This exercise contains points of knowledge:
Identifier, keyword, comment, variable, data type, constant
Basic data types:
- Integer type (int)
- Floating Point Type (float)
- Character type (char)
- Boolean type
java provides a series of access controllers to set different levels of access based on class es, variables, methods (mothod), and construction methods.
There are four main types of access rights for java: - Default (default mode)
- Private (private mode)
- Public (public)
- Protected
Topic 1
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:

-
Write steps:
- Define class Test1
- Define main method
- Console Output 5 Lines String Type Constant Value
- Console Output 5 Line Character Type Constant Value
Answer:
public class Test1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Console output any 5-line string type constant value System.out.println("Learning is like a spring-blossom"); System.out.println("No increase,Day lengthens"); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("No damage,Loss in the year"); System.out.println("Come on!juvenile"); // Console output any 5-line character type constant value System.out.println('J'); System.out.println('A'); System.out.println('V'); System.out.println('A'); System.out.println('!'); } }
Question 2
- Follow the `steps to write the code as shown in the diagram:
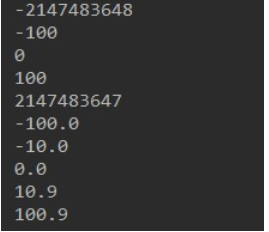
- Write steps:
- Define class Test2
- Define main method
- Console Output 5 Lines Integer Type Constant
- Console Output 5 Rows Decimal Type Constant Value
Reference Answer:
public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Console output any 5-line integer type constant value System.out.println(-2147483648); System.out.println(-100); System.out.println(0); System.out.println(100); System.out.println(2147483647); // Console Output Any 5 Rows Decimal Type Constant Value System.out.println(-100.0); System.out.println(-10.0); System.out.println(0.0); System.out.println(10.9); System.out.println(100.9); } }
Question 3
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:
-
Write steps:
- Define Class Test3
- Define main method
- Console Output All Boolean Type Constants
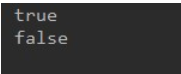
public class Test3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Console Output All Boolean Type Constants System.out.println(true); System.out.println(false); } }
Question 4
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:
-
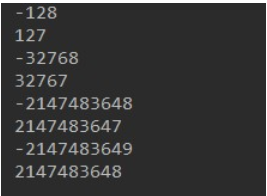
-
Write steps:
- Define Class Test4
- Define main method
- Define two byte type variables, assign the maximum and minimum values within the byte type range, and output to the console.
- Define two short type variables, assign values within the short type range, and output to the console.
- Define two variables of type int, assign values within the range of type int, and output them to the console.
- Define two long type variables, assign values that exceed the range of int type, and output them to the console.
Reference Answer:
public class Test4 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Define two byte type variables, assign the maximum and minimum values within the byte type range, and output to the console. byte num1 = -128; byte num2 = 127; System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num2); // Define two short type variables, assign values within the short type range, and output to the console. short num3 = -32768; short num4 = 32767; System.out.println(num3); System.out.println(num4); // Define two variables of type int, assign values within the range of type int, and output them to the console. int num5 = -2147483648; int num6 = 2147483647; System.out.println(num5); System.out.println(num6); // Define two long type variables, assign values that exceed the range of int type, and output them to the console. long num7 = -2147483649L; long num8 = 2147483648L; System.out.println(num7); System.out.println(num8); } }
Topic 5
- Write the code step by step as shown:

- Write steps:
- Define Class Test5
- Define main method
- Define two float type variables, assign them to each other, and output them to the console.
- Define two variables of type double, assign values to each, and output them to the console.
Reference Answer:
public class Test5 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Define two float type variables, assign them to each other, and output them to the console. float num1 = -3.14F; float num2 = 3.14F; System.out.println(num1); System.out.println(num2); // Define two double s, assign values to each, and output to the console. double num3 = -3.4; double num4 = 3.4; System.out.println(num3); System.out.println(num4); } }
Sixth topic
- Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:

- Write steps:
- Define Class Test6
- Define main method
- Define five char type variables, assign values, and output to the console.
- Define two boolean type variables, assign values to each, and output to the console.
Reference Answer:
public class Test6 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Define five char type variables, assign values, and output to the console. char ch1 = '9'; char ch2 = 'J'; char ch3 = 'a'; char ch4 = ' '; char ch5 = '@'; System.out.println(ch1); System.out.println(ch2); System.out.println(ch3); System.out.println(ch4); System.out.println(ch5); // Define two boolean type variables, assign values to each, and output to the console. boolean b1 = true; boolean b2 = false; System.out.println(b1); System.out.println(b2); } }
Topic 7
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:
-

