Using classes as member variables in Java
Any type can be a member variable of a class
Like the String class in the first contact, it is a class that references data types.
Using a class type as a member variable is equivalent to creating an object and passing the address value of the object to the member variable.
Operate on member variables as object names.
1, Class as member variable
case analysis
1. Define a Computer class
2. Define two member variables in the Person class, one of which is defined by Computer
3. Write test class and test code function
//Define Computer class class Computer{ private String CPU; private String RAM; //Parameterless construction method, getter and setter methods public Computer() {} public Computer(String CPU, String RAM) {this.CPU = CPU;this.RAM = RAM;} public String getCPU() {return CPU;} public void setCPU(String CPU) {this.CPU = CPU;} public String getRAM() {return RAM;} public void setRAM(String RAM) {this.RAM = RAM;} } //Define the Person class class Person{ private String name; //Class as member variable private Computer computer; //Parameterless construction method, getter and setter methods public Person() {} public Person(String name, Computer computer) {this.name = name;this.computer = computer;} public String getName() {return name;} public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;} public Computer getComputer() {return computer;} public void setComputer(Computer computer) {this.computer = computer;} //Define a member method for printing information public void useComputer(){ System.out.println(name+"The configuration of the computer in use is,\nCPU: "+computer.getCPU()+"\n Memory:"+computer.getRAM()); } } public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //Assign values to variables of Computer through construction method Computer computer = new Computer("i9-9900k","32G"); //Assign a value to the variable of Person through the construction method Person person = new Person("Zhang Sanfeng",computer); //Use useComputer method to view data transfer results person.useComputer(); } }
Operation results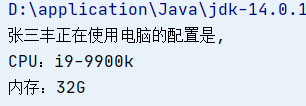
2, Interface as member variable
case analysis
1. Define an interface Use as member variable of Person
2. Interface Use must have an implementation class to Use
3. Define interface Use as member variable in People
4. Create member methods in the People class, use the member variables of the interface, and call the abstract methods in the interface.
5. Create test class and test code function
interface Use{ void use(); } //Create the implementation class of the interface class UseComputerImpl implements Use{ @Override public void use() {System.out.println("Using computer");} } //Define a People class with the interface as a member variable class People{ private String name; //Interface type as member variable private Use use; //No parameter and parameter construction method, because getter and setter methods are not used, which is omitted here. In normal use, it is not recommended to omit public People() {} public People(String name, Use use) {this.name = name;this.use = use;} //Create a member method that uses the interface to print information public void useComputer(){ System.out.print(name); //Using interface objects, calling implementation class methods use.use(); } } //Test class, test the code written public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { //Create implementation class objects (automatically transitioning up to interface types) Use use = new UseComputerImpl(); //Pass data to member variables using People's parametric construction People people = new People("Zhang Sanfeng",use); //Use the object of People to call the useComputer method to view the data transfer results people.useComputer(); } }
Operation results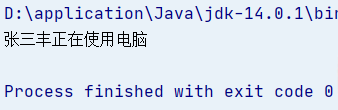
Let's expand
Use inner class and inner class of anonymous object to pass parameters
In this way, the writing of implementation class can be omitted
You need to supplement the related knowledge of internal classes, please click here
Create a new Test2 test class. The above code remains unchanged
public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //Using anonymous inner classes to create interface objects Use use = new Use() { @Override public void use() { System.out.println("Using computer"); } }; //Pass data to member variables using People's parametric construction People peopleOne = new People("Zhang San",use); //Use the object of People to call the useComputer method to view the data transfer results peopleOne.useComputer(); //===================================================== //Use anonymous inner class and anonymous object to pass parameters People peopleTwo = new People("Li Si", new Use() { @Override public void use() { System.out.println("Using computer"); } }); //Use the object of People to call the useComputer method to view the data transfer results peopleTwo.useComputer(); } }
Operation results