kolla ansibel deploy openstack high availability cluster
reference resources: https://docs.openstack.org/kolla-ansible/latest/user/quickstart.html
kolla installation node requirements:
- 2 network interfaces
- 8GB main memory
- 40GB disk space
For the installation of kolla, the target machine is required to have two network cards. Add a new network card in vmware workstation:
- ens33, NAT mode, management network, tenant network can be reused with the network, and static IP can be configured normally.
- ens37, bridge mode, does not need to configure the IP address. In fact, this is used by the br ex binding of neutron. The virtual machine accesses the external network through this network card.
Node planning
- Three control nodes (network node and control node are combined), one computing node + one storage node (cinder lvm)
- The first control node is also the kolla ansible deployment node
- The control node and the computing node have two network cards, the storage node has one network card, the network card 1NAT mode serves as the management network, the network card 2 bridge mode serves as the external network.
- The operating system uses CentOS7.8 minimal, and the CPU memory of all nodes is configured as 2C4G.
Node and IP planning
| Node name | IP address | role |
|---|---|---|
| control01 | ens33: 192.168.93.60 ens37: |
Control node |
| control02 | ens33: 192.168.93.61 ens37: |
Control node |
| control03 | ens33: 192.168.93.62 ens37: |
Control node |
| compute01 | ens33: 192.168.93.63 ens37: |
Calculation node |
| storage01 | ens33: 192.168.93.64 |
Storage node |
If you need to add an additional disk to the storage01 node to enable the cinder, take / dev/sdb as an example, and execute on the storage01 node
pvcreate /dev/sdb vgcreate cinder-volumes /dev/sdb
Note that the volume group name is cinder volumes, and the default is globals.yml agreement.
[root@kolla ~]# cat /etc/kolla/globals.yml | grep cinder_volume_group #cinder_volume_group: "cinder-volumes"
All nodes configure IP addresses according to the plan
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens33 UUID=752fa178-bbb6-4ab3-84ee-aa86a34a16b4 DEVICE=ens33 ONBOOT=yes IPADDR=192.168.93.61 PREFIX=24 GATEWAY=192.168.93.2 DNS1=114.114.114.114 DNS2=8.8.8.8 IPV6_PRIVACY=no [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens37 TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens37 UUID=c1513435-9706-3d76-802b-00c4e901ee82 DEVICE=ens37 ONBOOT=yes IPV6_PRIVACY=no
Basic configuration
Without special instructions, all the following operations are performed in the kolla ansible deployment node, namely the control01 node.
Installation dependency
yum install -y python-devel libffi-devel gcc openssl-devel libselinux-python
Install Ansible
yum install -y ansible
Configure alicloud pip source
mkdir ~/.pip cat > ~/.pip/pip.conf << EOF [global] trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com index-url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ EOF
Install kolla ansible
Correspondence between kolla version and openstack version: https://releases.openstack.org/teams/kolla.html
yum install -y epel-release yum install -y python-pip pip install -U pip pip install kolla-ansible==9.1.0 --ignore-installed PyYAML
Copy kolla ansible configuration
mkdir -p /etc/kolla chown $USER:$USER /etc/kolla ##Copy globals.yml and passwords.yml cp -r /usr/share/kolla-ansible/etc_examples/kolla/* /etc/kolla ##Copy all-in-one and multinode inventory files cp /usr/share/kolla-ansible/ansible/inventory/* .
Modify ansible configuration file
$ vim /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg [defaults] host_key_checking=False pipelining=True forks=100
Modify the multi node inventory file, and other defaults are OK
$ cat multinode [control] # These hostname must be resolvable from your deployment host control01 control02 control03 [network] control01 control02 control03 [compute] compute01 [monitoring] control01 [storage] storage01 ...
