There was a wave of simulated interview at station b on Saturday. Three college students were a little disappointed
Because I think they are all back-end developers, and I'm android developers. I'm not familiar with spring and I'm afraid of making a fool of myself, so I've been mending spring knowledge all day on Saturday
As a result, no one answered the first question of IOC... I don't know how to ask it later
The last video was sent out because my classmates said they didn't want to send it out. There's no way. I can only delete it because the video is very large. If you re code, edit, export and upload, it will take at least two hours to start. I really don't want to waste time on this kind of thing
In the future, we still need to set the threshold for the mock interview
OK, today, let's talk about my harvest from learning spring. All the following knowledge points come from the Silicon Valley course: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Vf4y127N5? from=search&seid=5808667601204981268&spm_ id_ from=333.337.0.0,
On the basis of my study notes, touch up and tell the readers
IOC
When we want to create an object in java, we usually use two methods, new and reflection
However, the reflection is generally slow. The normal process uses new
At this time, there will be a big problem in the project, that is, the degree of coupling
For example, to construct a Person class and let him drive a Car, simply use the new method. It is necessary for the Person to hold the Car. Obviously, in theory, Person and Car should be independent entities, so IOC is required, that is, control inversion
In the natural world, creating life is God's ability. Once life has the power to create life independently, it will be a disaster
In the programming world, creating objects is also a God's ability. If all objects can create objects indiscriminately, the project will be almost impossible to maintain
xml
So the spring framework takes back this ability. If you want to create an object, you need to declare it in the configuration file
<bean id = "userDaoImpl" class = "com.littlesong.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
Pass in the id and fully qualified class name, and each object is a bean
Then we can write this in the test class
@Test
public void testBean1() {
//1 load spring configuration file
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
//2 get the object created by configuration
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
First get the context, and then pass in the id name through the context to get the UserService class
Therefore, the ability to create objects is entrusted to spring. No matter which class you are, when you want to call a method of a class, you only need to obtain it through context, which completely relieves the dependency
In addition, there is a similar global context in android development, which also plays a great role in decoupling before
The above is just a simple object. What if it is a slightly complex object like the following?
public class Emp {
private String ename;
private String gender;
//Employees belong to a department and are represented in object form
private Dept dept;
//get method for generating dept
public Dept getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(Dept dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public void add() {
System.out.println(ename+"::"+gender+"::"+dept);
}
}
When obtaining Emp, we also need to inject name, gender and other information at the same time, which can also be specified with xml tags
<!--inside bean-->
<bean id="emp" class="com.littlesong.spring5.bean.Emp">
<!--Set two common properties-->
<property name="ename" value="lucy"></property>
<property name="gender" value="female"></property>
<!--Set object type properties-->
<property name="dept">
<bean id="dept" class="com.littlesong.spring5.bean.Dept">
<property name="dname" value="Security Department"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
But I believe you have found a problem. That is, if each class is configured in this way, don't write code. Just write configuration files every day. This is also the reason for the emergence of spring boot. However, in addition to xml configuration, we also have annotation
annotation
spring has four built-in annotations to create Bean objects
@Component @Service @Controller @Repository
For example, it can be written like this
@Service
public class UserService {
@Value(value = "abc")
private String name;
}
When we define UserService in this way, if there are other classes to use UserService
Can directly
public void testService1() {
ApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);//Where did userService come from?
userService.add();
}
You may be curious that we have configured id in xml and can get it through getBean, but here we only have Service annotation. Why can we get objects through "userService"? This is because the @ Service annotation defaults that its id is the initial lowercase of the class name. You can do this if you want to customize it
@Service(value = "otherService")
Of course, we can guess when we are executing this line of code
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
Because there is no configuration file, spring must scan annotations in the global scan, so it is necessary to configure the scan switch and have a user-defined scan scope to specify scanning under some packages, which is faster
<context:component-scan base-package="com.littlesong.spring5.aopanno"></context:component-scan>
In addition to the universal tool of context, we can also use the annotation @ Autowired
@Service
public class UserService {
//Injection dao
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
}
At this time, when we need to use userDao, we can use it directly instead of new
Of course, there are many annotations of spring, each with its own purpose, which will not be repeated here, but they all play the role of replacing xml files
AOP
AOP is another idea of spring, which is translated into aspect oriented programming in Chinese
When we define our own schedule, we often say: news at 6 o'clock and rest at 7 o'clock; No one will start from 0 o'clock to calculate how much time they spend on what things, and then launch their rest time at what time
In fact, this is an aspect oriented idea
In the back end, many events will occur. We need to know the timing before and after the occurrence of event A, and then insert other methods, namely before and after methods
For example, before can be used for initialization, and after can be used to print logs
At the same time, we also hope to have some global before or global after. At this time, it needs to be separated from specific events. How can spring understand what we mean?
