Experimental requirements: Kubernetes was successfully deployed to prepare for subsequent experiments
1. Environmental requirements
Server requirements:
• recommended minimum hardware configuration: 2-core CPU, 2G memory, 20G hard disk
• it is better for the server to access the external network. There will be a need to pull the image from the Internet. If the server cannot access the Internet, it is necessary to download the corresponding image in advance and import it into the node
Software environment:
| Software | edition |
|---|---|
| operating system | CentOS7.5_x64 |
| Docker | 18.06.1-ce |
| Kubernetes | 1.17 |
Server planning:
| role | IP |
|---|---|
| k8s-master | 192.168.183.160 |
| k8s-node1 | 192.168.183.162 |
| k8s-node2 | 192.168.183.163 |
| MySQL | 192.168.183.170 |
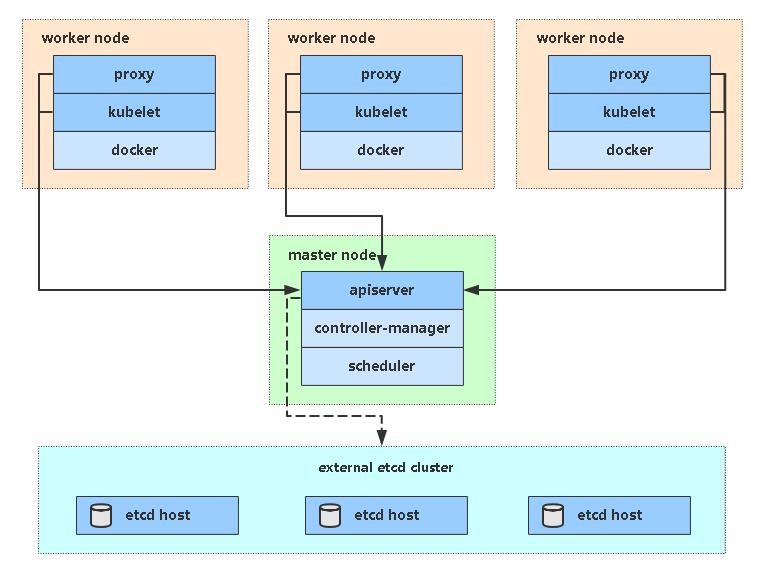
2. Basic environment (all nodes)
1) Configure network
[root@localhost ~]# nmcli connection modify "ens33" ipv4.method manual ipv4.addresses "192.168.183.160/24" ipv4.gateway "192.168.183.2" ipv4.dns "114.114.114.114" connection.autoconnect yes [root@localhost ~]# nmcli con down ens33 && nmcli con up ens33 Connection 'ens33' successfully deactivated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/1) Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/4) [root@localhost ~]# ping -c3 baidu.com PING baidu.com (220.181.38.148) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 220.181.38.148 (220.181.38.148): icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=39.6 ms 64 bytes from 220.181.38.148 (220.181.38.148): icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=39.7 ms 64 bytes from 220.181.38.148 (220.181.38.148): icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=39.6 ms --- baidu.com ping statistics --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2003ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 39.616/39.677/39.742/0.235 ms [root@localhost ~]#
2) Turn off firewall
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service. Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service.
3) Permanent and temporary shutdown of SELinux, swap
[root@localhost ~]# sed -i "s/=enforcing/=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config && setenforce 0 [root@localhost ~]# sed -ri 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab && swapoff -a
4) Add hosts in master
[root@localhost ~]# cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF 192.168.183.160 k8s-master 192.168.183.162 k8s-node1 192.168.183.163 k8s-node2 EOF
5) The chain that passes bridged IPv4 traffic to iptables
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf << EOF net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 EOF # take effect [root@k8s-master ~]# sysctl --system
6) Time synchronization
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install ntpdate -y [root@k8s-master ~]# ntpdate time.windows.com
3. Install docker / kubedm / kubelet (all nodes)
1) Install the specified version of Docker
#Replace with domestic image source [root@k8s-master ~]# wget https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo -O /etc/yum.repos.d/docker-ce.repo #Install Docker and start and set startup and self startup [root@k8s-master ~]# yum install -y docker-ce-18.06.1.ce-3.el7 Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile [root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl start docker.service && systemctl enable docker.service Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service. #View version [root@k8s-master ~]# docker --version Docker version 18.06.1-ce, build e68fc7a [root@k8s-master ~]#
2) Configure docker accelerator
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat > /etc/docker/daemon.json << EOF
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://b9pmyelo.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
#Restart verification successful
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl restart docker
3) Configure alicloud YUM software source
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo << EOF [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF [root@k8s-master ~]#
4) Install kubedm, kubelet, kubectl
[root@k8s-master ~]# yum install -y kubelet-1.17.0 kubeadm-1.17.0 kubectl-1.17.0 [root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet.service Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kubelet.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service.