Configure ssh security free
ssh-keygen ssh-copy-id 192.168.93.61 ssh-copy-id 192.168.93.62 ssh-copy-id 192.168.93.63 ssh-copy-id 192.168.93.64 ssh-copy-id 192.168.93.65
Configure host name (all nodes)
hostnamectl set-hostname control01 hostnamectl set-hostname control02 hostnamectl set-hostname control03 hostnamectl set-hostname compute01 hostnamectl set-hostname storage01
Configure host name resolution (kolla will configure host name resolution in pre configuration, and only operate in deployment node here)
cat > /etc/hosts <<EOF 192.168.93.61 control01 192.168.93.62 control02 192.168.93.63 control03 192.168.93.64 compute01 192.168.93.65 storage01 EOF
Check whether the inventory configuration is correct. Execute:
ansible -i multinode all -m ping
Generate kolla password
kolla-genpwd
Modify keystone_admin_password can be modified to user-defined, which is used in the login dashboard
sed -i 's#keystone_admin_password:.*#keystone_admin_password: kolla#g' /etc/kolla/passwords.yml $ cat /etc/kolla/passwords.yml | grep keystone_admin_password keystone_admin_password: kolla
Modify global profile globals.yml
cp /etc/kolla/globals.yml{,.bak} cat >> /etc/kolla/globals.yml <<EOF #version kolla_base_distro: "centos" kolla_install_type: "binary" openstack_release: "train" #vip kolla_internal_vip_address: "192.168.93.200" #docker registry docker_registry: "registry.cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com" docker_namespace: "kollaimage" #network network_interface: "ens33" neutron_external_interface: "ens37" neutron_plugin_agent: "openvswitch" enable_neutron_provider_networks: "yes" #storage enable_cinder: "yes" enable_cinder_backend_lvm: "yes" #virt_type nova_compute_virt_type: "qemu" EOF
Modify the official installation yum source of docker as Alibaba cloud yum source, and configure docker image acceleration. Specify to use Alibaba cloud image acceleration.
$ vim /usr/share/kolla-ansible/ansible/roles/baremetal/defaults/main.yaml docker_yum_url: "https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/{{ ansible_distribution | lower }}" docker_custom_config: {"registry-mirrors": ["https://uyah70su.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]}
Deploy openstack
Easy is executed when bootstrap servers are running_ The install PIP command installs pip. If the network is slow and the task is stuck here all the time, you can manually install PIP in all nodes in advance (optional).
mkdir ~/.pip cat > ~/.pip/pip.conf << EOF [global] trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com index-url=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/ EOF yum install -y epel-release yum install -y python-pip pip install -U pip
Start deploying openstack
kolla-ansible -i ./multinode bootstrap-servers #Deployment check kolla-ansible -i ./multinode prechecks #Pull image kolla-ansible -i ./multinode pull #Execute deployment kolla-ansible -i ./multinode deploy
OpenStack client
Generate an openrc file with administrator user credentials set
kolla-ansible post-deploy
cat /etc/kolla/admin-openrc.sh
Using docker as the openstack client
docker pull registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/davycloud/centos-binary-openstack-base:train
The kolla ansible deployment node starts a temporary container:
docker run -d --name client \ --restart always \ -v /etc/kolla/admin-openrc.sh:/admin-openrc.sh:ro \ -v /usr/share/kolla-ansible/init-runonce:/init-runonce:rw \ registry.cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/kollaimage/centos-binary-openstack-base:train sleep infinity
Enter the container to execute the openstack command
[root@control01 ~]# docker exec -it client bash ()[root@7863d16d6839 /]# source /admin-openrc.sh ()[root@7863d16d6839 /]# openstack service list +----------------------------------+-------------+----------------+ | ID | Name | Type | +----------------------------------+-------------+----------------+ | 2ab6a571b71444adb69f10d18a876c55 | keystone | identity | | 4b0ea157a8dc4ef5adc720dda56902ce | cinderv2 | volumev2 | | 57b38f38444949f98e6f3ed46b5a24e6 | cinderv3 | volumev3 | | 84431d0e3727426f82faf4a9bb898045 | heat | orchestration | | 8a8675bc425a45ac9e83140b18a8c864 | nova_legacy | compute_legacy | | b54c859fa8214ca68bb5002e5e58ade2 | glance | image | | b9adda688c024c56aace1902340cadf7 | heat-cfn | cloudformation | | c301474681f74271a39b74d29899d7ee | nova | compute | | c3fb659dea224e3ab8655f77976cc98f | placement | placement | | edfa32d4099a435397497b19b055fd10 | neutron | network | +----------------------------------+-------------+----------------+
kolla provides a script for quickly creating demo instances, modifying the external network configuration of init RunOnce sample scripts.
()[root@7863d16d6839 /]# vi init-runonce # This EXT_NET_CIDR is your public network,that you want to connect to the internet via. ENABLE_EXT_NET=${ENABLE_EXT_NET:-1} EXT_NET_CIDR=${EXT_NET_CIDR:-'192.168.1.0/24'} EXT_NET_RANGE=${EXT_NET_RANGE:-'start=192.168.1.200,end=192.168.1.250'} EXT_NET_GATEWAY=${EXT_NET_GATEWAY:-'192.168.1.1'} ()[root@7863d16d6839 /]# bash init-runonce
The script will first download the cirros image from github. If the network is slow, you can download it to the cache directory in advance
docker exec -it client mkdir -p /opt/cache/files/ wget https://github.com/cirros-dev/cirros/releases/download/0.4.0/cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img docker cp cirros-0.4.0-x86_64-disk.img client:/opt/cache/files/
Run a cirros instance according to the prompt after the script is executed
openstack server create \
--image cirros \
--flavor m1.tiny \
--key-name mykey \
--network demo-net \
demo1
Visit horizon
Find vip address in 3 control nodes
[root@control03 ~]# ip a | grep ens33 2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP group default qlen 1000 inet 192.168.93.63/24 brd 192.168.93.255 scope global noprefixroute ens33 inet 192.168.93.200/32 scope global ens33
Browser access: http://192.168.93.200 , user name and password are in admin-openrc.sh It can be found in. The default is admin/kolla
cat /admin-openrc.sh
View network topology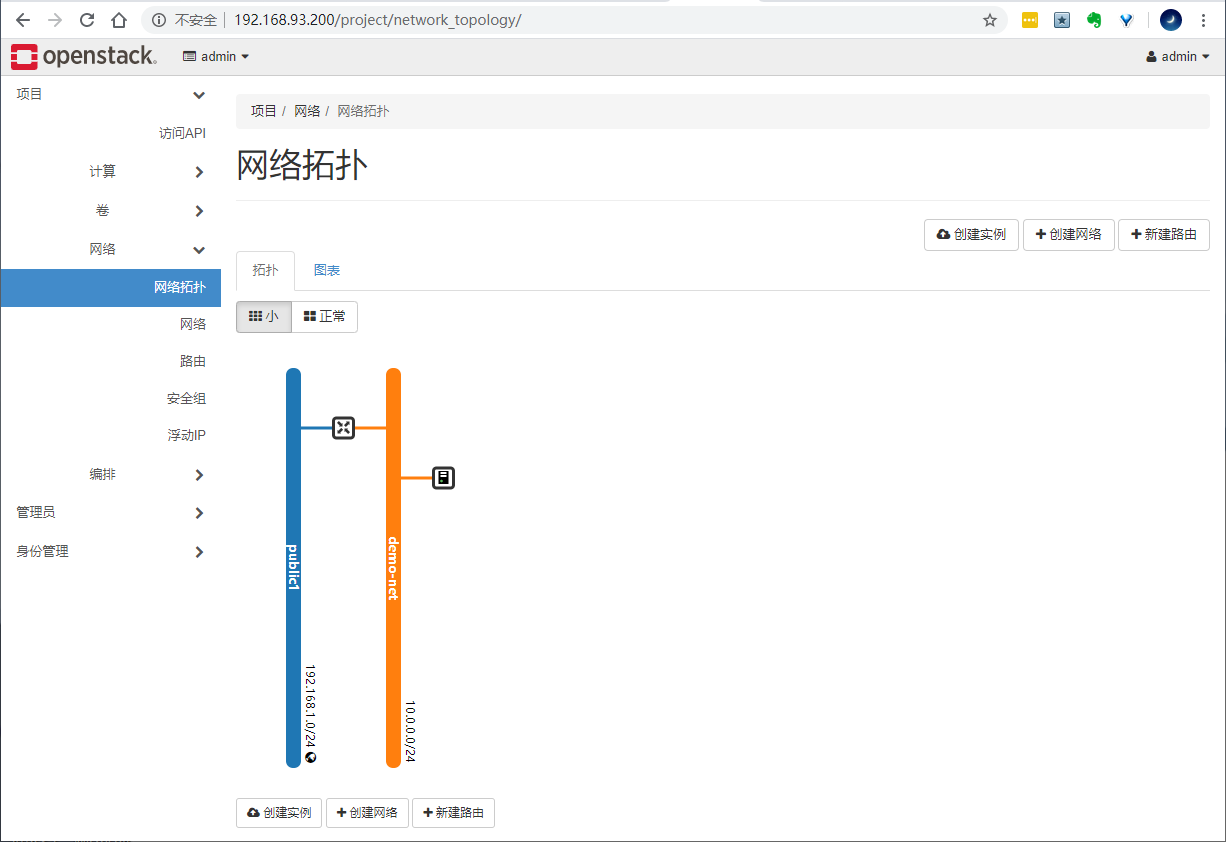
