1, MySQL database
1. Create database
CREATE DATABASE jdbc CHARACTER SET 'utf8';
2. build tables
CREATE TABLE user ( id int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, userName varchar(20) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) );
3. Add data
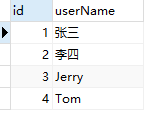
2, Connect MySQL database through JDBC
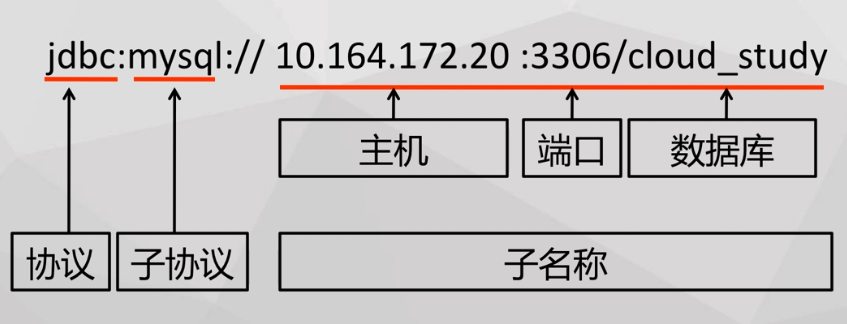
1.JDBC URL

2.Statement
boolean execute(String SQL): if the ResultSet object can be retrieved, the Boolean value returned is true, otherwise false. When you need to use real dynamic SQL, you can use this method to execute SQL DDL statements.
int executeUpdate(String SQL): returns the number of rows affected by the execution of the SQL statement. Using this method to execute SQL statements is to get the number of affected rows, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statements.
ResultSet executeQuery(String SQL): returns a ResultSet object. Use this method when you want to get a result set, just like you use a SELECT statement.
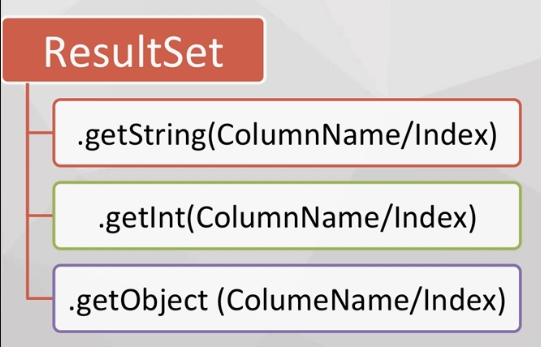
3.ResultSet object
Execute SQL Statement through executeQuery() method of Statement object to get ResultSet object
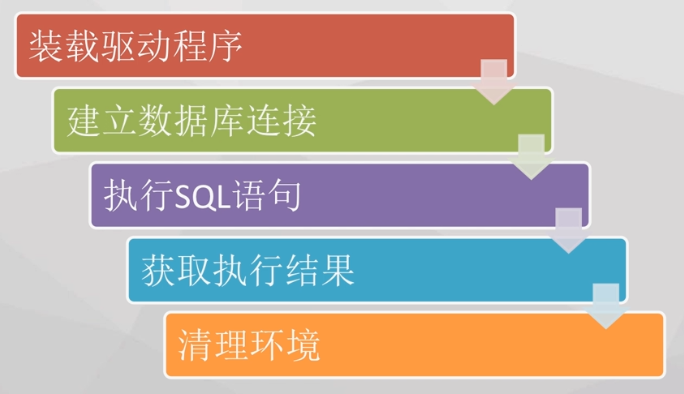
4. Specific steps and codes
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbc?useSSL=false";
static final String USER = "root";
static final String PASSWORD = "123456";
public static void hello() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
//1. Load driver
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
//2. Establish database connection
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASSWORD);
//3. Execute SQL statement
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select userName from user");
//4. Get execution results
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("Hello " + rs.getString("userName"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5. Clean up the environment
try {
if (conn != null) conn.close();
if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
if (rs != null) rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}