JDBC operates on MySQL database diagrams: 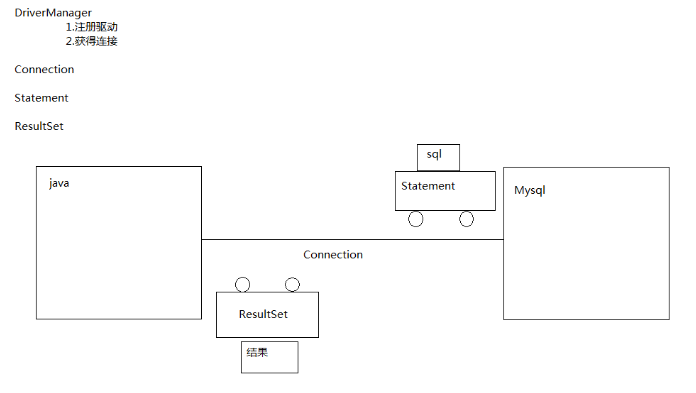
JDBC simple column:
//Import Driver Class Library
//Registration driven
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
//Connect to the database
String user="root";
String password="mysql520";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", user, password);//test is the database name
//Operating database
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql="insert into student values(null,'guomei',22)";
st.execute(sql);//st.executeUpdate(sql);
//close resource
st.close();
conn.close();Use st.executeUpdate or st.execute to add, delete and change
But queries need to use st.executeQuery
// Operating database
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
String sql="select * from student";
ResultSet resultSet = st.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
System.out.println("id:"+id+"======="+"name:"+name+"====="+age);
}Driver Manager details
// 1.Registration driven
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());//This method is used to register in the jar package, so reflection method is recommended.
System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// Recommended wayUri address
// full url format: big protocol: subprotocol: / / IP address: port number / library name? Parameter key = parameter value
// Complete: jdbc: mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day05? UseUnicode = true & characterEncoding = utf8
// Simple: jdbc: mysql://day05? UseUnicode = true & characterEncoding = utf8, which can be ignored if local host: 3306 is connectedIt is generally recommended to write complete and no parameter keys = parameter values
Conection details
Functions: 1. Links representing databases
2. Statement objects that transport sql statements can be created based on this object
Method:
******** Statement createStatement() Creates a state object
Callable Statement prepareCall (String sql) calls stored procedures in the database (stored procedures are not learned)
******** PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) Creates PreparedStatement objects (afternoon school)
Statement object
This object can be understood as a "car" that delivers sql statements to the database.
Method:
void addBatch(String sql) adds statements to the car. (for batch execution of SQL statements); insert update delete
int[] executeBatch() delivers the statements on board to the database for execution. The return value stores the number of rows affected by the execution of each statement. Because it is multiple statements, it is assembled by numbers.
void clearBatch() clears statements from the car.
These three methods are related to the batch implementation of sql (the last class demonstration in the afternoon)------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
boolean execute(String sql) executes an SQL statement. If the statement returns a result set with a return value of true(select), if the statement does not return a result set with false(insert update delete);
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql) executes a query with a result set. The result set is wrapped in the resultset object. (select)
int executeUpdate(String sql) executes a statement without a result set. It returns the number of rows affected by the statement. (insert update delete)
Conclusion:
Use: executeQuery method when executing query statements
Use: executeUpdate method when executing add, delete and change statements
ResultSet object
Function: When the execution statement is a query statement, the resultSet object is used to encapsulate the query results.
Method:
boolean next() method lets the pointer (cursor) in the result set move down one line and determines whether the change line has data. Return true, not false
String getString(int cloumnCount) retrieves String-type data from the row currently pointed to. It is retrieved according to the index location of the column.
String getString(String columnName) retrieves data of String type from the row currently pointed to. It is selected by column name.
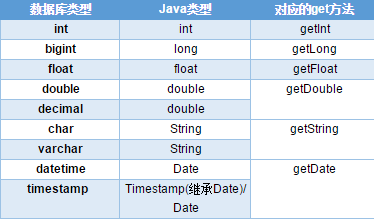
There are many kinds of getXXX series methods, but not for different types of databases.
