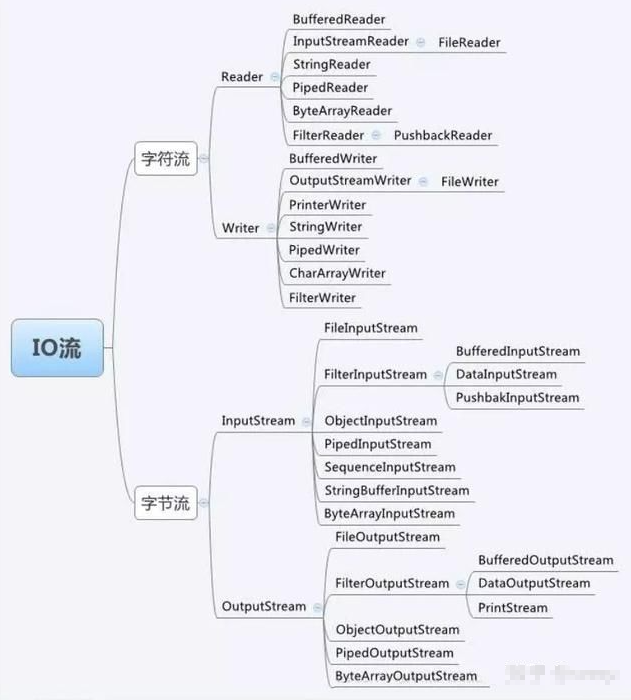
0x01: byte stream
Byte stream base class
1. InputStream
InputStream: the base class of byte input stream. The abstract class is a superclass representing all classes of byte input stream.
Common methods:
// Reads the next byte of data from the input stream abstract int read() // A certain number of bytes are read from the input stream and stored in the buffer array b int read(byte[] b) // Read the maximum len data bytes in the input stream into the byte array int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) // Skip and discard n bytes of data in this input stream long skip(long n) // Close this input stream and release all system resources associated with the stream void close()
Every day, I will share with you the latest java technology information. There are excellent java technology contents. Welcome to share them in my column.

2. OutputStream
OutputStream: base class of byte output stream. Abstract class is a superclass representing all classes of output byte stream.
Common methods:
// Writes b.length bytes from the specified byte array to this output stream void write(byte[] b) // Writes len bytes from the offset off in the specified byte array to this output stream void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) // Writes the specified byte to this output stream abstract void write(int b) // Close this output stream and free all system resources associated with this stream void close() // Refresh this output stream and force all buffered output bytes to be written out void flush()
Byte file operation stream
1. FileInputStream
FileInputStream: byte file input stream, which obtains input bytes from a file in the file system and is used to read the original byte stream such as image data.
Construction method:
// Create a FileInputStream by opening a connection to the actual file, which is specified by the file object file in the file system FileInputStream(File file)
// Create a FileInputStream by opening a connection to the actual file, which is specified by the path name in the file system FileInputStream(String name) common methods: override and override the common methods of the parent class.
// Read the file on disk f:
//hell/test.txt
//Construction method 1
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("f://hello//test.txt"));
int i = 0;
//Read one byte at a time
while ((i = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
// System.out.print(i + " ");
// 65 66 67 68
//Why output 65 66 67 68? Because when characters are stored at the bottom, they are stored values. That is, the ASCII code corresponding to the character.
System.out.print((char) i + " ");
// A B C D
}
//Close IO stream
inputStream.close();
// Read the file f://shell/test.txt under disk F
//Construction method 2
InputStream inputStream2 = new FileInputStream("f://hello/test.txt");
// Byte array
byte[] b = new byte[2]; int i2 = 0;
// Read one byte array at a time
while ((i2 = inputStream2.read(b)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(b, 0, i2) + " ");
// AB CD }
//Close IO stream
inputStream2.close();Note: reading one byte array at a time improves the operation efficiency. The IO stream must be closed after use.
2. FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream: byte File output stream is used to write data to File and other locations from the program.
Construction method:
// Creates a File output stream that writes data to the File represented by the specified File object //java learning and exchange: 737251827 enter to receive learning resources and ask questions about leaders with ten years of development experience for free! FileOutputStream(File file) // Creates a File output stream that writes data to the File represented by the specified File object FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append) // Creates an output file stream that writes data to a file with the specified name FileOutputStream(String name) // Creates an output file stream that writes data to a file with the specified name FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)
Common methods: override and override the common methods of the parent class.
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("test.txt"));
// Write data
outputStream.write("ABCD".getBytes());
// Close IO stream
outputStream.close();
// Content append write
OutputStream outputStream2 = new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true);
// Output newline
outputStream2.write("\r\n".getBytes());
// Output additional content
outputStream2.write("hello".getBytes());
// Close IO stream
outputStream2.close();Note; If the output destination file does not exist, it will be created automatically. If the drive letter is not specified, it will be created in the project directory by default; When outputting line breaks, be sure to write \ R \ NAND not just write \ n, because different text editors have different recognition of line breaks.
Byte buffered stream (efficient stream)
1. BufferedInputStream
BufferedInputStream: byte buffered input stream, which improves reading efficiency.
