preface
There is a very important content in Java, the idea of java reflection. Learning java reflection well is very important for our subsequent development and understanding other people's code. Therefore, it is most important to lay a good foundation for reflection.
catalogue
1, What is the reflection mechanism
2, Advantages and disadvantages of java reflection mechanism
3, How to get reflection through java
4, Operations that can be done through java reflection
4.1. java reflection obtains the construction method object and uses it
4.2. java reflection gets the member variable object method of the class
4.3. java method for obtaining member method objects
5, To sum up, use the full steps of reflection
1, What is the reflection mechanism
Java reflection mechanism is to know all the properties and methods of any class in the running state; For any object, you can call any of its methods and properties; This kind of dynamically acquired information and the function of dynamically calling object methods are called the reflection mechanism of Java language.
Static compilation: determine the type and bind the object during compilation;
Dynamic compilation: determine the type and bind the object at run time;
2, Advantages and disadvantages of java reflection mechanism
Advantages: it can dynamically obtain class instances at runtime to improve flexibility;
Disadvantages: the performance of using reflection is low, and the bytecode needs to be parsed to parse the objects in memory;
Relatively insecure, undermining encapsulation (because private methods and properties can be obtained through reflection)
3, How to get reflection through java
1. - class name. Class attribute
Code example:
Class<Student> c1 = Student.class;
2. - object name. getClass() method
Code example:
Student s = new Student();
Class<? extends Student> c3 = s.getClass();3. - class. Forname (full class name) method
Code example
Class<?> c4 = Class.forName("com.Test.Student");4, Operations that can be done through java reflection
4.1. java reflection obtains the construction method object and uses it
Class gets the method of constructing the method object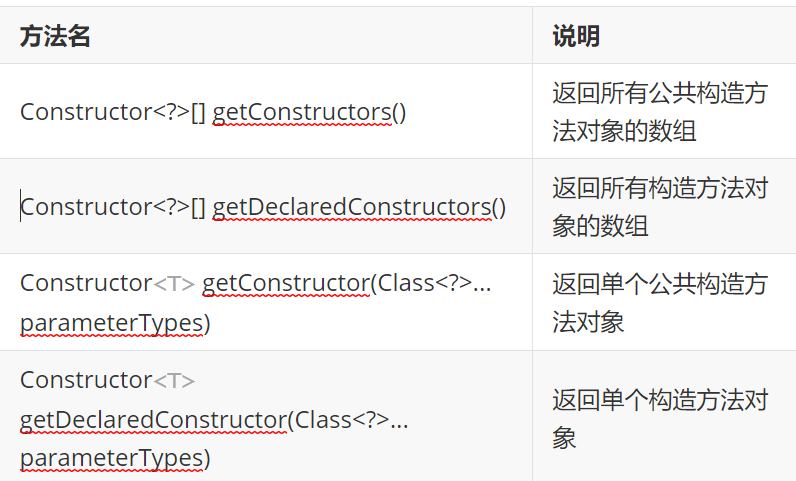
Code example
package com.homework10.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
/**
* @author wang
* @packageName com.homework10.Constructor
* @className ConstructorTest
* @date 2021/11/9 17:52
*/
public class ConstructorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
//Load class
Class<?> c = Class.forName("com.homework10.Constructor.Student");
//Because there is only one public parameterless constructor in my class, what I call this constructor is the parameterless constructor in my class and is public
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor);//public com.homework10.Constructor.Student()
//An example of this place is to get the specified non-public constructor
Constructor<?> conName = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(conName);//private com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String)
System.out.println("============");
//Gets an array of all public constructor methods
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c.getConstructors();
for (Constructor consPublic : constructors) {
System.out.println(consPublic);
}//public com.homework10.Constructor.Student()
System.out.println("============");
//Gets an array of all constructor methods
Constructor<?>[] constructors1 = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor constructor1 : constructors1) {
System.out.println(constructor1);
}
/*
protected com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String)
com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String,int)
private com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String)
public com.homework10.Constructor.Student()
*/
}
}
If we want to create objects and assign values to member variables, we can use the following method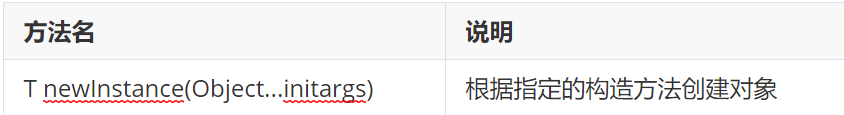
For example, we can do this
Constructor<?> conName = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(conName);//private com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String)
Object obj = conName.newInstance("Fei Zhang");
System.out.println(obj);But note that if our construction method is non-public, it will report an error
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalAccessException: Class com.homework10.Constructor.ConstructorTest can not access a member of class com.homework10.Constructor.Student with modifiers "private"
at sun.reflect.Reflection.ensureMemberAccess(Reflection.java:102)
at java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject.slowCheckMemberAccess(AccessibleObject.java:296)
at java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject.checkAccess(AccessibleObject.java:288)
at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:413)
at com.homework10.Constructor.ConstructorTest.main(ConstructorTest.java:26)
If the above error occurs, it is because when we call the constructor, our constructor is decorated with private, so the reflective object cannot be accessed. To access it, you have to do the following operations.
