Homology strategy:
What is homology strategy?
-
Homology policy is a requirement (constraint) on network security given by the browser
-
It is agreed that the addresses of the requesting party and the target party must ensure that the domain name and port number of the transmission protocol are completely consistent
-
When you're sending a request
-
If the full address of the open page and the full address of the receiving server
=>As long as the transmission protocol or domain name or port number is different
=>It is called triggering the homology strategy
=>After you trigger the same origin policy, the browser does not allow you to obtain the data returned to you by the server
Homology: the transport protocol is exactly the same as the domain name and port number
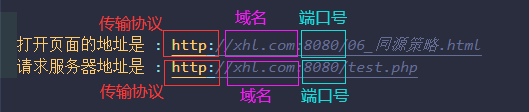
Non homologous: the transport protocol is different from any one of the domain name and port number

Cross domain request:
-
When a request triggers a homology policy
-
And we also need to request data from non homologous servers
-
We call a request that triggers a homology policy a cross domain request
Common solutions for cross domain requests:
1. jsonp
Implementation of jsonp:
-
Use the src attribute of the script tag to request a non homologous server address
-
Requirement: the content given by the server must be a legal and executable js code
-
Requirement: the js code given by the server needs to be in the format of 'function name (data)'
script tag:
- A label that introduces an external file
- The meaning of this tag is that all the imported content will be executed as js code by default
- Meaning of script tag:
=>Is to import an external file
=>Whatever the file name and suffix is
=>Just read the contents of this file
=>The read content is executed as js code
src attribute:
- Function: label the connection path of introducing an external resource
- characteristic:
=>SRC attribute is an attribute given by W3C standard to introduce external resources
=>The browser does not care whether the content introduced by src is cross domain or not through the external address introduced by src attribute
=>Therefore, it is not affected by the browser homology policy
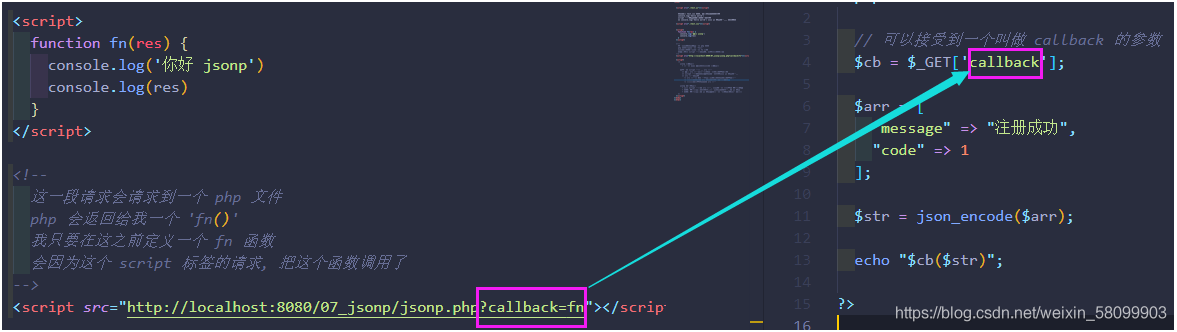
jsonp technology is a cross domain approach that has nothing to do with ajax technology- Using script tags and src attributes
- Using the script tag will execute the requested content as js code
- Using src attribute is not affected by homology strategy
- Requirement: the returned string from the backend must be a legal js format string
2. CORS (cross domain resource sharing)
-
A cross domain request scheme that has nothing to do with the front end
-
Front end: how to send ajax requests
-
Enable cors configuration from the backend
Back end enable cors configuration
<?php
// Cross domain
// Tell the browser here, don't worry, I'm willing to give him data
// Tell the browser which domain names can request me
// Indicates the allowed domain name, * indicates universal configuration
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
// CORS
// Tell the browser which request methods are allowed
header("Access-Control-Request-Methods:GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS");
// Tell the browser what additional request header information is allowed
header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers:x-requested-with,content-type,test-token,test-sessid,authorization');
echo 'hello world';
?>
3. Proxy
-
Proxy mode cross domain: any server can set and configure the proxy
-
apache server
=>Proxy http request address free
=>The proxy https request address requires a certificate
-
nginx server
=>Proxy http and https are free
=>Note: the request path must be in English without Chinese characters
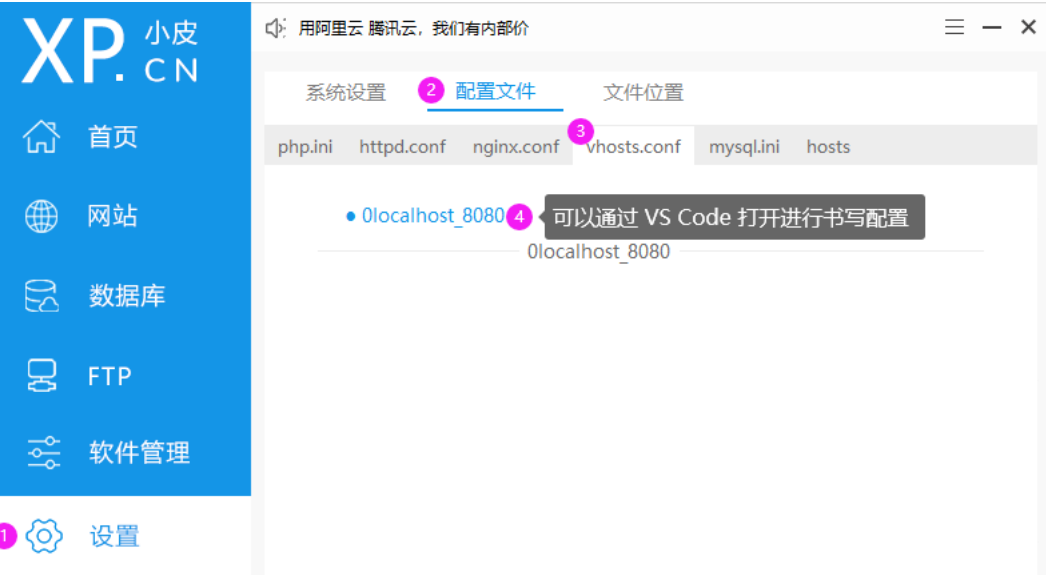
To configure an agent with a skin:
- Open the small leather panel
=> Take the server from apache Switch to nginx
- Open the small leather panel
=> Click settings in the left sidebar => Click profile => Select to vhosts.conf file => Click 0 localhost_8080
- Found closed parentheses for server
=> On the previous line of closed parentheses, Write code configuration
location /xx {
proxy_pass You requested a cross domain address;
}
/xx: You wrote it casually, It's called a proxy identifier
proxy_pass Back address, Is the cross domain address when you request
- Be sure to restart the server

front end:
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// Note: when you send a request, the request address must directly write the proxy identifier
// In this way, the server will find that you are requesting a proxy identifier. I have indeed configured it
// nginx will help you forward the request to the proxy_ The address configured by pass
xhr.open('GET', '/xhl')
xhr.onload = function () {
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
xhr.send()
Back end:
<?php echo 'hello world'; ?>

reference resources:
Browser's same origin policy and cross domain request_ Learning Edition