginx { script "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh" } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface eth0 virtual_router_id 51 # VRRP route ID instance, each instance is unique priority 100 # Priority, standby server setting 90 advert_int 1 # Specifies the notification interval of VRRP heartbeat package, 1 second by default authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 10.0.0.188/24 } track_script { check_nginx } } mkdir /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ -p vim /usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh count=$(ps -ef |grep nginx |egrep -cv "grep|$$") if [ "$count" -eq 0 ];then /etc/init.d/keepalived stop fi chmod +x /usr/local/nginx/sbin/check_nginx.sh //Second: nginx cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo << EOF [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 EOF stream { log_format main '$remote_addr $upstream_addr - [$time_local] $status $upstream_bytes_sent'; access_log /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log main; upstream k8s-apiserver { server 10.0.0.3:6443; server 10.0.0.8:6443; } server { listen 6443; proxy_pass k8s-apiserver; } }
————Configuration start:
//Turn off the firewall first: [root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld.service [root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0 //Put the script file in the home directory: [root@localhost ~]# ls anaconda-ks.cfg initial-setup-ks.cfg keepalived.conf nginx.sh Public template video picture document download music desktop //Establish local yum Warehouse: [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx] name=nginx repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/ gpgcheck=0 [root@localhost ~]# yum list [root@localhost ~]# yum install nginx -y / / download nginx //Next, add four layers of forwarding: [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf //Add the following modules: stream { log_format main '$remote_addr $upstream_addr - [$time_local] $status $upstream_bytes_sent'; access_log /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log main; upstream k8s-apiserver { server 192.168.100.110:6443; //master01 Of IP address server 192.168.100.109:6443; //master02 Of IP address } server { listen 6443; proxy_pass k8s-apiserver; } } [root@localhost ~]# systemctl start nginx / / start the service //Next is deployment keepalived Services: [root@localhost ~]# yum install keepalived -y //Modify profile( nginx01 yes master): [root@localhost ~]# cp keepalived.conf /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf cp: Is it covered?"/etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf"? yes [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf //Delete and modify as follows: ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { # Receiving email address notification_email { acassen@firewall.loc failover@firewall.loc sysadmin@firewall.loc } # Mailing address notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc smtp_server 127.0.0.1 smtp_connect_timeout 30 router_id NGINX_MASTER } vrrp_script check_nginx { script "/etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh" ##Detect the path of the script, which will be created later } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state MASTER interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 100 ##priority advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.100.100/24 ##Virtual IP address } track_script { check_nginx } } //nginx02(yes backup),The configuration is as follows: ! Configuration File for keepalived global_defs { # Receiving email address notification_email { acassen@firewall.loc failover@firewall.loc sysadmin@firewall.loc } # Mailing address notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc smtp_server 127.0.0.1 smtp_connect_timeout 30 router_id NGINX_MASTER } vrrp_script check_nginx { script "/etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh" ##Detect the path of the script, which will be created later } vrrp_instance VI_1 { state BACKUP interface ens33 virtual_router_id 51 priority 90 ##Priority lower than master advert_int 1 authentication { auth_type PASS auth_pass 1111 } virtual_ipaddress { 192.168.100.100/24 ##Virtual IP address } track_script { check_nginx } } //Create test script [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh count=$(ps -ef |grep nginx |egrep -cv "grep|$$") if [ "$count" -eq 0 ];then systemctl stop keepalived fi [root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/nginx/check_nginx.sh / / authorization [root@localhost ~]# Systemctl start kept. Service / / start the service [root@localhost ~]# ip a / / view ip address
1. At this time, the virtual ip on nginx01 verifies the address drift. You can use pkill nginx in lb01 to stop the nginx service, and then use ip a command on lb02 to check whether the address has drifted.
2. Recover. At this time, on nginx02, we start nginx service first, then keepalived service, and then check with ip a command. The address drifts back again, but there is no virtual ip on nginx02.