Violent reflex
Method (under Constructor class)
oid setAccessible (boolean flag) sets the accessible flag of this reflection object to the Boolean value indicated.
describe
Set the accessible flag of this reflective object to the Boolean value indicated. A value of true indicates that the reflective object should suppress checking when using Java language access control. A value of false indicates that the reflective object should check when using Java language access control and indicate the variation in the class description. Callers can use this method in class C to enable access to declaring class declaring class D if any of the following:
As follows:
Constructor<?> conName = c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(conName);//private com.homework10.Constructor.Student(java.lang.String)
conName.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = conName.newInstance("Fei Zhang");
System.out.println(obj);Output results:
Student{name = 'Zhang Fei', age=0, address='null '}
4.2. java reflection gets the member variable object method of the class
Class gets the method of the member variable object
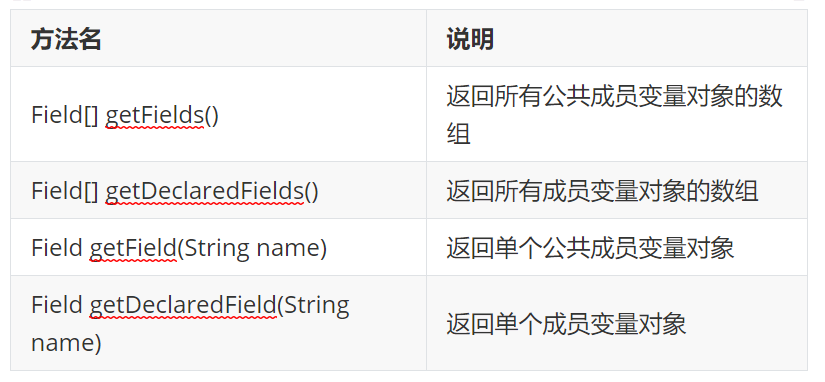
The Field class is used to assign values to member variables
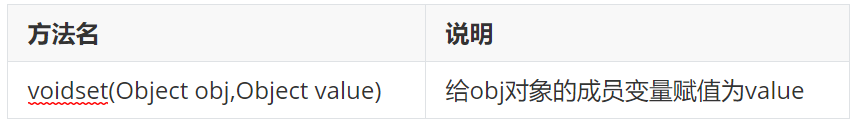
Sample code
package com.homework10.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
/**
* @author wang
* @packageName com.homework10.Constructor
* @className FieldTest
* @date 2021/11/9 23:37
*/
public class FieldTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//Load class
Class<?> c = Class.forName("com.homework10.Constructor.Student");
//Instantiate object
Constructor con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
Field nameField = c.getDeclaredField("name");
//This is consistent with the construction method. If private is modified, it will be reflected violently
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(obj,"Fei Zhang");
System.out.println(obj);
System.out.println(nameField);
//Student{name = 'Zhang Fei', age=0, address='null '}
//private java.lang.String com.homework10.Constructor.Student.name
//You can see that the name attribute of the output has been modified, and other attributes can also be modified. There is no demonstration here.
//Then the operations such as member variable object array obtained by method reflection are similar to the construction method.
