1, Class definition in OpenCV
The definition of KalmanFilter class
class CV_EXPORTS_W KalmanFilter
{
public:
CV_WRAP KalmanFilter(); //Construct the default Kalman filter object
CV_WRAP KalmanFilter(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F); //The method of constructing KalmanFilter object completely
void init(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams=0, int type=CV_32F); //Initializing the KalmanFilter object will replace the original KF object
CV_WRAP const Mat& predict(const Mat& control=Mat()); //Calculate predicted status value
CV_WRAP const Mat& correct(const Mat& measurement); //Update status values based on measurements
Mat statePre; //Predicted value (x'(k)): x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
Mat statePost; //State value (x(k)): x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
Mat transitionMatrix; //State transition matrix
Mat controlMatrix; //Control matrix B
Mat measurementMatrix; //Measurement matrix H
Mat processNoiseCov; //System error Q
Mat measurementNoiseCov; //Measurement error R
Mat errorCovPre; //Minimum mean square error (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
Mat gain; //Kalman gain (K(k)): K(k)=P'(k)*Ht*inv(H*P'(k)*Ht+R)
Mat errorCovPost; //Corrected minimum mean square error (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
// Temporary matrix
Mat temp1;
Mat temp2;
Mat temp3;
Mat temp4;
Mat temp5;
};
The implementation of correlation function,
#include "precomp.hpp"
namespace cv
{
KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter() {}
KalmanFilter::KalmanFilter(int dynamParams, int measureParams, int controlParams, int type)
{
init(dynamParams, measureParams, controlParams, type);
}
void KalmanFilter::init(int DP, int MP, int CP, int type)
{
CV_Assert( DP > 0 && MP > 0 );
CV_Assert( type == CV_32F || type == CV_64F );
CP = std::max(CP, 0);
statePre = Mat::zeros(DP, 1, type); //Predicted value x(k)=A*x(k-1)+B*u(k)
statePost = Mat::zeros(DP, 1, type); //Corrected state value x(k)=x'(k)+K(k)*(z(k)-H*x'(k))
transitionMatrix = Mat::eye(DP, DP, type); //State transition matrix
processNoiseCov = Mat::eye(DP, DP, type); //System error Q
measurementMatrix = Mat::zeros(MP, DP, type); //Measurement matrix
measurementNoiseCov = Mat::eye(MP, MP, type); //measurement error
errorCovPre = Mat::zeros(DP, DP, type); //Minimum mean square error (P'(k)): P'(k)=A*P(k-1)*At + Q)
errorCovPost = Mat::zeros(DP, DP, type); //Corrected minimum mean square error (P(k)): P(k)=(I-K(k)*H)*P'(k)
gain = Mat::zeros(DP, MP, type); //Kalman gain
if( CP > 0 )
controlMatrix = Mat::zeros(DP, CP, type); //Control matrix
else
controlMatrix.release();
temp1.create(DP, DP, type);
temp2.create(MP, DP, type);
temp3.create(MP, MP, type);
temp4.create(MP, DP, type);
temp5.create(MP, 1, type);
}
const Mat& KalmanFilter::predict(const Mat& control)
{
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();
// update the state: x'(k) = A*x(k)
statePre = transitionMatrix*statePost;
if( !control.empty() )
// x'(k) = x'(k) + B*u(k)
statePre += controlMatrix*control;
// update error covariance matrices: temp1 = A*P(k)
temp1 = transitionMatrix*errorCovPost;
// P'(k) = temp1*At + Q
gemm(temp1, transitionMatrix, 1, processNoiseCov, 1, errorCovPre, GEMM_2_T);//GEMM? 2? T indicates to transpose the second parameter.
// handle the case when there will be measurement before the next predict.
statePre.copyTo(statePost);
errorCovPre.copyTo(errorCovPost);
return statePre;
}
const Mat& KalmanFilter::correct(const Mat& measurement)
{
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();
// temp2 = H*P'(k)
temp2 = measurementMatrix * errorCovPre;
// temp3 = temp2*Ht + R
gemm(temp2, measurementMatrix, 1, measurementNoiseCov, 1, temp3, GEMM_2_T);//Calculate measurement covariance
// temp4 = inv(temp3)*temp2 = Kt(k)
solve(temp3, temp2, temp4, DECOMP_SVD);//Solve function, used to solve the linear equation temp3*temp4=temp2
// K(k)
gain = temp4.t();
// temp5 = z(k) - H*x'(k)
temp5 = measurement - measurementMatrix*statePre; //measurement error
// x(k) = x'(k) + K(k)*temp5
statePost = statePre + gain*temp5;
// P(k) = P'(k) - K(k)*temp2
errorCovPost = errorCovPre - gain*temp2;
return statePost;
}
}
2, What needs to be explained
The relevant formulas of Kalman filter will not be pasted out. The above update and prediction functions can be compared with those formulas, and the following are some key points to explain.
(1) gemm() function
gemm() is the generalized multiplication of matrix
void gemm(const GpuMat& src1, constGpuMat& src2, double alpha, const GpuMat& src3, double beta,GpuMat& dst, int flags=0, Stream& stream=Stream::Null())
Corresponding:
dst = alpha*src1*src2 +beta* src3
It should be noted that the last parameter given in the program is GEMM ﹣ 2 ﹣ T, which means to transpose the second parameter.
(2) solve() function
bool solve(InputArray src1, InputArray src2, OutputArray dst, int flags=DECOMP_LU)
It is used to solve linear equation A*X=B, left side of src1 linear system (equivalent to A above), right side of src2 linear system (equivalent to B above), solution of dst output (equivalent to X requiring solution), and flag is the method used.
(3) Why can we use solve() function to solve Kalman gain
The significance of Kalman gain K is to minimize the posterior estimation error covariance, and bring K into the expression of the posterior estimation error covariance,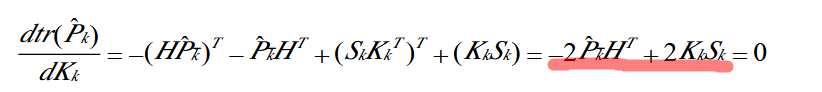
By derivation, the optimal K value can be calculated. General expression: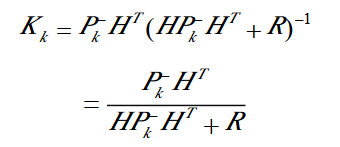
The basis of using SOLVE() function is the red line part above, which is equivalent to directly solving the linear equation.
For specific derivation, please refer to:
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/a5a6068619e8b8f67c1cb98b.html
(4) A typical example -- tracking mouse position
#include "opencv2/video/tracking.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const int winHeight=600;
const int winWidth=800;
Point mousePosition= Point(winWidth>>1,winHeight>>1);
//mouse event callback
void mouseEvent(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void *param )
{
if (event==CV_EVENT_MOUSEMOVE) {
mousePosition = Point(x,y);
}
}
int main (void)
{
RNG rng;
//1.kalman filter setup
const int stateNum=4; //State value 4 × 1 vector (x,y, △ x, △ y)
const int measureNum=2; //Measured value 2 × 1 vector (x,y)
KalmanFilter KF(stateNum, measureNum, 0);
KF.transitionMatrix = *(Mat_<float>(4, 4) <<1,0,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1); //Transfer matrix A
setIdentity(KF.measurementMatrix); //Measurement matrix H
setIdentity(KF.processNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-5)); //System noise variance matrix Q
setIdentity(KF.measurementNoiseCov, Scalar::all(1e-1)); //Measurement noise variance matrix R
setIdentity(KF.errorCovPost, Scalar::all(1)); //Posterior error estimate covariance matrix P
rng.fill(KF.statePost,RNG::UNIFORM,0,winHeight>winWidth?winWidth:winHeight); //Initial state value x(0)
Mat measurement = Mat::zeros(measureNum, 1, CV_32F); //The initial measurement value x'(0) must be defined first because this value will be updated later
namedWindow("kalman");
setMouseCallback("kalman",mouseEvent);
Mat image(winHeight,winWidth,CV_8UC3,Scalar(0));
while (1)
{
//2.kalman prediction
Mat prediction = KF.predict();
Point predict_pt = Point(prediction.at<float>(0),prediction.at<float>(1) ); //Predicted value (x',y')
//3.update measurement
measurement.at<float>(0) = (float)mousePosition.x;
measurement.at<float>(1) = (float)mousePosition.y;
//4.update
KF.correct(measurement);
//draw
image.setTo(Scalar(255,255,255,0));
circle(image,predict_pt,5,Scalar(0,255,0),3); //predicted point with green
circle(image,mousePosition,5,Scalar(255,0,0),3); //current position with red
char buf[256];
sprintf_s(buf,256,"predicted position:(%3d,%3d)",predict_pt.x,predict_pt.y);
putText(image,buf,Point(10,30),CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX,1,Scalar(0,0,0),1,8);
sprintf_s(buf,256,"current position :(%3d,%3d)",mousePosition.x,mousePosition.y);
putText(image,buf,cvPoint(10,60),CV_FONT_HERSHEY_SCRIPT_COMPLEX,1,Scalar(0,0,0),1,8);
imshow("kalman", image);
int key=waitKey(3);
if (key==27){//esc
break;
}
}
}
Other examples can refer to:
https://blog.csdn.net/haima1998/article/details/80641628

