The Definition of Hedonic Patterns
Flyweight Pattern is mainly used to reduce the number of objects created to reduce memory footprint and improve performance. This type of design pattern belongs to the structural pattern, which provides a way to reduce the number of objects and improve the object structure required by the application.
Enjoyment pattern code example
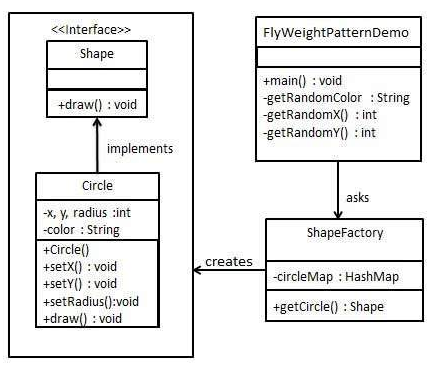
Create a Shape interface and an entity class Circle that implements the Shape interface. The next step is to define the factory class ShapeFactory
ShapeFactory has a Circle HashMap, where the key name is the color of the Circle object. Whenever a request is received, a circle of a particular color is created. ShapeFactory checks the circle object in its HashMap and returns it if it finds the Circle object. Otherwise, it creates a new object stored in HashMap for subsequent use and returns the object to the client.
FlyWeightPatternDemo, our demo class uses ShapeFactory to get Shape objects. It will pass a message to ShapeFactory (red / green / blue/ black / white) to get the color of the object it needs.
UML diagrams
Step 1: Create an interface
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}Step 2: Create entity classes that implement interfaces
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color
+", x : " + x +", y :" + y +", radius :" + radius);
}
}Step 3: Create a factory to generate objects of entity classes based on given information
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
private static final HashMap<String, Shape> circleMap = new HashMap<>();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}Step 4: Use the factory to get objects of entity classes by passing color information
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] =
{ "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle =
(Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}Step 5: Verify the output
Creating circle of color : Black
Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Green
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100
Creating circle of color : White
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Red
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100
Creating circle of color : Blue
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100
Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100Advantages and disadvantages of hedonic model
Advantage
It greatly reduces the creation of objects, reduces the memory of the system, and improves the efficiency.
shortcoming
To improve the complexity of the system, it is necessary to separate the external state from the internal state, and the external state has the inherent nature. It should not change with the change of the internal state, otherwise the system will be chaotic.
Applicable scenario
1. The system has a large number of similar objects.
2. Scenarios requiring buffer pools.