}
}4.3. java method for obtaining member method objects
Class gets the method of the member method object
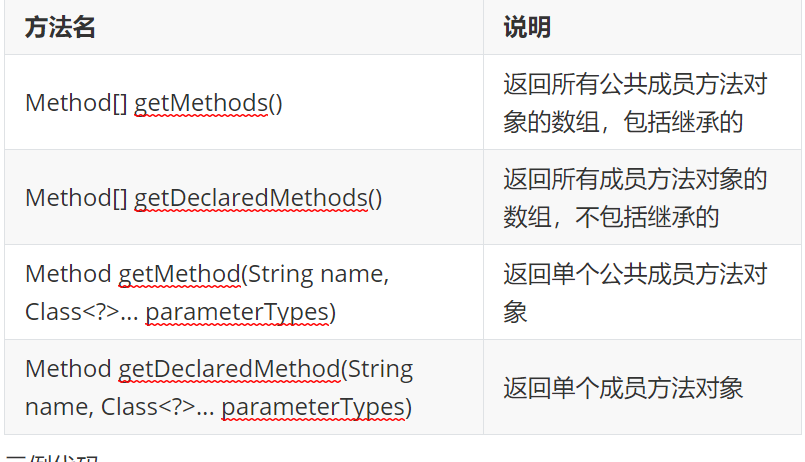
The Method class is used to execute the Method

The difference of this method is that when we operate on array objects, if we get all the member method arrays, it will all the member methods, including the parent class.
Sample code
Method[] methods = c.getMethods();
for(Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
/*
public java.lang.String com.homework10.Constructor.Student.toString()
public java.lang.String com.homework10.Constructor.Student.method3(java.lang.String,int)
public void com.homework10.Constructor.Student.method2(java.lang.String)
public void com.homework10.Constructor.Student.method1()
public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
*/Get the code instance of the specified member method object, and the public code can call the method directly
//This is consistent with obtaining the specified member variable object. The method name needs to be written, and the public member method does not need to be written
Method me = c.getDeclaredMethod("function");
//It should be noted here that the same is true, to violent reflection, if the method is non-public.
me.setAccessible(true);
//obj objects were created at the beginning
me.invoke(obj);
/*
Method content: private void function(){
System.out.println("function");
}
Output result: function
*/5, To sum up, use the full steps of reflection
1. Create an object with a fully qualified class name
2. Get the constructor object and get an object through the constructor new
3. Get an attribute object through the class object
4. Get a method object through the class object
5. Let the method execute
Example code of the whole process:
package com.homework10.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author wang
* @packageName com.homework10.Constructor
* @className Test
* @date 2021/11/10 0:03
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
//Create an object with a fully qualified class name
Class<?> c = Class.forName("com.homework10.Constructor.Student");
//Get the constructor object, and create an object through the constructor new. The instance is constructed with null parameters, and the actual parameters can also be used. However, in order to demonstrate the whole process, I use the following code
Constructor con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
//Get a property object through the class object
Field nameField = c.getDeclaredField("name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(obj,"Fei Zhang");
Field ageField = c.getDeclaredField("age");
ageField.setAccessible(true);
ageField.set(obj,25);
Field addressField = c.getDeclaredField("address");
addressField.set(obj,"Chongqing City");
//Get a method object through the class object. Here, the toString method is used. All exceptions of this class are thrown to simplify the example
Method m = c.getDeclaredMethod("toString");
//Let the method execute
System.out.println(m.invoke(obj));
}
}
/*
Output results
Student{name='Zhang Fei ', age=25, address =' Chongqing '}
*/Attachment: Student class
package com.homework10.Constructor;
/**
* @author wang
* @packageName com.homework10.Constructor
* @className Student
* @date 2021/11/9 17:52
*/
public class Student {
//Member variables: one private, one default, and one public
private String name;
int age;
public String address;
//Construction method: one private, one default and two public
public Student() {
}
private Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected Student(String name, int age, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
//Member method: one private, four public
private void function() {
System.out.println("function");
}
public void method1() {
System.out.println("method");
}
public void method2(String s) {
System.out.println("method:" + s);
}
public String method3(String s, int i) {
return s + "," + i;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
Finally, thank you for watching. Please give me a free praise. Thank you for your support. We will continue to share java knowledge for you in the next issue.
