I. Preface
Any report has a data source, which is the source of all data. JasperSoft is no exception, of course, because it supports rich data source adapters. For example, common Jdbc, MongoDB, Json, JNDI, and even our custom implementation of JRDataSource are possible.
As shown in the figure below, this is the data source adaptation supported by version 6.8 of JasperSoft. With the iteration of JasperSoft software, more and more data sources are supported.
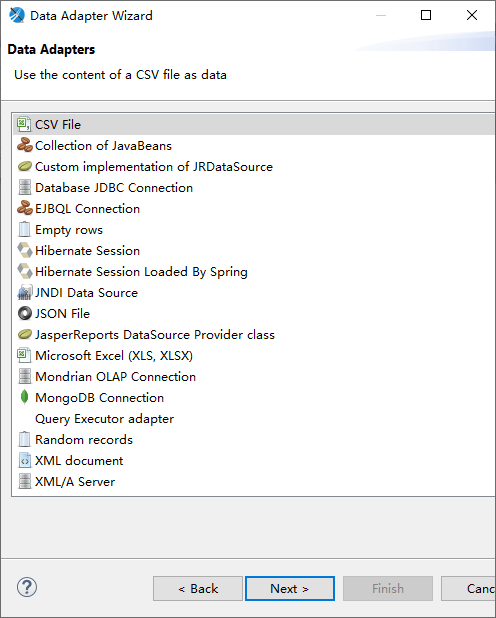
JDBC Data Source
JasperSoft supports a wide range of data sources. Here we use JDBC data sources commonly used to demonstrate the use of Jasper templates. We can also refer to other data sources. Official Documents.
1. Creating Data Sources
JasperSoft's data sources are created in a variety of ways.
Click File - > Select Data Adapter
On JasperSoft projects in the Project Explorer area, or in any blank space
Including when we create templates, we can also create data sources. Quick buttons are also provided at the top.
2. Configuring Data Sources
Select Data Adapter, specify the name of the data source, and where to save it. In a Jasper project, multiple data sources can be created.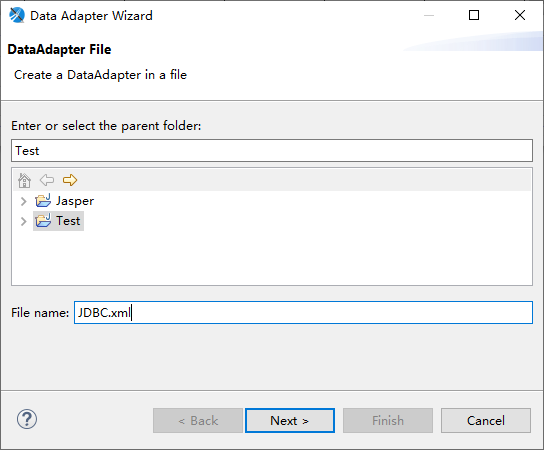
Select the Database JDBC Connection option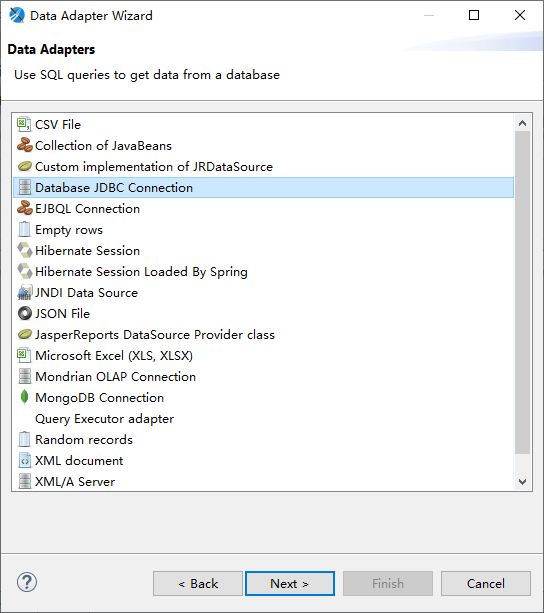
Select Next to configure the data source properties
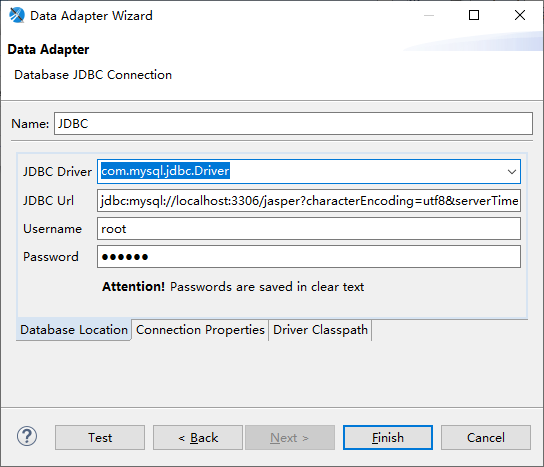
Name: Any name is OK
- JDBC Driver: Drop down the selection box, select Mysql, and remove the prefix and suffix. Another thing to note is that Mysql uses a new driver name (com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver) from 6.x.
- JDBC Url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jasper?characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=UTC
- Username: Username
- Password: Password
Driver Classpath: We also need to configure the JDBC driver package to go to mvnrepository download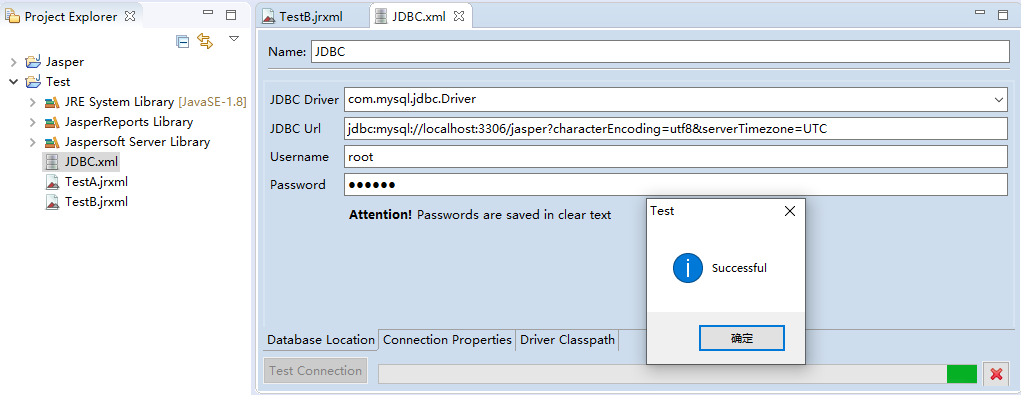
3. Use data sources
After configuring the Jdbc data source, the data source can be further used. The data source only needs to be configurated once and can be reused.
When creating a template, you can specify the configured data source file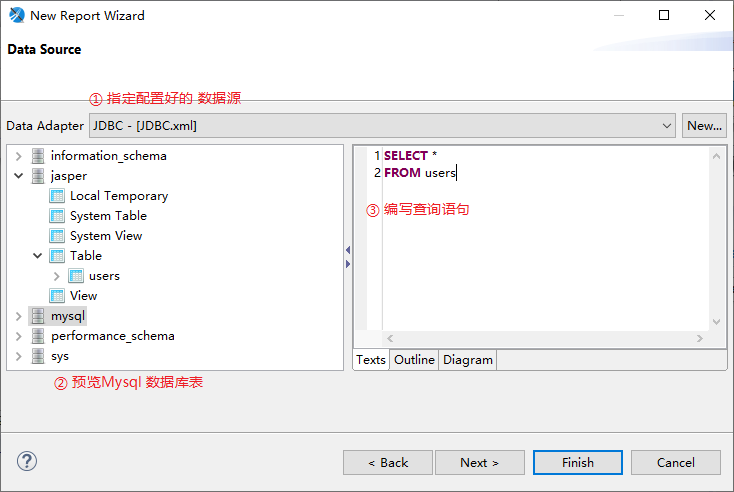
Click Next to configure the queried fields and Finsh to complete the configuration. Finsh is selected here and can be configured later.
