Article catalog
catalogue
preface
html gives the web content, css adds the skeleton to the web page, and JavaScript is needed to make the web page move and interact with users
1, What is JavaScript?
JavaScript is a client-side programming language, which includes ECMA Script and web API.
ECMA specifies the core knowledge of js basic syntax. For example: variables, branch statements, loop statements, objects, etc.
Web API includes DOM operation documents, such as moving, size, adding and deleting page elements. BOM operation browser, such as page pop-up window, detecting window width, storing data to browser, etc
2, Writing position of JS
1. Inline
<h2 onclick="alert('Click')">title</h2>2. Embedded
<body>
<script>
// JS code is written here
// Pop up warning window
alert('It will pop up here');
</script>
</body>3. External chain
<!-- Note: if you want to use src External link a JS File, then script Never write code in the label --> <script type="text/javascript" src="index.js"></script>
3, Input / output statement
If you want to see something in js, you must use input and output statements
1. Enter a statement
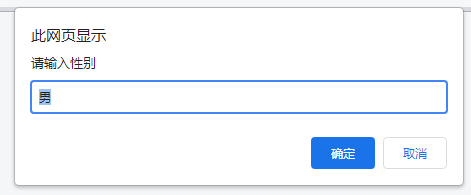
The first quotation mark is the prompt information, and the second quotation mark is the default input
prompt('Please enter gender', 'male');effect:
2. Output statement
| sentence | explain |
| document.write('<h1>666</h1>'); | You can display the content in the body |
| alert('pop up here '); | Pop up warning box |
| console.log('the console will print this string '); | Print on console |
document.write('<h1>666</h1>');effect:

alert( 'Pop up here' );

console.log('The console will print this string');
4, Definition and use of variables
1. Define variables
| let | Valid in local variable {} |
| var | global variable |
let and var define variables differently:
let defined variables are not allowed to be redefined, while var defined variables can be redefined
let defined variables have block level scope, while var defined variables do not have block level scope
Pre resolution:
let defines the variable code
let phone;// Variable name phone = 13312341234; document.write(phone);
2. Notes on variables
2.1 variables defined with let cannot be redefined and can be changed
let uname = 'Spider-Man'; uname = 'Iron Man'; uname = 'Ultraman';
2.2 if we want to use more variables, we can define multiple variables at the same time
let a,b,c;
2.3 if a variable is only defined but no data is saved, it is undefined by default
let age; console.log(age);
effect:
3. Variable naming convention
Rules (must not be violated)
-
Variable names must not be keywords
-
Variable names can contain numbers, letters, underscores$
-
Variable names cannot start with numbers
-
Variable names cannot contain spaces
-
Variable names are case sensitive
Specification (recommended)
-
It is suggested that the variable name should be meaningful
-
Hump nomenclature For example: userNameSex:
5, Array
Because variables can only save one data at a time, it is inconvenient to save multiple data
Array: used to save a combination of multiple data. let variable name = [value 1, value 2, value 3, value 4, value 5,...];
Need to use Variable name [subscript] The subscripts of value 1, value 2, value 3, value 4, value 5,... Are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
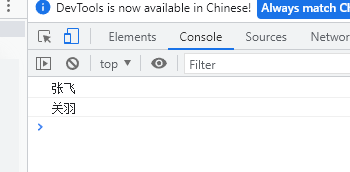
let arr = ['Fei Zhang', 'Guan Yu', 'Zhao Yun', 'Zhang Liao', 'army officer's hat ornaments']; console.log( arr[0] ); console.log( arr[1] );
effect:
Any array has an attribute: length, which is used to view the length of the array (the number of arrays)
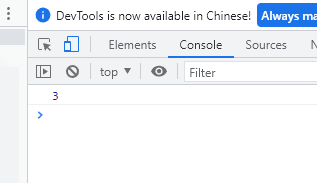
let arr = ['aa', 'bb', 'cc']; console.log(arr.length);
effect:
6, Data type
| Number type | number |
| Character type | Chinese characters, letters and symbols |
| Boolean type | ture,fasle |
| undefined type | undefined object is null |
| null type | null means that the variable is empty |
1. Number type
The 'Number' type is also a Number type
let age = 23; let pi = 3.14; let num = 2;
2. Character type
It is usually wrapped in quotation marks, such as Chinese characters, letters and symbols
let uname = 'Delireba'; let userName = 'wahaha'; let str = 'study hard and make progress every day.?: !*';
String splicing
If the variable is wrapped in quotation marks, it becomes an ordinary string. The string cannot be written directly next to anything else. In the string, there is a splicing operation of + identification string
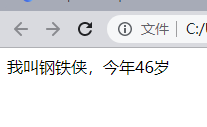
let uname = 'Iron Man';
let age = 46;
document.write('My name is' + uname + ',this year' + age + 'year');
effect:
Template string:
If you want to identify variables: just ${variables}
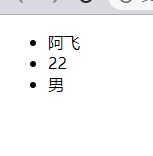
let uname = 'A Fei';
let age = 22;
let sex = 'male'
document.write(`<ul>
<li>${uname}</li>
<li>${age}</li>
<li>${sex}</li>
</ul>`);effect:
3. Boolean type
Describes the type of true and false values. There are only two values, true (true) and false (false)
4. undefined type
If a variable is defined without assignment, it is undefined, which means that the variable is empty
let num; console.log(num);
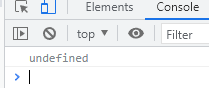
5. null type
Indicates that the variable is empty
7, Display conversion
1. To numeric type
let n = '26'; n=Number(n);
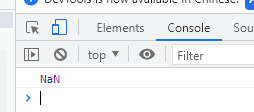
If the string contains non numeric characters, the result of conversion is NaN
let n = '26a'; let m = Number(n); console.log(m);
effect:
What happens when there are numbers in the string that need to be taken out?
| parseInt: | Rounding, (take out the integer part) |
| parseFloat: | Take floating point number, (take floating point number) |
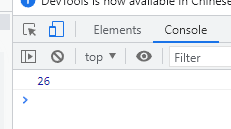
parseInt: rounding, (take out the integer part)
let n = '26.67.34a'; //parseInt: rounding, (take out the integer part) let re = parseInt( n ) console.log( re );
effect:
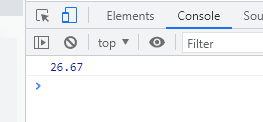
parseFloat: floating point number, (floating point number)
let n = '26.67.34a'; // parseFloat: floating point number, (floating point number) let re = parseFloat(n) console.log(re);
effect:
2. To string
| String (variable name) | |
| Variable name. toString(); | toString is not allowed for null and undefined |
String to string
let num = 123; let re = String( num); console.log( re );
Variable name. toString();
let num = 123; let re = num.toString(); // toString is not allowed for null and undefined console.log( re );
3. To boolean type
Use Boolean (variable name) to convert variables to Boolean types. Since Boolean types only have true and false, except
0, '', null, undefined and NaN will be converted to false, and the rest will be converted to true