JDBCUtils Tool Class
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
static{
try {
//0 Read Configuration File
Properties prop = new Properties();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("src/db.properties");//Place easily modified content in db.properties
prop.load(is);
is.close();
driver = prop.getProperty("driver");
url = prop.getProperty("url");
user = prop.getProperty("user");
password = prop.getProperty("password");
//1 Registration Driver
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//1 Get Connections
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
//2 Get Connections
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create connection!");
}
return conn;
}
//2 Releasing resources
//1 > The parameter may be empty
//2 > Calling the close method throws an exception to ensure that it can continue to close even if an exception occurs
//3 > Close order, from small to large
public static void close(Connection conn , Statement st , ResultSet rs){
try {
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(st!=null){
st.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(conn!=null){
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getConnection());
}
}Where db.properties file
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test;
user=root;
password=mysql520;SQL details:
Assemble SQL statements
//Assemble sql statements
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME='"+name+"' AND PASSWORD='"+password+"';";Solving the problem of SQL injection
//Demonstrate using PrepareStatement object to solve sql injection problem
public void fun2() throws Exception{
String name ="xxx' OR 1=1 -- ";
String password ="1234";
//1 Get Connections
Connection conn= JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2 Assemble sql statements
String sql = "SELECT * FROM student WHERE NAME=? AND PASSWORD=?";
//3 Get PrepareStatement
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4 Set parameters to ps objects
ps.setString(1, name);
ps.setString(2, password);
//5 Transport parameters, execute sql and get results
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
//5 Decide whether the login is successful or not based on the results
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("Login successfully!");
}else{
System.out.println("Login failed!");
}
//6 Closing resources
JDBCUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}Storing large text to database by JDBC
//PrepareStatement object must be used to store large text
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//1 Get Connections
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2 writing sql
String sql = "insert into mytext values(null,?)";
//3 Create PrepareStatement
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4 Setting parameters
//Parametric 1: Index of parameters
//Parametric 2: Stream of text to be saved
//Parametric 3: File length
File file = new File("src/text.txt");
FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);
ps.setCharacterStream(1, reader, (int)file.length());
//5 implementation of sql
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(result);
//6 Closing resources
JDBThe tables in the database need to have a column text (column name) text (column type)
create table mytext(
id int primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
text text
)Storing pictures to database by JDBC
//Demonstration to store pictures in mysql
//PrepareStatement objects must be used to store images
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//1 Get Connections
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2 writing sql
String sql = "insert into myblob values(null,?)";
//3 Create PrepareStatement
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4 Setting parameters
//Parametric 1: Index of parameters
//Parametric 2: Stream of images to be saved
//Parametric 3: Picture file length
File f = new File("src/wg.PNG");
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(f);
ps.setBinaryStream(1, is, (int)f.length());
//5 implementation of sql
int result = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(result);
//6 Closing resources
JDBCUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}Pictures are generally defined as file types
create table myblob(
id int primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
file blob
)Batch execution of SQL:
//1 Use Statement Object batch execution sql
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//1 Get connected
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2 Get Statement
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
//3 Add multiple strips sql Statement tostin
st.addBatch("create table t_stu ( id int primary key auto_increment , name varchar(20) )");
st.addBatch("insert into t_stu values(null,'tom')");
st.addBatch("insert into t_stu values(null,'jerry')");
st.addBatch("insert into t_stu values(null,'jack')");
st.addBatch("insert into t_stu values(null,'rose')");
//4 implement sql
int[] results = st.executeBatch();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(results));
//5close resource
JDBCUtils.close(conn, st, null);
}
//2 Use PrepareStatement Object batch execution sql
public void fun2() throws Exception{
//1 Get connected
Connection conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2 write sql Sentence
String sql = "insert into t_stu values(null,?)";
//3 Establish PrepareStatement
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//4 loop.Add parameter
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
ps.setString(1, "user"+i);
ps.addBatch();
}
//5 Batch execution
int[] results =ps.executeBatch();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(results));
//5close resource
JDBCUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}Classroom Notes Download Address:
[1] JDBC Learning Notes - Download Channel - CSDN.NET
[2] Baidu Disk Link: http://pan.baidu.com/s/1slDA8bV Password: 5vii