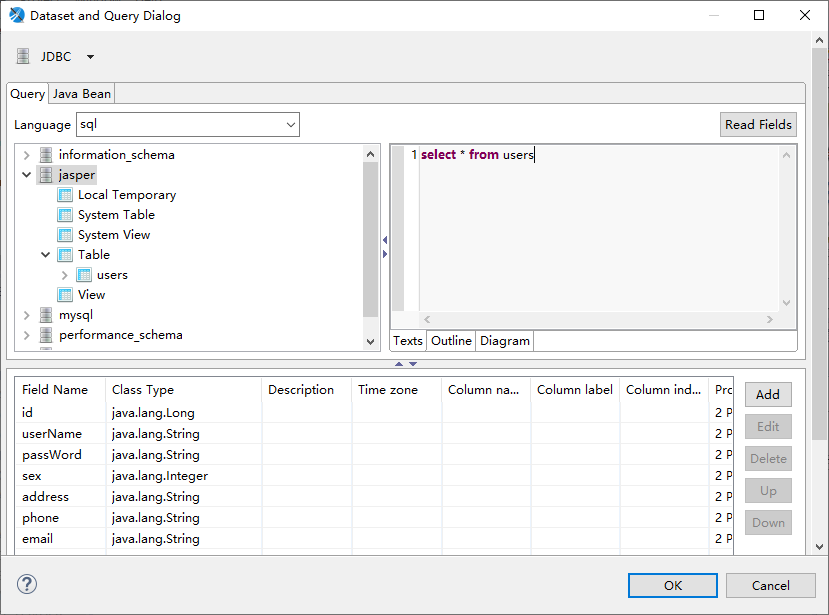
Once the template has been created, you can import Fields using query statements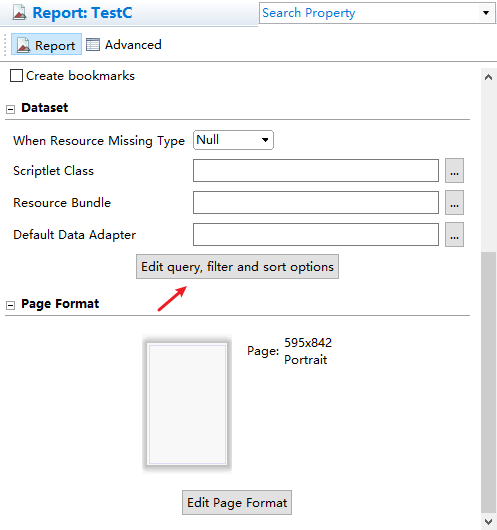
4. Test cases
Click OK to complete Fileds import. Drag Fileds into our template, set font size and location, and click Preview.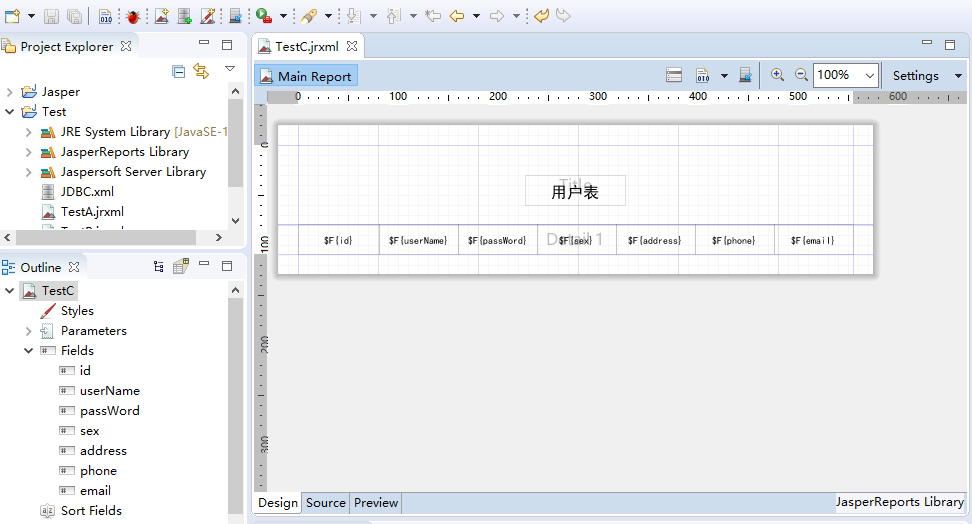
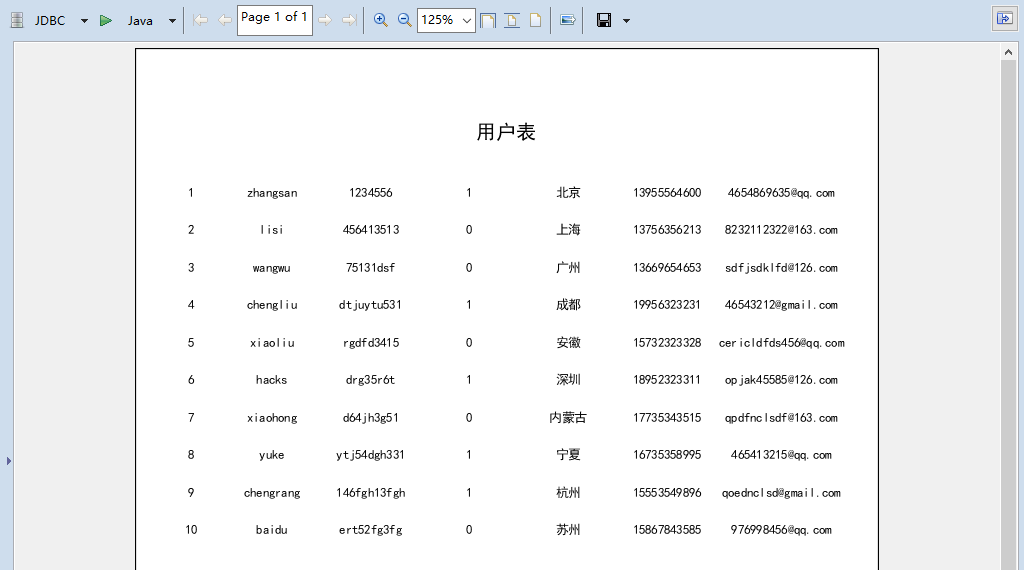
This is just a simple query. When you encounter complex SQL statements, you can use the dynamic parameter Parameters.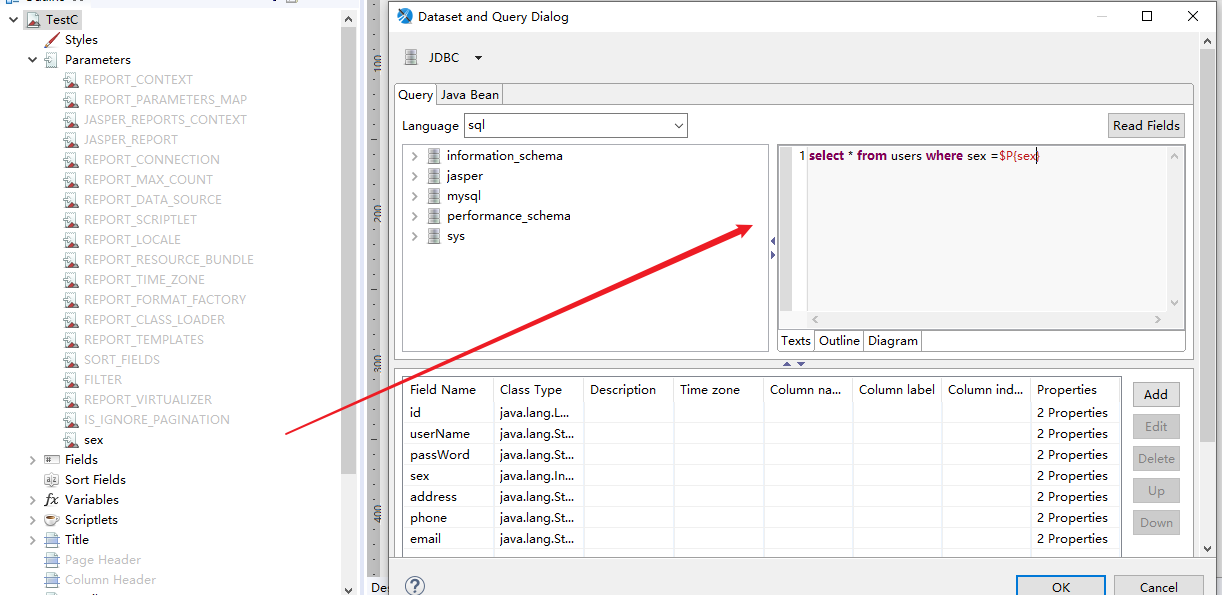
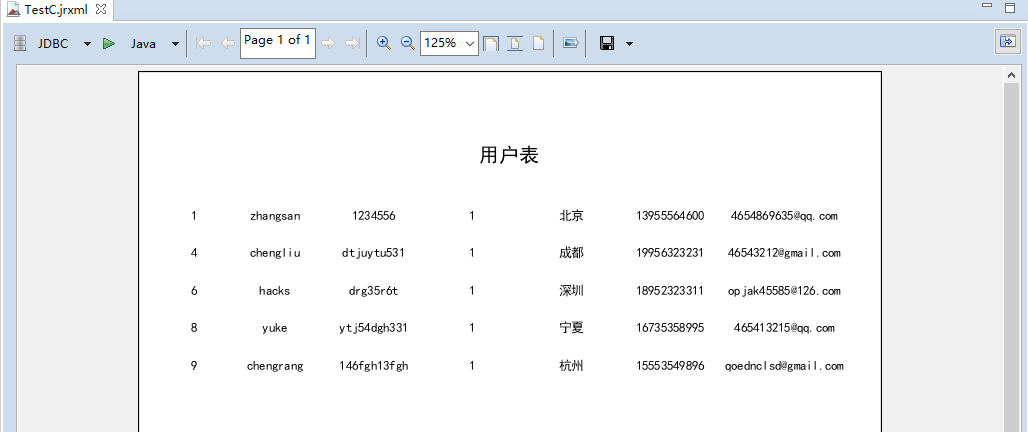
5.Java instance
Previous examples help to preview effects, but more requirements are used in projects.
Basic configuration of Pom.xml, where jasperfonts is a custom font package