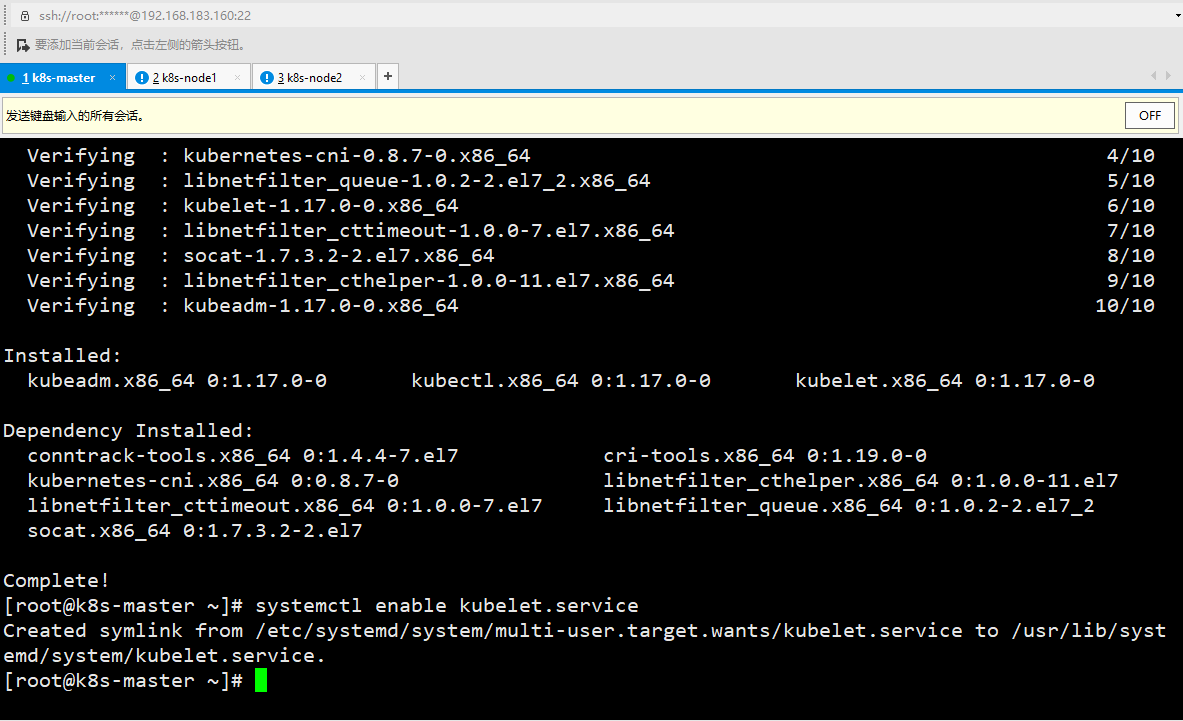
4. Deploy Kubernetes Master
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm init \ --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.183.160 \ --image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \ --kubernetes-version v1.17.0 \ --service-cidr=10.96.0.0/12 \ --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
• -- apiserver advertisement address
• -- image repository is inaccessible in China because the default image address is k8s.gcr.io. Here, specify the address of Alibaba cloud image repository
• -- kubernetes version k8s version, consistent with the above installation
• -- service CIDR cluster internal virtual network, Pod unified access portal
• - - pod network CIDR pod network,
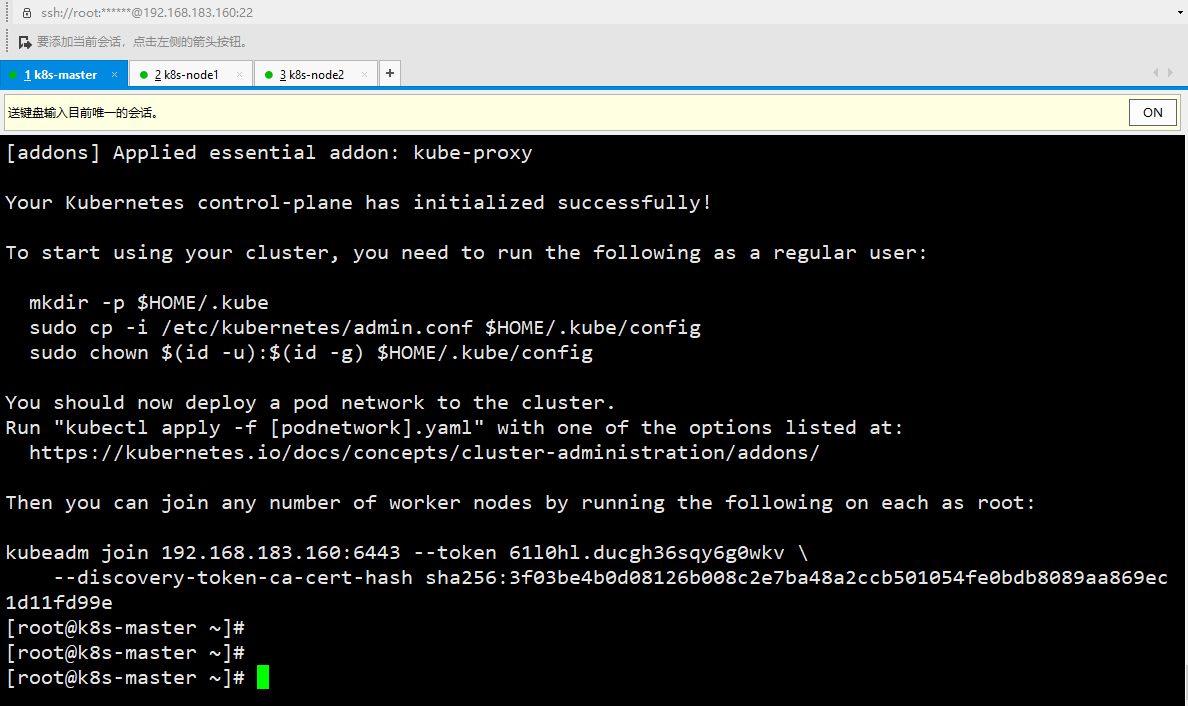
After initialization, a join command will be output. Remember first, use the following command.
Copy the connection k8s authentication file used by kubectl to the default path:
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube [root@k8s-master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config [root@k8s-master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config #View work nodes [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master NotReady master 4m55s v1.17.0
5. Deploy Pod network plug-in (CNI)
Method 1: direct use of official; If the Pod image download fails, use method 2
#The network access may fail. You can execute it several more times [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml podsecuritypolicy.policy/psp.flannel.unprivileged created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created serviceaccount/flannel created configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds created [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -n kube-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE