jdbc tutorial
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jdbc/jdbc-sample-code.htm (English)
http://www.yiibai.com/jdbc/jdbc-sample-code.html#article-start (Chinese)
jdbc curd example
http://www.codejava.net/java-se/jdbc/jdbc-tutorial-sql-insert-select-update-and-delete-examples (English)
http://www.cnblogs.com/sbj-dawn/p/7111990.html (Chinese)
2 Create a sampledb
http://blog.csdn.net/qqduxingzhe/article/details/78251057
mysql 5.7.X install
Execute the following statement in your MySQL Workbench:
create database SampleDB;
use SampleDB;
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`fullname` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`)
);4 Database Connection
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sampledb";
String username = "root";
String password = "secret";
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL, username, password);
if (conn != null) {
System.out.println("Connect OK");
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}After that, close
conn.close();5 Perform insert
User information:
username: bill
password: secretpass
fullname: Bill Gates
email: bill.gates@microsoft.com
Here is the code:
String sql = "INSERT INTO Users (username, password, fullname, email) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement statement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, "bill");
statement.setString(2, "secretpass");
statement.setString(3, "Bill Gates");
statement.setString(4, "bill.gates@microsoft.com");
int rowsInserted = statement.executeUpdate();
if (rowsInserted > 0) {
System.out.println("A new user Insert success!");
}// conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// Create a precompiled statement that calls setXXX(xx, xx) for data filling
// statement.executeUpdate();
//Perform updates, additions, deletions
// Returns the number of rows operated on
Other methods of PreparedStatement:
setBoolean(int parameterIndex, boolean x)
setDate(int parameterIndex, Date x)
setFloat(int parameterIndex, float x)
// ...6 Execute select
Code:
String sql = "SELECT * FROM Users";
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery(sql);
int count = 0;
while (result.next()){
String name = result.getString(2);
String pass = result.getString(3);
String fullname = result.getString("fullname");
String email = result.getString("email");
String output = "User #%d: %s - %s - %s - %s";
System.out.println(String.format(output, ++count, name, pass, fullname, email));
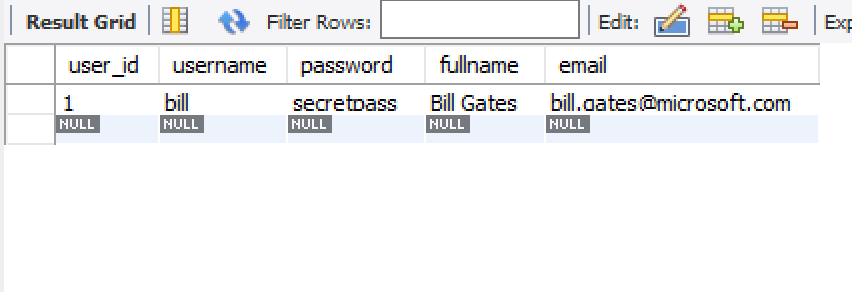
}Output:
User #1: bill - secretpass - Bill Gates - bill.gates@microsoft.com
resultset.next();
// Whether the next line exists,
//(Existence, data)
//(No, no data, exit the while loop)
resultset can be regarded as a two-dimensional table.
(I imagine that the column header is the name of each column of the table in the database and the index of each column.)
Each row is data (also known as records)
According to the data type in the database, the corresponding Java data type,
Select the corresponding method to get the data
Username ==> String ==> getString (username index / username string)
More methods of result
getString(columnIndex/ columnString)
getInt(columnIndex/ columnString)
getFloat(columnIndex/ columnString)
getDate(columnIndex/ columnString)
getTimestamp(columnIndex/ columnString)
// ...Tips:
getXXX( columnIndex/ columnString);
index is faster than String
7 Execute update
Code:
String sql = "UPDATE Users SET password=?, fullname=?, email=? WHERE username=?";
PreparedStatement statement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, "123456789");
statement.setString(2, "William Henry Bill Gates");
statement.setString(3, "bill.gates@microsoft.com");
statement.setString(4, "bill");
int rowsUpdated = statement.executeUpdate();
if (rowsUpdated > 0) {
System.out.println("An existential user Update success!");
}8 Execute delete
Code: Delete existing bill
String sql = "DELETE FROM Users WHERE username=?";
PreparedStatement statement = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1, "bill");
int rowsDeleted = statement.executeUpdate();
if (rowsDeleted > 0) {
System.out.println("One user Delete successful");
}epilogue
This is CURD.
The key points are:
Translation Method: bing Translation
http://www.bing.com/Translator
Statements that use static SQL queries.
PreparedStatement is used for parameterized SQL queries, and setXXX () method is used to set parameter values.
Use the execute () method to execute regular queries.
Use the executeUpdate () method to execute insert, update, or delete queries
Use the executeQuery () method to execute the selection query.
The row returned from the SELECT query is accessed circularly using the result set, which is advanced to the next row in the final set using its next () method, and the column value is retrieved using the getXXX () method.
end