Java console input streams System.in and Scanner
System.out is commonly used to output data in the console
System.in can input data from the console
Step 1: system. In
package stream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Console input
try (InputStream is = System.in;) {
while (true) {
// Tap in a, then tap back to see
// 97 13 10
// 97 is the ASCII code of a
// 13 10 corresponding to carriage return
int i = is.read();
System.out.println(i);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Step 2: scanner reads the string
Although System.in.read can read data, it is not convenient
With Scanner, you can read line by line
package stream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
String line = s.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}Step 3: scanner reads integers from the console
Using Scanner to read integers from the console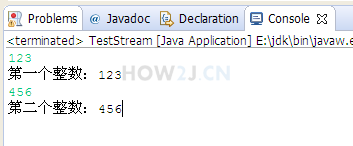
package stream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("First integer:"+a);
int b = s.nextInt();
System.out.println("Second integer:"+b);
}
}Practice: Auto create class
Automatically create a class file with one property.
Through the console, get the class name, property name and property type. According to a template file, create the class file automatically, and provide setter and getter for the property
public class @class@ {
public @type@ @property@;
public @class@() {
}
public void set@Uproperty@(@type@ @property@){
this.@property@ = @property@;
}
public @type@ get@Uproperty@(){
return this.@property@;
}
}Answer:
package stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Accept customer input
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter a name for the class:");
String className = s.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the type of property:");
String type = s.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the name of the property:");
String property = s.nextLine();
String Uproperty = toUpperFirstLetter(property);
// Read template file
File modelFile = new File("E:\\project\\j2se\\src\\Model.txt");
String modelContent = null;
try (FileReader fr = new FileReader(modelFile)) {
char cs[] = new char[(int) modelFile.length()];
fr.read(cs);
modelContent = new String(cs);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//replace
String fileContent = modelContent.replaceAll("@class@", className);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@type@", type);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@property@", property);
fileContent = fileContent.replaceAll("@Uproperty@", Uproperty);
String fileName = className+".java";
//Replaced content
System.out.println("Replaced content:");
System.out.println(fileContent);
File file = new File("E:\\project\\j2se\\src",fileName);
try(FileWriter fw =new FileWriter(file);){
fw.write(fileContent);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("File saved in:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
}
public static String toUpperFirstLetter(String str){
char upperCaseFirst =Character.toUpperCase(str.charAt(0));
String rest = str.substring(1);
return upperCaseFirst + rest;
}
}