-
Step illustrations:
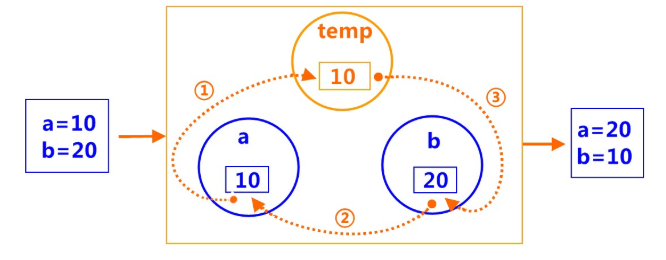
-
Development Tip: Define the format in which variables are not assigned
// Data type variable name;
int temp; -
Write steps:
- Define Class Test7
- Define main method
- Define and assign two integer variables a, b
- Console Output Variables a, b Before Interchange
- Define a third-party variable temp, no assignment
- Use third-party variable temp to exchange values of a and b
- Console Output Variable a, b Interchangeable Value
Reference Answer:
class Test7{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 20 ; System.out.println("Before interchange"); System.out.println("a =" + a); System.out.println("b= " + b); int temp; temp = a; a = b; b = temp; System.out.println("After interchange"); System.out.println("a = " + a); System.out.println("b = "+b); } }
Extended title:
Question 8
- Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:

- Development Tip: Symbols for Four Operations
Plus: +
Subtraction: -
Multiply: *
Except: / - Write steps:
- Define Class Test8
- Define main method
- Defines two variables of type int, x and y, with x assigned to 100 and Y assigned to 200
- Define a new variable add, save the sum of variables x, y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable sub, save the difference between the variables x and y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable mul, save the product of variables x, y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable div, save the quotient of the variables x, y, and print it to the console
Reference Answer:
class Test8{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x = 100; int y = 200; int add = x + y; int sub = y - x; int mul = x * y; int div = x / y; System.out.println("x,y And for: " + add); System.out.println("x,y The difference is: " + sub); System.out.println("x,y The product of is: " + mul); System.out.println("x,y Business for: " + div); } }
Item 9
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:
-
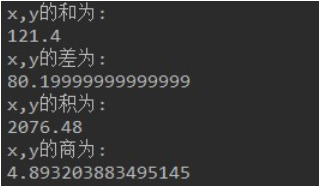
-
Development Tip: Observe the results of numeric operations of decimal type.
Decimal operations often suffer from loss of precision, so it is not recommended to use basic types of operations. -
Write steps:
- Define class Test9
- Define main method
- Defines two double type variables x, y, with X assigned to 100.8 and Y assigned to 20.6
- Define a new variable add, save the sum of variables x, y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable sub, save the difference between the variables x and y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable mul, save the product of variables x, y, and print to the console
- Define a new variable div, save the quotient of the variables x, y, and print it to the console
-
Tips:
- Addition: +
- Subtraction: -
- Multiplication: *
- Division: /
Reference Answer:
public class Test9 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Define two variables of type double x,y and assign any value. double x = 100.8; double y = 20.6; // Define new variables, save the sum of variables x,y, and print to the console double add = x + y; System.out.println("x,y And for:"); System.out.println(add); // Define a new variable, save the difference between the variables X and y, and print to the console double sub = x - y; System.out.println("x,y The difference is:"); System.out.println(sub); // Define a new variable, save the product of the variables x,y, and print to the console double mul = x * y; System.out.println("x,y The product of is:"); System.out.println(mul); // Define a new variable, save the quotient of the variable x,y, and print to the console double div = x / y; System.out.println("x,y Business:"); System.out.println(div); } }
Topic 10
-
Write the code step by step as shown in the diagram:
-

-
Development Tip: Output without line breaks
System.out.print("integer type-byte:"); //remove ln, no line break after output
System.out.println(10); //with ln, with line breaks after output -
Write steps:
- Define class Test10
- Define main method
- Define a byte type variable and assign it a value of 10. Wrap the output type description and output the variable value.
- Define a short type variable and assign it a value of 100, no line break output type description, line break output variable value.
- Defines an int type variable and assigns it a value of 1000, no line break output type description, and line break output variable value.
- Define a long type variable and assign it a value of 10000, no line break output type description, line break output variable value.
- Define float type variable and assign it to 100000.0, no line break output type description, line break output variable value.
- Defines a double type variable and assigns it to 1000000.0, no line break output type description, line break output variable value.
- Define a char type variable and assign it a value of'Z', no line break output type description, line break output variable value.
- Defines a boolean type variable and assigns it false, does not wrap the output type description, and wraps the output variable value.
Reference Answer:
public class Test10 { public static void main(String[] args) { // Define Variables byte b = 10; // Output string without wrapping System.out.print("Integer type-byte:"); // Line Break Output Variable Value System.out.println(b); short s = 100; System.out.print("Integer type-short:"); System.out.println(s); int i = 1000; System.out.print("Integer type-int:"); System.out.println(i); long l = 10000; System.out.print("Integer type-long:"); System.out.println(l); float f = 100000.0F; System.out.print("Decimal Type-float:"); System.out.println(f); double d = 1000000.0; System.out.print("Decimal Type-double:"); System.out.println(d); char c = 'Z'; System.out.print("Character type-char:"); System.out.println(c); boolean bo = false; System.out.print("Boolean type-boolean:"); System.out.println(bo); } }