Verification 2: verify whether load balancing is realized
1. Modify the homepage content of nginx01 (master):
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html <h1>Welcome to master nginx!</h1>
2. Modify the homepage content of nginx02 (backup):
[root@localhost ~]# vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html <h1>Welcome to backup nginx!</h1>
3. Access by browser: http://192.168.100.100/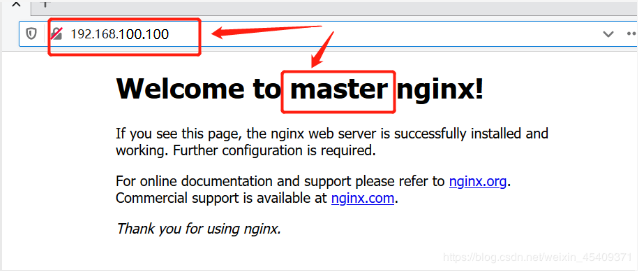
At this time, load balancing and high availability functions have been fully realized!!!
————Next, deploy the node node:
//Start to modify the unified VIP of node configuration file (bootstrap.kubeconfig,kubelet.kubeconfig) Modification content: server: https://192.168.195.100:6443 (all changed to vip) [root@localhost cfg]# vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/bootstrap.kubeconfig [root@localhost cfg]# vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kubelet.kubeconfig [root@localhost cfg]# vim /opt/kubernetes/cfg/kube-proxy.kubeconfig //Restart service: [root@localhost cfg]# systemctl restart kubelet.service [root@localhost cfg]# systemctl restart kube-proxy.service //Check the modification: [root@localhost cfg]# grep 100 * bootstrap.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.100.100:6443 kubelet.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.100.100:6443 kube-proxy.kubeconfig: server: https://192.168.100.100:6443 //Next, view the k8s log of nginx on scheduler 1: [root@localhost ~]# tail /var/log/nginx/k8s-access.log 192.168.220.140 192.168.100.110:6443 - [09/Feb/2020:13:14:45 +0800] 200 1122 192.168.220.140 192.168.100.109:6443 - [09/Feb/2020:13:14:45 +0800] 200 1121 192.168.220.136 192.168.100.110:6443 - [09/Feb/2020:13:18:14 +0800] 200 1120 192.168.220.136 192.168.100.109:6443 - [09/Feb/2020:13:18:14 +0800] 200 1121 It can be seen