Catalog
5. Mixed Constructor/Prototype Approach
JavaScript custom object
- Object: In JavaScript, an object is data that has attributes and methods.
- There are seven ways to customize JavaScript objects: direct creation, object initializer, constructor, prototype, hybrid constructor/prototype, dynamic prototype and factory model. Here are five common ways to customize JavaScript objects: direct creation, object initializer, constructor, prototype, hybrid constructor/prototype, dynamic prototype and factory model.
1. Direct Creation
Create grammar directly:
var object variable name = new Object();
Object variable name. property1 = value1;
...;
Object variable name. propertyN = valueN;
Object variable name. methodName1 = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
...;
Object variable name. methodNameN = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
Examples:
Results:
2. Object initializer
Object initializer mode, create grammar:
var Object variable name = {
property1 : value1,
property2 : value2,
...,
propertyN : valueN,
methodName1 : function([parameter_list]){
//Function Body
},
...,
methodNameN : function([parameter_list]){
//Function Body
}
}
Examples:

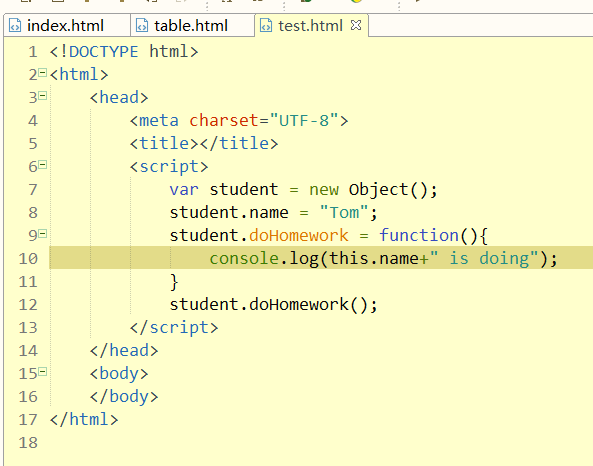
var student = {
name : "Xiao Wang",
age : 20,
getName : function(){
//this cannot be defaulted
return this.name;
},
doHomework : function(name){
console.log(name+"I am learning......");
}
}
var age = student.age;
var name = student.getName();
console.log(name+":"+age);
student.doHomework(name);//Call methodResults:

3. Constructor Mode
Constructor way to create grammar:
function constructor ([parameter list]){
this. Attribute = attribute value;
...
this. Attribute N = Attribute value N;
this. Function 1 = method1;
...
this. Function N = methodN;
}
Function method 1 ([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
...
Function method N ([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
or
function constructor ([parameter list]){
this. Attribute = attribute value;
...
this. Attribute N = Attribute value N;
this. Function 1 = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
} ;
...
this. Function N = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
} ;
}
Summary:
- Compared with the above two ways, using constructor to create objects can save code effectively.
- If an object is created by a constructor, this can not be omitted, which is also the difference between ordinary functions.
- Using constructor method to create objects, the left side method is more preferable, which improves the code reuse.
Examples:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Constructor approach</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
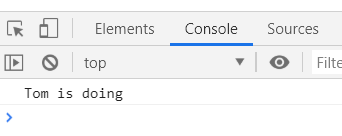
function Student(age){
this.name = "Xiao Wang";
this.age = age;
this.doHomework = doHomework;
}
function doHomework(name){
console.log(name+"I am learning......");
}
var student = new Student(89);
var name = student.name;//Call properties
var age = student.age;
console.log(name+":"+age);
student.doHomework(name);//Call method
</script>
</body>
</html>

Results:

or
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Constructor approach</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function Student(age){
this.name = "Xiao Wang";
this.age = age;
this.doHomework = function (name){
console.log(name+"I am learning......");
}
}
var student = new Student(89);
var name = student.name;//Call properties
var age = student.age;
console.log(name+":"+age);
student.doHomework(name);//Call method
</script>
</body>
</html> 
Results:
4. prototype Prototype
Prototype prototype, creating grammar:
function object constructor (){
}
Object constructor. prototype. Attribute name = attribute value;
Object constructor. prototype. Function name = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
Examples:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>prototype Prototype approach</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
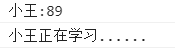
function Student(){
}
Student.prototype.name = "Xiao Wang";
Student.prototype.age = 21;
Student.prototype.doHomework = function (name){
console.log(this.age+"Year old"+name+"I am learning......");
}
var student = new Student();
var name = student.name;//Call properties
var age = student.age;
console.log(name+":"+age);
student.doHomework(name);//Call method
</script>
</body>
</html>
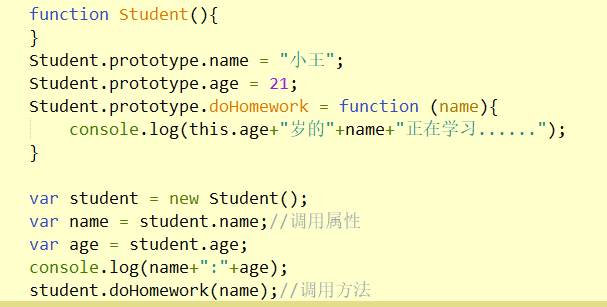
Results:

5. Mixed Constructor/Prototype Approach
Hybrid constructor/prototype approach:
Constructor method is easy to dynamically assign attributes, but this method also defines the method in the construction method body, which makes the code more cluttered; while prototype method is not easy to dynamically assign attributes, but the attributes and methods defined in this way are separated; so take advantage of strengths to complement weaknesses - constructor defines attributes, The prototype way defines the method.
Create grammar:
function object constructor ([parameter list]){
}
Object constructor. prototype. Function name = function([parameter list]){
// Function Body
}
Examples:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Mixed Constructive Functions/prototype</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function Student(age){
this.name = "Xiao Wang";
this.age = age;
this.doHomework = function (name){
console.log(this.age+"Year old"+name+"I am learning......");
}
}
//prototype functions are class-level
Student.prototype.read = function(){
//this represents the object that calls the function
console.log(this.age+"Year old"+this.name+"Reading......");
}
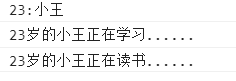
var student = new Student(23);
var name = student.name;//get attribute
var age = student.age;
console.log(age+":"+name);
student.doHomework(name);//Call method
student.read();
</script>
</body>
</html>
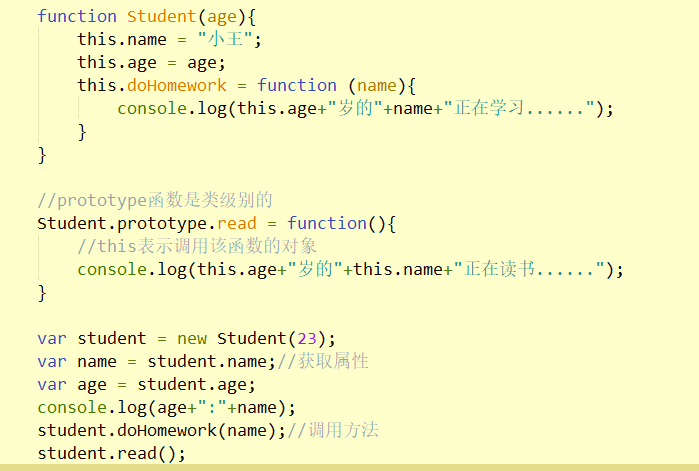
Results: