Reflection advanced explanation
Warm reminder: if you don't know much about reflection, you can go to a few introductory articles to learn more!
Review:
Why reflection: call private content in a class at will.Class is more flexible.Reflection: get a member method / member variable in a class specificallyReflection fixation steps:
2.1. Obtain the construction method of class through class object2.2. Creating objects by construction method2.3. CallGet member method:getMethod gets the public method in the current class or parent classgetDeclaredMethod gets any method of the current class (regardless of the access modifier)Get member variable:getField gets the public field in the current class or parent classgetDeclaredField gets any field of the current class (regardless of the access modifier)Executive member method:Object obj = method object. Invoke (object, parameter 1, parameter 2 );Execute member variable:field object. set assignmentfield object. get value |
|---|
1, Advanced case 1: execute public method
Code implementation: /* * Execute the public method: * getDeclaredMethod Get any method in the current class (ignoring the access modifier), which is suitable for reflection calling the current class method * getMethod The current class or parent class obtains the public method, which is suitable for reflection calling the parent class public method * * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object (equivalent to getting the whole watermelon) Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo2.Person"); //1.2. Obtaining method through class object (equivalent to extracting watermelon pulp from watermelon through super ability) Method t1 = clazz.getMethod("t1"); //1.3. Set available out of class (only for private, even if public is added, no error will be reported) t1.setAccessible(true); //2. Execution (equivalent to eating watermelon pulp) //2.1. Obtain the construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2. Create an object through the construction method (equivalent to Person person = new Person();) Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call method (equivalent to person.t1()) t1.invoke(person); }
-
getDeclaredMethod gets any method in the current class (ignoring the access modifier), which is suitable for reflection calling the current class method
-
getMethod the current class or parent class obtains the public method, which is suitable for reflection calling the parent class public method
2, Advanced case 2: execute private field
Code implementation: public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo2.Person"); //1.2. Get fields through class objects Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name"); //1.3. Set available out of class name.setAccessible(true); //2, implementation //2.1. Obtaining the construction method Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2 creating objects Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call //assignment name.set(person,"Xiao Liu"); //Value Object o = name.get(person); //Strong turn String str = (String) o; System.out.println(str); }
3, Advanced case 3: execute public field
Code implementation: public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo2.Person"); //1.2. Get fields through class objects Field name = clazz.getField("n1"); //1.3. Set available out of class (private only) //name.setAccessible(true); //2, implementation //2.1. Obtaining the construction method Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2 creating objects Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call //Value Object o = name.get(person); //Strong turn String str = (String) o; System.out.println(str); }
-
getDeclaredField gets any field of the current class (regardless of the access modifier), which is suitable for getting the current class
-
getField gets the public field in the current class and the parent class, which is applicable to getting the parent class public
4, Advanced 4: create objects through private construction method
/* * Creating objects for a privatized constructor class by reflection * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Person"); //1.2. Obtain private nonparametric construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(); //1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex) c.setAccessible(true); //2, implementation //2.1 creating objects Object obj = c.newInstance(); //Strong turn Person person = (Person) obj; }
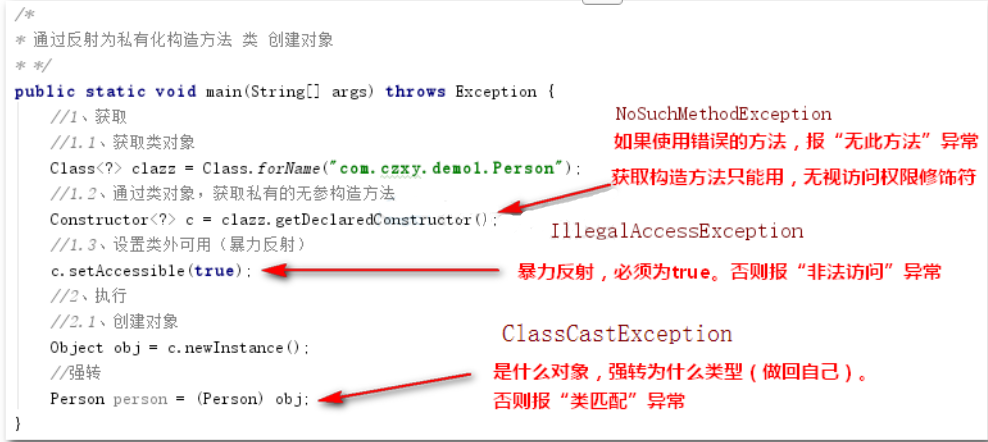
Gets the object of the class of the privatized constructor, which depends on reflection.
5, Advanced 5: creating objects through the public construction method
/* * Creating objects by reflecting common classes * getConstructor Get any public constructor of the current class * getDeclaredConstructor Gets any constructor of the current class (regardless of the access modifier) * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Phone"); //1.2. Obtain private nonparametric construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex) // c.setAccessible(true); //2, implementation //2.1 creating objects Object obj = c.newInstance(); //Strong turn Phone person = (Phone) obj; }
-
getConstructor gets any public constructor of the current class
-
getDeclaredConstructor gets any constructor of the current class (regardless of the access modifier)
6, Advanced 6: create an object through the construction method with parameters
Preparation Code:
public class Phone { public Phone() { System.out.println("Public nonparametric construction-phone"); } private Phone(String name,Integer age) { System.out.println("Private nonparametric construction-phone"+name+age); } }
- Requirement Description:
Create the mobile phone object through the structure with parameters.
name: HUAWEI
age:100
- Code implementation:
/* * Creating objects with a band parameter construct * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Phone"); //1.2. Get the construction method (String, Integer) through the class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, Integer.class); //1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex) c.setAccessible(true); //2, implementation //2.1. Create an object through the construction method Object phone = c.newInstance("HUAWEI", 100); }
7, Reflection advanced 1-get all member methods & Field & construction methods
getMethods(); get all public decorated methods in the current class and parent classgetDeclaredMethods(); get all methods in the current class (regardless of access rights)getFields(); get all public decorated fields in the current class and parent classgetDeclaredFields(); gets all fields in the current class (regardless of the access modifier)getConstructors(); get all the public decorated constructors in the current classgetDeclaredConstructors(); get all construction methods in the current class (ignore access modifier) |
|---|
Conclusion:
All methods without Declared can obtain all public contents of the current class and parent class
All methods with Declared can obtain all contents of the current class
8, Advanced 2: three ways to get class objects
/* * Three ways to get class objects * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Class.forName Class<?> clazz1 = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo2.Person"); //2. class name Class<Person> clazz2 = Person.class; //3. Object name. getClass() [get object] Person p = new Person(); Class<? extends Person> clazz3 = p.getClass(); //For the above three kinds of object acquisition methods, the acquired Class objects are all the same in heap memory System.out.println(clazz1==clazz2); System.out.println(clazz1==clazz3); }
Today's summary:
Reflection: get member variables / member methods in a class specificallyFixing steps:1. Get1.1. Get class object1.2. Obtain content (member variable, member method) through class object1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex)2, implementation2.1. Obtain the construction method of the class through the class object2.2. Create objects according to the construction method2.3 calling contentGet member method / member variable / construction method:Unclaimed: public content in current class and parent classdeclared: any content of the current class (regardless of the access modifier)getMethods()
|
|---|
Please give yourself a compliment!
Make a little progress every day`~~~~~