2. BufferedOutputStream
BufferedOutputStream: byte buffered output stream, which improves write efficiency.
Construction method:
// Creates a new buffered output stream to write data to the specified underlying output stream BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) // Creates a new buffered output stream to write data with the specified buffer size to the specified underlying output stream BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size) Common methods: // Writes len bytes from the offset off in the specified byte array to the buffered output stream void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) // Writes the specified byte to this buffered output stream void write(int b) // Flush this buffered output stream void flush()
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("test.txt", true));
// Output newline
bos.write("\r\n".getBytes());
// Output content
bos.write("Hello Android".getBytes());
// Flush this buffered output stream
bos.flush();
// Close flow
bos.close();0x02: character stream
Character stream base class
1. Reader
Reader: an abstract class that reads character streams
Common methods:
// Read single character int read() // Read characters into array int read(char[] cbuf) // Read characters into a part of an array abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) // Skipping characters long skip(long n) // Close the flow and release all resources associated with it abstract void close()
2. Writer
Writer: an abstract class that writes to a character stream
Common methods:
// Write character array void write(char[] cbuf) // Write a part of a character array abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) // Write a single character void write(int c) // Write string void write(String str) // Write a part of a string void write(String str, int off, int len) // Adds the specified character to this writer Writer append(char c) // Adds the specified character sequence to this writer Writer append(CharSequence csq) // Adds a subsequence of the specified character sequence to this writer.Appendable Writer append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) // Close this stream, but refresh it first abstract void close() // Flush the buffer of the stream abstract void flush()
Character conversion stream
1. InputStreamReader
InputStreamReader: byte stream character stream. The character set it uses can be specified by name or explicitly given. Otherwise, the platform default character set will be accepted.
Construction method:
// Create an InputStreamReader that uses the default character set InputStreamReader(InputStream in) // Creates an InputStreamReader that uses the given character set InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs) // Create an InputStreamReader that uses the given character set decoder InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec) // Creates an InputStreamReader that uses the specified character set InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName)
Unique methods:
//Returns the name of the character encoding used by this stream
String getEncoding()
//Use default encoding
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt"));
int len;
while ((len = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);
//Love life, love Android
}
reader.close();
//Specify encoding
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt"),"utf-8");
int len;
while ((len = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);
//????????Android
}
reader.close();
//Note: Eclipse uses GBK encoding by default, so the test.txt file is GBK encoding. When utf-8 encoding is specified, it will be garbled.
2. OutputStreamWriter
OutputStreamWriter: byte stream character stream.
Construction method:
// Create an OutputStreamWriter that uses the default character encoding //java learning and exchange: 737251827 enter to receive learning resources and ask questions about leaders with ten years of development experience for free! OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) // Creates an OutputStreamWriter that uses the given character set OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs) // Creates an OutputStreamWriter that uses the given character set encoder OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc) // Creates an OutputStreamWriter that uses the specified character set OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) Unique methods: //Returns the name of the character encoding used by this stream String getEncoding()
Character buffer stream (efficient stream)
1. BufferedReader
BufferedReader: character buffer stream, which reads text from the character input stream and buffers each character, so as to realize efficient reading of characters, arrays and lines.
Construction method:
// Create a buffered character input stream that uses the default size input buffer BufferedReader(Reader in) // Creates a buffered character input stream using an input buffer of the specified size BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz)
Unique methods:
// Read a text line
String readLine()
//Generate character buffer stream object
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("test.txt")));
String str;
//Read one line at a time
while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
// Love life, love Android
}
//Close flow
reader.close();
BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter: character buffer stream, which writes text to the character output stream and buffers individual characters, thus providing efficient writing of single characters, arrays and strings.
Construction method:
// Create a buffered character output stream using the default size output buffer BufferedWriter(Writer out) // Creates a new buffered character output stream using an output buffer of the given size BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) Unique methods: // Write a line separator void newLine()
FileReader,FileWriter
FileReader: InputStreamReader Class, a convenient class for reading character files, using the default character encoding. FileWriter: OutputStreamWriter Class, a convenient class for writing character files, using the default character encoding.
0x03: high efficiency flow efficiency comparison
Read a video file under disk f into the project: file size 29.5 MB
Reading mode 1:
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d://AOI Kong. mp4 ");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("AOI that thing.mp4");
int len;
// start time
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Read one byte at a time
while ((len = inputStream.read()) != -1) {
outputStream.write(len);
}
// Time milliseconds
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 213195
//Close stream to release resources
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();Reading mode 2:
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d://AOI Kong. mp4 ");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("AOI that thing.mp4");
int len;
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
// start time
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Read one byte array at a time
while ((len = inputStream.read(bs)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(bs, 0, len);
}
// Time milliseconds
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 281
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();Reading mode 3:
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("d://AOI Kong. mp4 ");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("AOI that.mp4");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
int len;
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
// start time
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
while ((len = bis.read(bs)) != -1) {
bos.write(bs, 0, len);
}
// Time milliseconds
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - begin);// 78
bis.close();
bos.close();Note: it can be seen that the reading and writing speed of efficient buffer stream is very fast, which is recommended.