Reasons for ingress
ClusterIP can only be accessed within a cluster
With NodePort, the test environment works fine, and when hundreds of services are running in a cluster, port management for NodePort is a disaster.
The LoadBalance approach is limited to cloud platforms, and ELB s are typically deployed on cloud platforms at additional cost.
Fortunately, k8s also provides a way for the cluster dimension to expose services, namely ingress.Ingress can be simply understood as a service of a service, which routes requests to one or more services by setting rules for request forwarding through a separate ingress object.This decouples the service from the request rules and allows for a unified consideration of business exposure from the business dimension rather than for each service individually. Here is a simple Ingres application diagram that enables simple request forwarding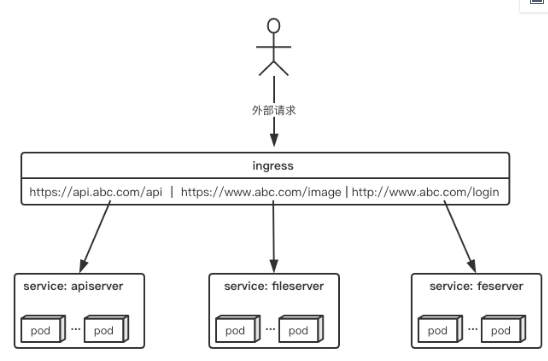
Ingress and ingress-controller
ingress object:
Refers to an api object in k8s, which is generally configured with yaml.The purpose is to define rules for how requests are forwarded to a service, which can be understood as a configuration template.
ingress-controller:
The program that implements reverse proxy and load balancing specifically, parses the rules defined by ingress, and implements request forwarding according to the configured rules.
Simply put, the ingress-controller is the component responsible for forwarding. It is exposed to the cluster entrance in various ways. The external request traffic to the cluster goes first to the ingress-controller. The ingress object is used to tell the ingress-controller how to forward requests, such as which domain names and path s to which services.
Adding an implementation of ingress for a service
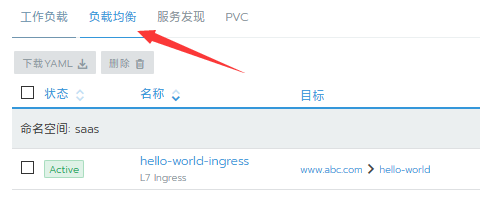
2Our ingress support https, so we need to configure the corresponding certificate for your domain name, we add it in the configuration file
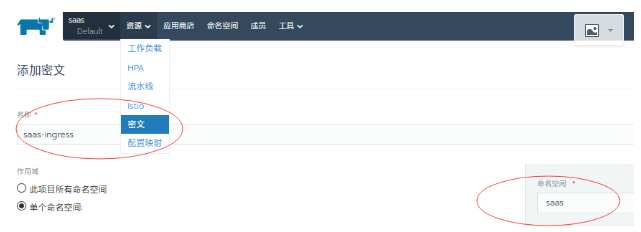
3Automatically add the nginx configuration item to the configuration file in the ingress-controller and reload it automatically to take effect
The configuration file changes when a new ingress service is registered
4 The nginx corresponding to your service is configured in the ymal of your service. Generally speaking, the gateway layer of the micro service should establish an ingress-nginx to provide services to the outside world!
- Note the name of ingress
- Fill in the ciphertext name you created earlier (ingress https certificate)
- Fill in the namespace where your service is located, not default
- Fill in the domain name of the service you want to forward
- Fill in the name of your service and the port of your pod
# Build Reflection Agent
kind: Ingress
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
metadata:
name: hello-world-ingress
namespace: saas
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "nginx"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
spec:
tls:
- hosts:
- www.abc.com
secretName: saas-tls
rules:
- host: www.abc.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: hello-world
servicePort: 9001
## start server www.abc.com
server {
server_name www.abc.com ;
listen 80 ;
listen [::]:80 ;
listen 443 ssl http2 ;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2 ;
set $proxy_upstream_name "-";
# PEM sha: c24ba9e405ed77662c0fd7546a908ef45ca76066
ssl_certificate /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem;
ssl_certificate_by_lua_block {
certificate.call()
}
location ~* "^/" {
set $namespace "saas";
set $ingress_name "hello-world-ingress";
set $service_name "hello-world";
set $service_port "{0 9001 }";
set $location_path "/";
rewrite_by_lua_block {
lua_ingress.rewrite({
force_ssl_redirect = true,
use_port_in_redirects = false,
})
balancer.rewrite()
plugins.run()
}
header_filter_by_lua_block {
plugins.run()
}
body_filter_by_lua_block {
}
log_by_lua_block {
balancer.log()
monitor.call()
plugins.run()
}
if ($scheme = https) {
more_set_headers "Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains";
}
port_in_redirect off;
set $balancer_ewma_score -1;
set $proxy_upstream_name "saas-hello-world-9001";
set $proxy_host $proxy_upstream_name;
set $pass_access_scheme $scheme;
set $pass_server_port $server_port;
set $best_http_host $http_host;
set $pass_port $pass_server_port;
set $proxy_alternative_upstream_name "";
client_max_body_size 1m;
proxy_set_header Host $best_http_host;
# Pass the extracted client certificate to the backend
# Allow websocket connections
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header X-Request-ID $req_id;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $the_real_ip;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $the_real_ip;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $best_http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port $pass_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $pass_access_scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Original-URI $request_uri;
proxy_set_header X-Scheme $pass_access_scheme;
# Pass the original X-Forwarded-For
proxy_set_header X-Original-Forwarded-For $http_x_forwarded_for;
# mitigate HTTPoxy Vulnerability
# https://www.nginx.com/blog/mitigating-the-httpoxy-vulnerability-with-nginx/
proxy_set_header Proxy "";
# Custom headers to proxied server
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
proxy_send_timeout 60s;
proxy_read_timeout 60s;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_buffer_size 4k;
proxy_buffers 4 4k;
proxy_request_buffering on;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_cookie_domain off;
proxy_cookie_path off;
# In case of errors try the next upstream server before returning an error
proxy_next_upstream error timeout;
proxy_next_upstream_timeout 0;
proxy_next_upstream_tries 3;
proxy_pass http://upstream_balancer;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
## end server www.abc.com