Similarly, annotations will be used, and these annotations come from a framework called AspectJ
//Enhanced class
@Component
@Aspect //Generate proxy object
@Order(3)
public class UserProxy {
}
Here, we generate a User proxy class, UserProxy, to help us simulate the occurrence of various things in the User class
The code is as follows
public class UserProxy {
//Same pointcut extraction
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.littlesong.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void pointdemo() {
}
//Before advice
//@The Before annotation indicates as a pre notification
@Before(value = "pointdemo()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before.........");
}
//Final notice
@After(value = "execution(* com.littlesong.spring5.aopanno.User.add(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after.........");
}
There is a lot of information above. In short, we use a ponitcut annotation to indicate that the entry takes you in the User.add method,
Then use the before and after annotations, so that our customized before and after methods will automatically run before and after User.add()
Therefore, we can easily know all the States before and after the operation of any method, so as to control the whole back-end system
Of course, there are not only before and after aspects, so the function is too weak. Although I haven't used too many annotations, in theory, spring should provide annotations for all effective aspects
other
As the back-end, it is necessary to deal with the database. The most common is mysql. Large projects may use nosql
All data modifications at the back end are essentially transactions one by one, so spring provides a transaction manager and provides different transaction managers according to different data sources
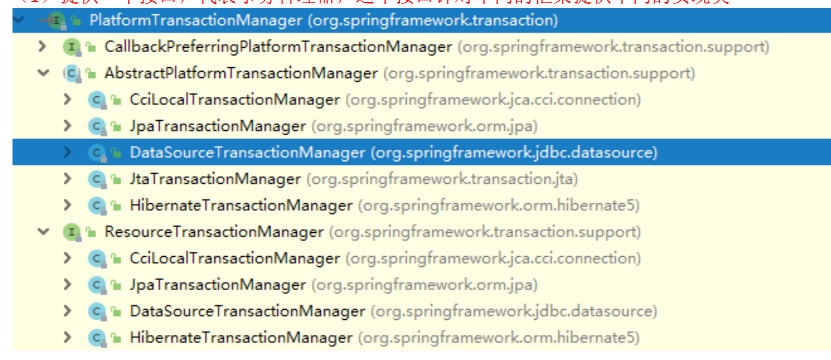
Among them, DataSource refers to the use of JDBC, which is a relatively primitive way to handle database transactions. However, Hibernate or Mybatis are generally used now, but the core will not change. They are all encapsulated by a layer of middleware between the back end and the database,
In addition, the characteristics of transactions are not the content of spring, and will not be repeated in this article
Finally, let's take a look at the architecture diagram of spring
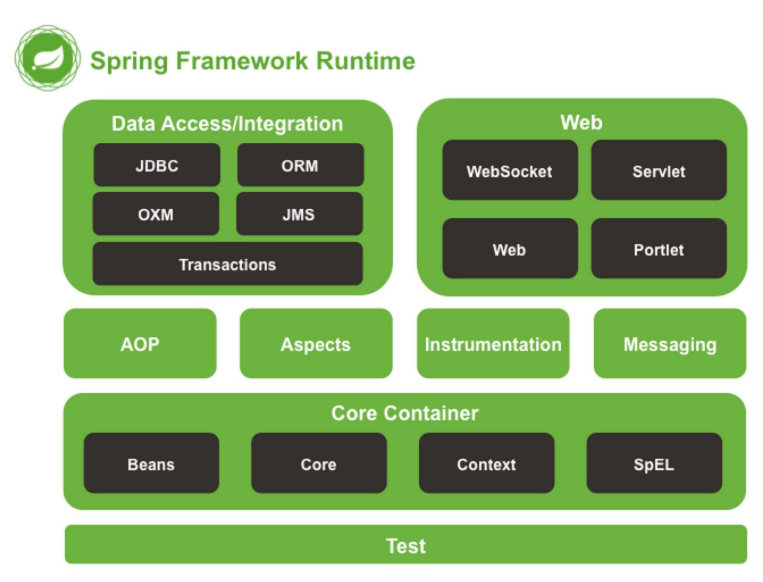
It can be seen that there are still a lot of contents, which are not fully covered in this article. However, after mastering the ideas of IOC and AOP, I believe other contents will be mastered quickly. More importantly, as far as I know, few companies will only use spring. spring boot, springMVC, dubbo, ZK, RQ and other frameworks emerge one after another. It can be said that learning spring is only the first step towards the back end, Although the back end is rolling this year
This is mainly because the supply of algorithmic Posts exceeds the demand, and many graduate students are forced to switch to the back end,
Maybe one day android won't work, I'll roll the back end, hahaha