<!--Jasper Report Engine--> <dependency> <groupId>net.sf.jasperreports</groupId> <artifactId>jasperreports</artifactId> <version>6.9.0</version> </dependency> <!--Jasper Custom font--> <dependency> <groupId>com.jasperfonts</groupId> <artifactId>jasperfonts</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> <!--Introduce JDBC Driver package--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Introduce Mysql drive--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Use Druid Connection pool--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.18</version> </dependency>
You need to configure database connections in application.properties
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jasper?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456
The code is as follows
@Controller @RequestMapping("report") public class JasperController { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @RequestMapping("/Jdbc") public void Jdbc(HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { //1. Get the compiled jasper template file stream InputStream reportStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Jasper/TestC.jasper"); //2. Getting the output stream ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream(); //2. Create parameter values and fill them in HashMap<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>(); hashMap.put("sex", 1); //3. Call Jasper Report Engine try { JasperRunManager.runReportToPdfStream(reportStream, outputStream, hashMap,dataSource.getConnection()); response.setContentType("application/pdf"); outputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Preview of results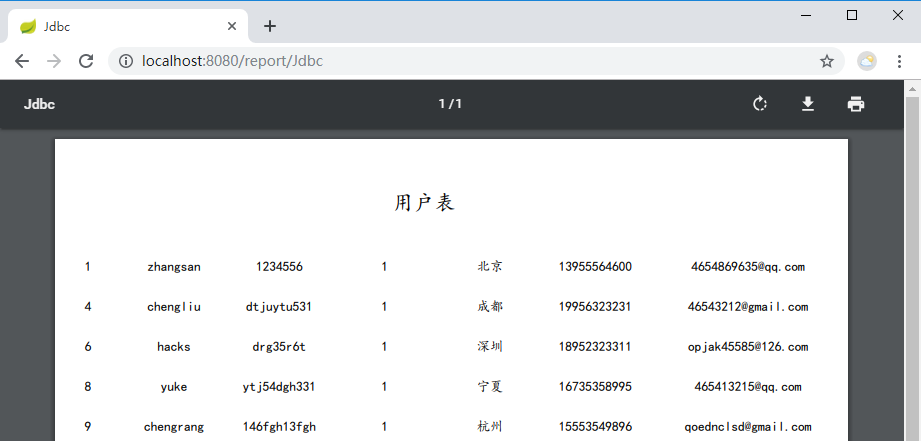
6. Summary
We can use JDBC data sources to populate Jasper reports in a way that improves efficiency by using faster debugging templates for what we see and get at the time of preview.