that the polling scheduling algorithm distributes the request traffic to two master s ————Next, the test creates the Pod: Operate on master01: [root@localhost kubeconfig]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx //View status: [root@localhost kubeconfig]# kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-dbddb74b8-zbhhr 1/1 Running 0 47s The creation is complete and running ***Attention to log issues * * *: [root@localhost kubeconfig]# kubectl logs nginx-dbddb74b8-zbhhr Error from server (Forbidden): Forbidden (user=system:anonymous, verb=get, resource=nodes, subresource=proxy) ( pods/log nginx-dbddb74b8-zbhhr) At this time, an error will be reported when viewing the log due to permission problems Solution (escalate permissions): [root@localhost kubeconfig]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-system-anonymous --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=system:anonymous clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-system-anonymous created At this time, check the log again and no error will be reported: //To view the Pod network: [root@localhost kubeconfig]# kubectl get pods -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE nginx-dbddb74b8-zbhhr 1/1 Running 0 7m11s 172.17.25.2 192.168.220.140 <none> As you can see, the pod created on master01 has been assigned to node01. We can operate on the node node of the corresponding network to directly access: To operate on node01: [root@localhost cfg]# curl 172.17.25.2
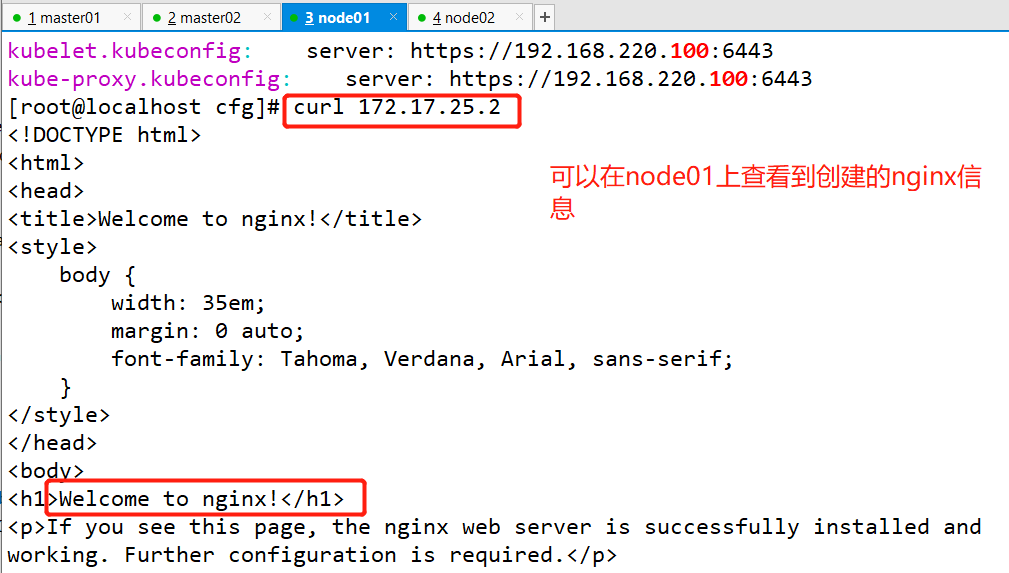
At this time, due to the function of the flannel network component, you can access this address on the browsers of node01 and node02: 172.17.25.2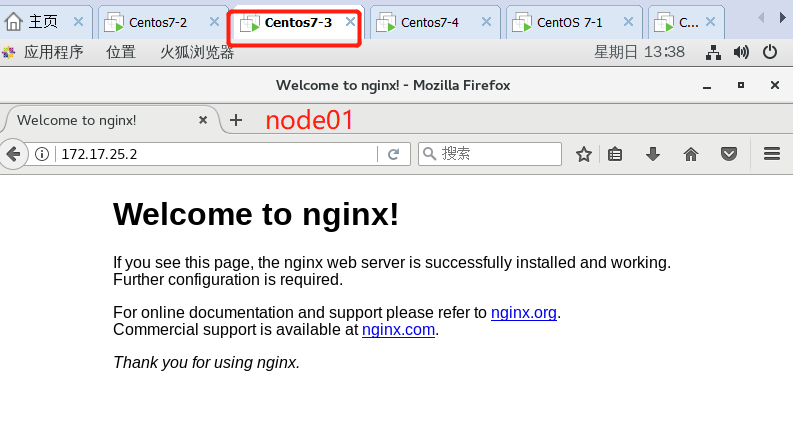
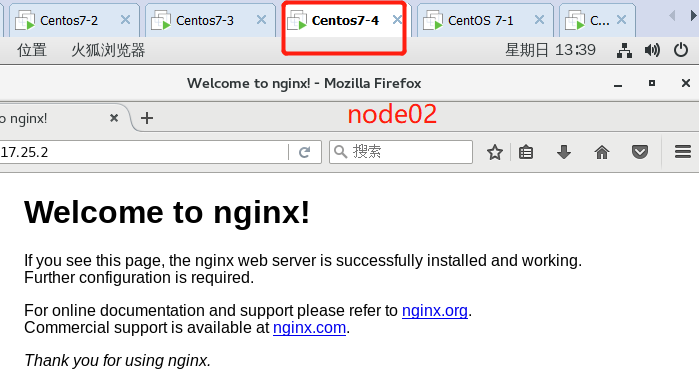
Because we just visited the web page, we can also view the log information on master01: