Cloud notes
AOP aspect oriented programming
Section (child): cross section of a transaction
Features: insert (expand) cross section function for the software without changing the original function of the software
For horizontal functions, AOP can greatly simplify software development:
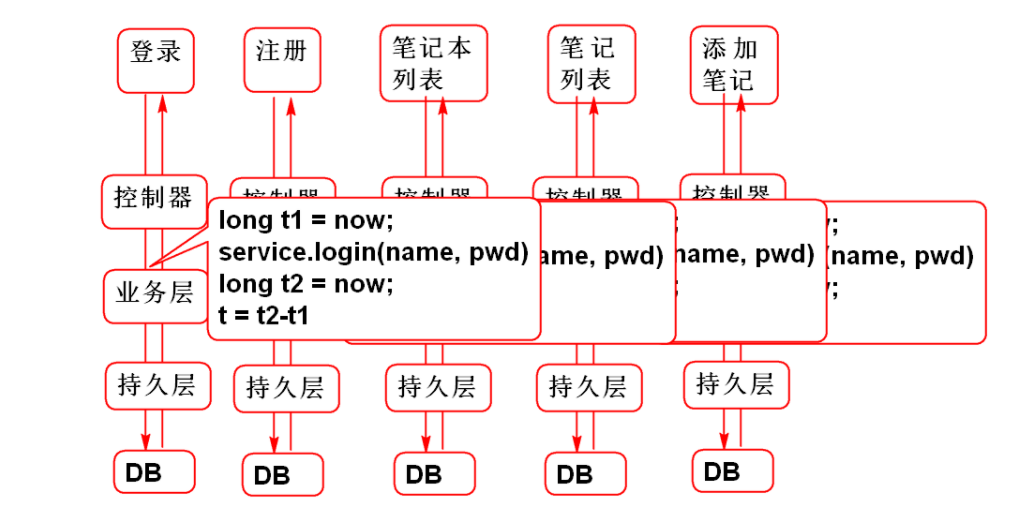
AOP not used:
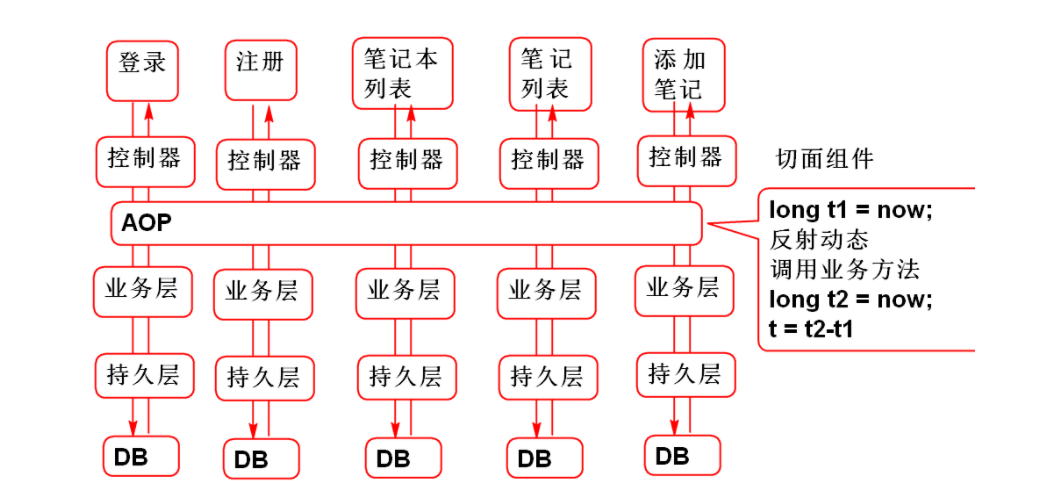
After using AOP:
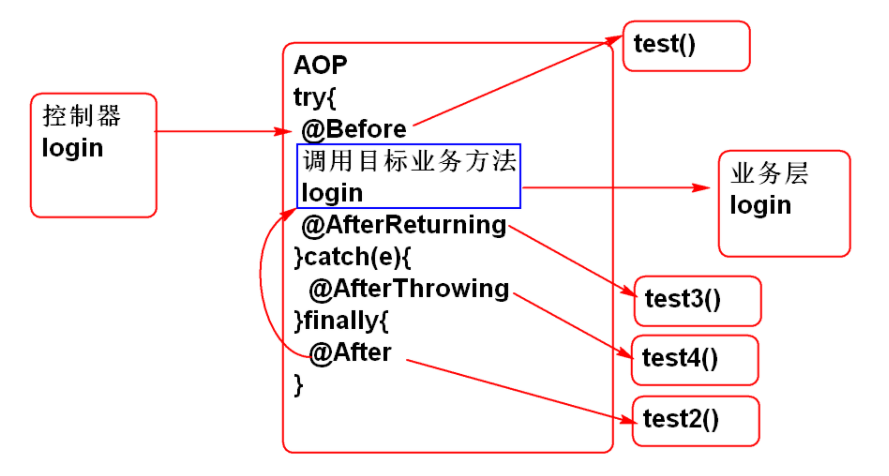
Develop an AOP case:
-
Import Aspect J package
Spring AOP bottom layer uses AspectJ implementation!
<dependency> <groupId>aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency>
-
Create slice component
@Component @Aspect public class DemoAspect { //Declare that the test method will run before all the methods of userService @Before("bean(userService)") public void test(){ System.out.println("Hello World!"); } } -
Configuring Spring AOP: spring-aop.xml
<!-- Configure component scanning --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.tedu.note.aop"/> <!-- send @Aspect Note effective --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
-
test
Hello World! Will be in userService Execute before business method
notice
Target method: the business method intercepted by AOP is called target method
Slice method execution timing: just before and after the target method
-
@Before: the slice method executes before the target method
-
@After: the slice method executes after the target method
-
@After returning: the facet method is executed after the normal end of the target method
-
@AfterThrowing: the facet method executes after the target method exception
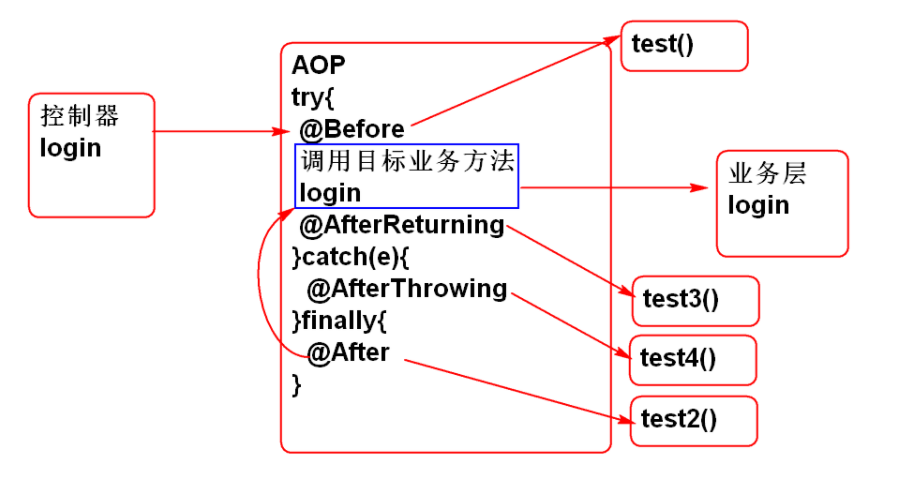
Case:
/**
* Creating a faceted component is an ordinary JavaBean
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class DemoAspect {
//Declare that the test method will run before all the methods of userService
@Before("bean(userService)")
public void test(){
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
@After("bean(userService)")
public void test2(){
System.out.println("After");
}
@AfterReturning("bean(userService)")
public void test3(){
System.out.println("AfterReturning");
}
@AfterThrowing("bean(userService)")
public void test4(){
System.out.println("AfterThrowing");
}
}Around notification
Surround notification can be invoked before and after the business method.
Case:
@Component
@Aspect
public class Demo1Aspect {
/**
* Surround notification method:
* 1. Must have return value Object
* 2. Must have parameter ProceedingJoinPoint
* 3. An exception must be thrown
* 4. You need to call jp.proceed() in the method.
* 5. Returns the return value of the business method
* @param jp
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Around("bean(userService)")
public Object test5(ProceedingJoinPoint jp)
throws Throwable{
Object val = jp.proceed();
System.out.println("Business results:"+val);
throw new UserNotFoundException(
"Just don't let me log in");
}
}breakthrough point
Used to locate the cut in position of APO: used to specify the cut in to the specific method class
-
bean component pointcuts
-
bean(userService)
-
bean(noteService)
-
bean(userService) || bean(noteService) || bean(notebookService)
-
bean(*Service)
-
-
Class pointcut
-
Within (class name)
-
Within (class name) | within (class name)
-
within(cn.tedu.note.service.impl.UserServiceImpl)
-
within(cn.tedu.note..impl.ServiceImpl)
-
-
Method pointcut (execution: execution)
-
Execution (modifier part of speech name. Method name (parameter type))
-
execution(* cn.tedu.note.service.UserService.login(..))
-
execution(* cn.tedu.note..Service.list*(..))
-
Note: consistent naming rules for classes and methods will help write effective pointcut expressions!
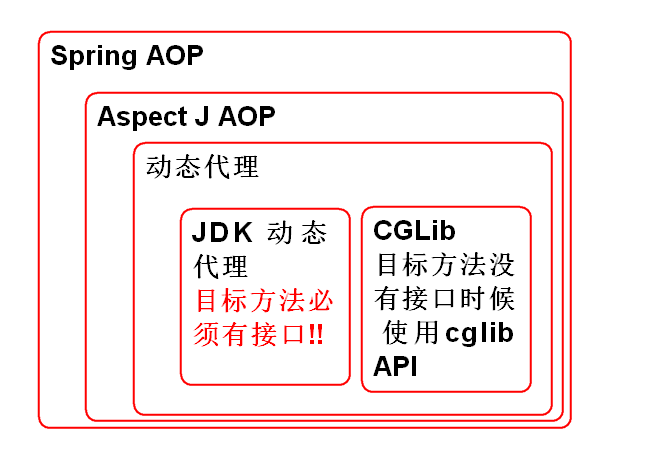
AOP underlying principle
Agent mode: do not change the original function to expand the new function for the software
AOP encapsulates the dynamic agent function and provides a simpler way to use it!
Classic interview questions:
AOP What is the underlying technology? answer: Dynamic agent technology is used.
Key points:
-
Spring AOP takes advantage of AspectJ AOP implementation!
-
The underlying layer of AspectJ AOP uses dynamic proxies
-
There are two kinds of dynamic agents
-
JDK dynamic proxy is automatically selected when the target method has an interface
-
Select CGLib dynamic proxy when the target method has no interface
-
The principle of AOP call can be analyzed by using exceptions:
java.lang.NullPointerException at cn.tedu.note.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.login(UserServiceImpl.java:34) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source) at org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(AopUtils.java:317) at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.invokeJoinpoint(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:183) at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:150) at org.springframework.aop.framework.adapter.MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.invoke(MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.java:51) at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:172) at org.springframework.aop.interceptor.ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke(ExposeInvocationInterceptor.java:91) at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:172) at org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(JdkDynamicAopProxy.java:204) at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy21.login(Unknown Source) at cn.tedu.note.controller.UserController.login(UserController.java:34) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source) at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invoke(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:215) at org.springframework.web.method.support.InvocableHandlerMethod.invokeForRequest(InvocableHandlerMethod.java:132) at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.java:104) at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.invokeHandleMethod(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:745) at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.handleInternal(RequestMappingHandlerAdapter.java:686) at org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.handle(AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter.java:80) at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doDispatch(DispatcherServlet.java:925) at org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet.doService(DispatcherServlet.java:856) at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.processRequest(FrameworkServlet.java:953) at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.doPost(FrameworkServlet.java:855) at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:650) at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.service(FrameworkServlet.java:829) at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:731) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:303) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208) at org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:52) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:241) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208) at cn.tedu.note.web.DemoFilter.doFilter(DemoFilter.java:28) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:241) at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:220) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:122) at org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:505) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:169) at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:103) at org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve.invoke(AccessLogValve.java:956) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:116) at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:423) at org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor.process(AbstractHttp11Processor.java:1079) at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$AbstractConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:625) at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint$SocketProcessor.run(JIoEndpoint.java:318) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(Unknown Source) at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(Unknown Source) at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)
AOP interceptor filter
-
Filter: intercept and process WEB requests!
-
Spring MVC Interceptor: intercepts the request process of spring MVC
-
AOP: intercept method requests between components in Spring
Declarative transaction
Programming transactions
Traditional programming transaction processing is very cumbersome:
try{
conn=open a connection
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//Database operation 1
//Database operation 2
//Database operation 3
conn.commit();
}catch(e){
conn.rollback();
}finally{
conn.close()
}Declarative transaction
The bottom layer of declarative transaction processing is realized by AOP, which can be used only by simple configuration

Use declarative transactions
-
Configure transaction manager
<!-- spring-mybatis.xml --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- Setting up annotation driven transaction management --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
Just use transaction annotations on business methods
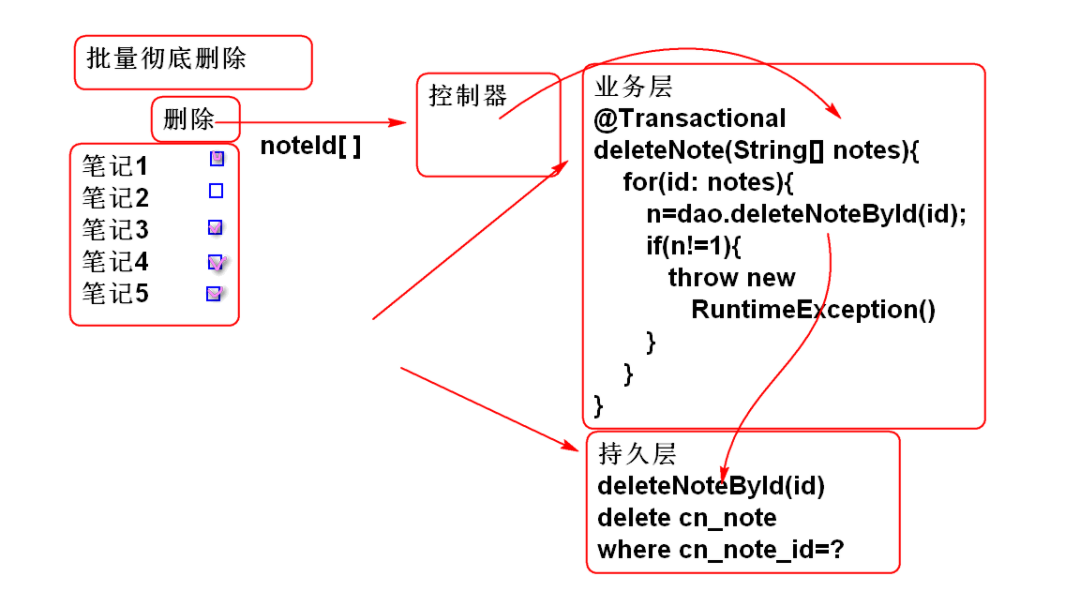
Case: batch deletion
-
Develop persistence layer
Persistent layer NoteDao
int deleteNoteById(String noteId);
SQL NoteMapper.xml
<delete id="deleteNoteById" parameterType="string"> delete from cn_note where cn_note_id=#{noteId} </delete> -
Business layer
Business layer interface method NoteService
int deleteNotes(String... noteIds) throws NoteNotFoundException;
Implement the business method NoteServiceImpl
@Transactional public int deleteNotes(String... noteIds) throws NoteNotFoundException { for(String id: noteIds){ int n=noteDao.deleteNoteById(id); if(n!=1){ throw new NoteNotFoundException("ID error"); } } return noteIds.length; }When an exception NoteNotFoundException is thrown, the Spring transaction rollback operation will be triggered
-
Test NoteServerTest
@Test public void testDeleteNotes(){ String id1 = "3febebb3-a1b7-45ac-83ba-50cdb41e5fc1"; String id2 = "9187ffd3-4c1e-4768-9f2f-c600e835b823"; String id3 = "ebd65da6-3f90-45f9-b045-782928a5e2c0"; String id4 = "A";//"fed920a0-573c-46c8-ae4e-368397846efd"; int n = service.deleteNotes( id1, id2, id3, id4); //int n = service.deleteNotes( // new String[]{id1, id2, id3, id4}); System.out.println(n); }An exception occurs when the submitted ID is wrong, and the database transaction is rolled back
task
-
Implement performance test function
-
Add declarative transaction management to the business layer