coredns-9d85f5447-5rbll 1/1 Running 0 26m coredns-9d85f5447-bzz8z 1/1 Running 0 26m etcd-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 26m kube-apiserver-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 26m kube-controller-manager-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 26m kube-flannel-ds-x2x6t 1/1 Running 0 15m kube-proxy-7p9st 1/1 Running 0 26m kube-scheduler-k8s-master 1/1 Running 0 26m [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master Ready master 29m v1.17.0
Method 2: Download and modify the image website
[root@k8s-master]# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
[root@k8s-master]# vim kube-flannel.yml
- name: install-cni
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.15.1
- name: install-cni
image: lizhenliang/flannel:v0.15.1
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.15.1
- name: kube-flannel
image: lizhenliang/flannel:v0.15.1
6. Join Kubernetes Node
Add a new Node to the cluster. Execute the kubedm join command output after executing kubedm init at 192.168.183.162/163 (Node):
[[root@k8s-node1 ~]# kubeadm join 192.168.183.160:6443 --token 61l0hl.ducgh36sqy6g0wkv \ > --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:3f03be4b0d08126b008c2e7ba48a2ccb501054fe0bdb8089aa869ec1d11fd99e [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master Ready master 30m v1.17.0 k8s-node1 Ready <none> 59s v1.17.0 k8s-node2 Ready <none> 59s v1.17.0
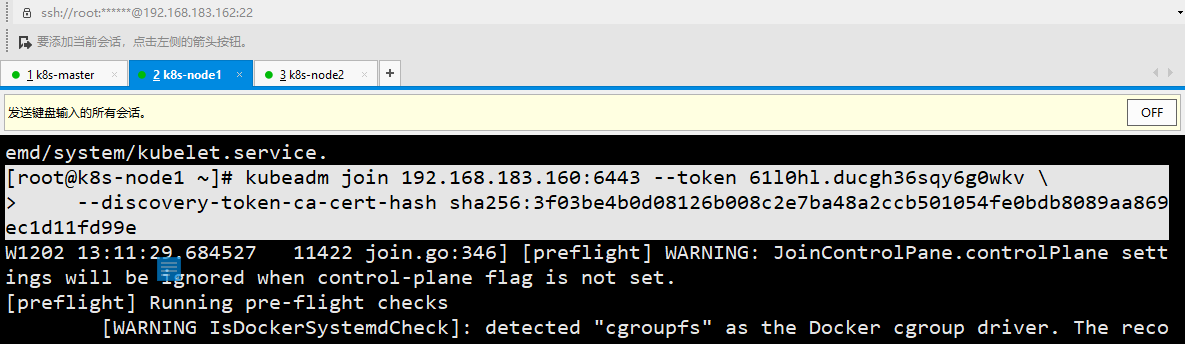
The default token is valid for 24 hours. When it expires, the token will not be available. In this case, you need to re create the token, which can be generated directly using the command:
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
7. Deploy Dashboard