Assign floating IP to an instance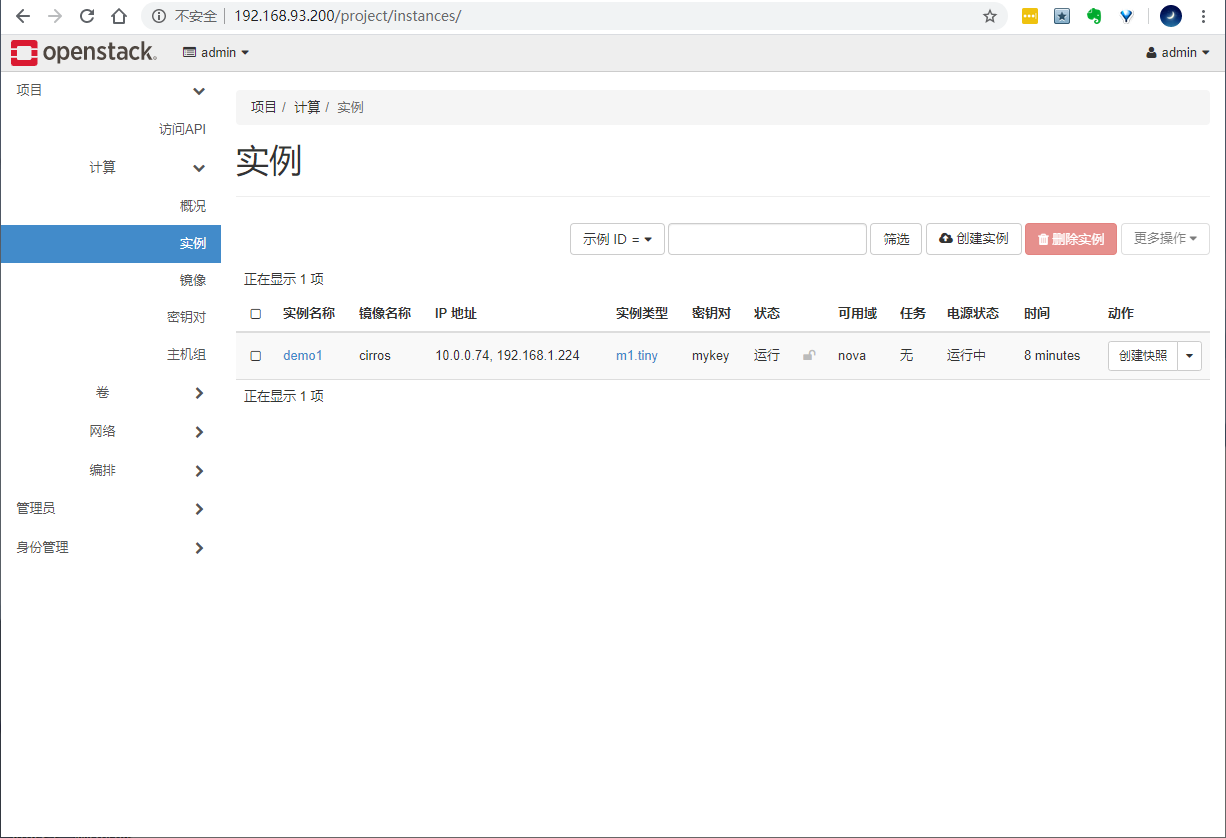
Connect to the instance and verify the access to the Internet. The default account password of cirros image is cirros/gocubsgo
[root@control01 ~]# ssh cirros@192.168.1.224 cirros@192.168.1.224's password: $ $ $ ip a 1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue qlen 1 link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 ::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1450 qdisc pfifo_fast qlen 1000 link/ether fa:16:3e:e4:16:00 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 10.0.0.74/24 brd 10.0.0.255 scope global eth0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:fee4:1600/64 scope link valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever $ $ ping -c 4 www.openstack.org PING www.openstack.org (104.20.110.33): 56 data bytes 64 bytes from 104.20.110.33: seq=1 ttl=53 time=178.064 ms 64 bytes from 104.20.110.33: seq=2 ttl=53 time=177.797 ms 64 bytes from 104.20.110.33: seq=3 ttl=53 time=178.392 ms --- www.openstack.org ping statistics --- 4 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 25% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 177.797/178.084/178.392 ms
Profile directory
Directory of configuration files of each component / etc/kolla/
Log file directory of each component / var/log/kolla/
Clean up cluster
kolla-ansible destroy --include-images --yes-i-really-really-mean-it vgremove cinder-volume