#The network access may fail. You can execute it several more times [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0-beta8/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml namespace/kubernetes-dashboard created serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created service/kubernetes-dashboard created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf created secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder created configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings created role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created service/dashboard-metrics-scraper created deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper created [root@k8s-master ~]# #Check whether the mirror runs successfully [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE dashboard-metrics-scraper-76585494d8-45xxk 1/1 Running 0 2m44s kubernetes-dashboard-5996555fd8-z64kw 1/1 Running 0 2m44s #Check whether the dashboard has been downloaded [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl describe pod kubernetes-dashboard-5996555fd8-z64kw -n kubernetes-dashboard
Exposed port
The default Dashboard can only access the inside of the cluster. Add type: NodePort and nodePort: 30001 in the Service to expose them to the outside. The range of effective ports is 30000-32767:
[root@k8s-master ~]# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0-beta8/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
[root@k8s-master ~]# vim recommended.yaml
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
nodePort: 30001
#Run to make its modification effective
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f recommended.yaml
namespace/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
service/kubernetes-dashboard configured
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs unchanged
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf configured
Warning: kubectl apply should be used on resource created by either kubectl create --save-config or kubectl apply
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder configured
configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings unchanged
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard unchanged
service/dashboard-metrics-scraper unchanged
deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper unchanged
[root@k8s-master ~]#
Access address using 360 browser: https://NodeIP:30001
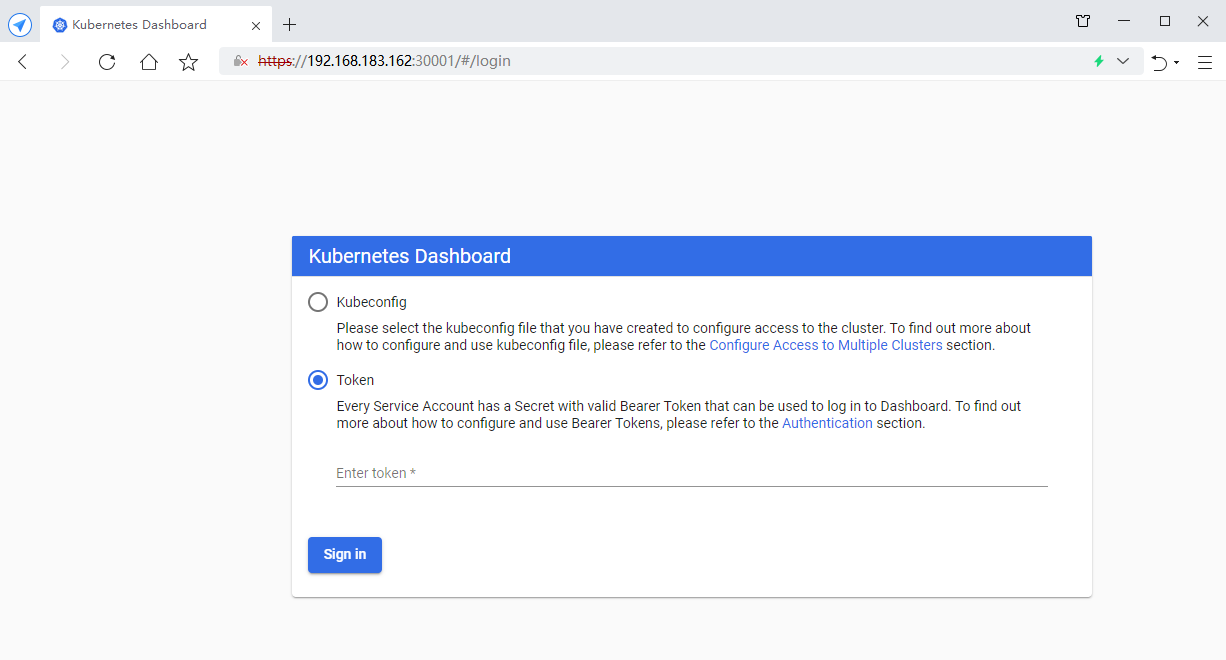
Create a service account and bind the default cluster admin administrator cluster role
# Create user
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create serviceaccount dashboard-admin -n kube-system
serviceaccount/dashboard-admin created
# User authorization
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create clusterrolebinding dashboard-admin --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:dashboard-admin
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/dashboard-admin created
# Obtain the user Token and copy the obtained Token to the browser
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl describe secrets -n kube-system $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | awk '/dashboard-admin/{print $1}')
Log in to the Dashboard using the output token
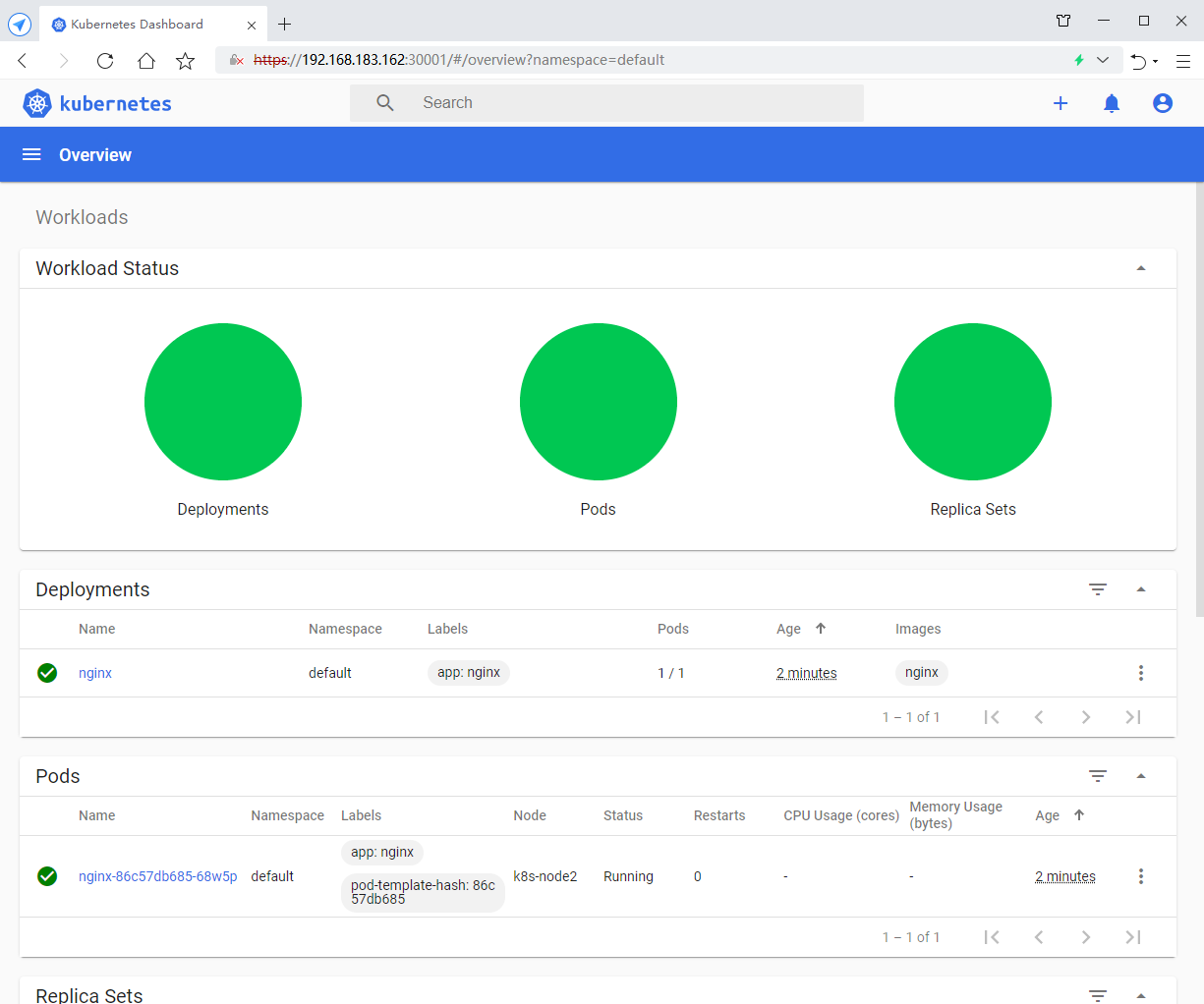
8. Test k8s cluster
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx deployment.apps/nginx created [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort service/nginx exposed [root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pod,svc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/nginx-86c57db685-tw5mh 1/1 Running 0 41s NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 32m service/nginx NodePort 10.96.29.124 <none> 80:31496/TCP 11s [root@k8s-master ~]#