1, Class and Java reflection
Class textFieldC=tetxField.getClass(); // Tetxfield is a JTextField class object
Main description of reflection accessibility
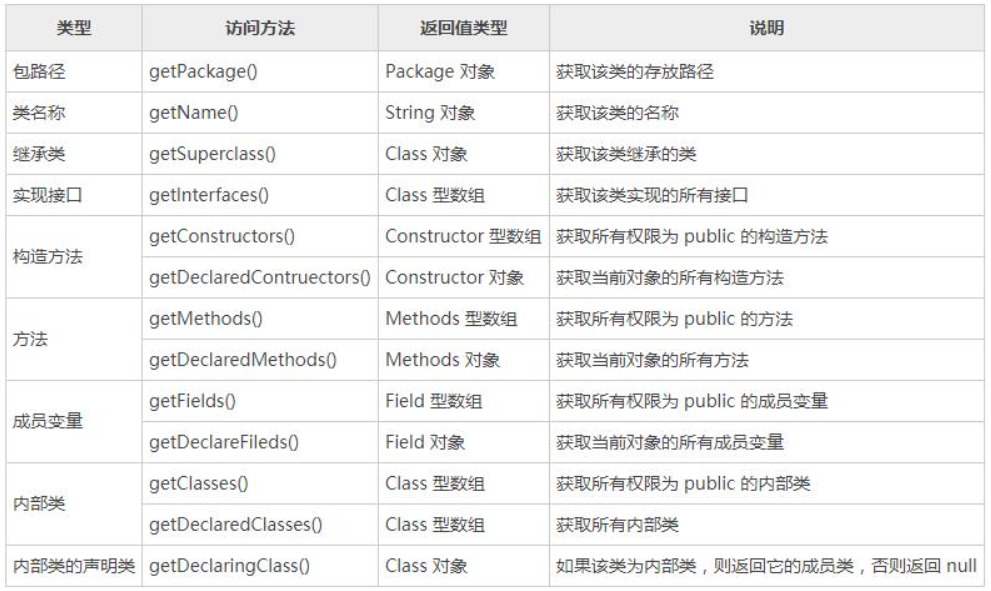
1. Access construction method
Each Constructor object represents a construction method, and the corresponding construction method can be manipulated by using the Constructor object.
- getConstructors() // Get public
- getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) // Gets the specified public
- getDeclaredConstructors() // Get all
- getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) // Gets the specified method
Create Demo1 class, declare String type member variables and three int type member variables, and provide three construction methods.
package bao;
public class Demo1{
String s;
int i,i2,i3;
private Demo1() {
}
protected Demo1(String s,int i) {
this.s=s;
this.i=i;
}
public Demo1(String... strings)throws NumberFormatException{
if(0<strings.length) {
i=Integer.valueOf(strings[0]);
}
if(1<strings.length) {
i2=Integer.valueOf(strings[0]);
}
if(2<strings.length) {
i3=Integer.valueOf(strings[0]);
}
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("s="+s);
System.out.println("i="+i);
System.out.println("i2="+i2);
System.out.println("i3="+i3);
}
}Write the Main class, in which all construction methods of reflective access to Demo1 are performed, and output whether the construction method is allowed to have a variable number of parameters, entry parameters and possible exception type information.
package bao;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 demo=new Demo1("10","20","30");
Class<? extends Demo1>demoC=demo.getClass();
//Get all construction methods
Constructor[] declaredConstryctors=demoC.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(int i=0;i<declaredConstryctors.length;i++) {
Constructor<?> constructor=declaredConstryctors[i];
System.out.println("To see if a variable number of parameters is allowed:"+constructor.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("The entry parameter types of the construction method are as follows:");
Class[]parameterTypes=constructor.getParameterTypes(); //Get all parameter types
for(int j=0;j<parameterTypes.length;j++) {
System.out.println(" "+parameterTypes[j]);
}
System.out.println("The entry of this constructor may throw an exception of type:");
//Get all possible exception information types thrown
Class[] exceptionTypes=constructor.getExceptionTypes();
for(int j=0;j<exceptionTypes.length;j++) {
System.out.println(" "+exceptionTypes[j]);
}
Demo1 example2=null;
while(example2==null) {
try {
if(i==2) {
example2=(Demo1)constructor.newInstance();
}else if(i==1) {
example2=(Demo1)constructor.newInstance("7",5);
}else {
Object[] parameters=new Object[] {new String[] {"100","200","300"}};
example2=(Demo1)constructor.newInstance(parameters);
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("An exception is thrown when creating an object. Execute the following setAccessible()method");
constructor.setAccessible(true); //Set allowed access
}
}
if(example2!=null) {
example2.print();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
/*Output results:
Check whether variable number of parameters are allowed: true
The entry parameter types of the construction method are as follows:
class [Ljava.lang.String;
The entry of this constructor may throw an exception of type:
class java.lang.NumberFormatException
s=null
i=100
i2=100
i3=100
Check whether parameters with variable number are allowed: false
The entry parameter types of the construction method are as follows:
class java.lang.String
int
The entry of this constructor may throw an exception of type:
s=7
i=5
i2=0
i3=0
Check whether parameters with variable number are allowed: false
The entry parameter types of the construction method are as follows:
The entry of this constructor may throw an exception of type:
An exception is thrown when creating an object. The setAccessible() method is executed below
s=null
i=0
i2=0
i3=0
*/
2. Accessing member variables
Each Field object represents a member variable, and the corresponding member variables can be manipulated by using the Field object.
- getFields()
- getField(String name)
- getDeclaredFields()
- getDeclaredField(String name)
Create Demo1 class, declare int, fioat, boolean and String member variables, and set different access rights.
package bao;
public class Demo1{
int i;
public float f;
protected boolean b;
private String s;
}
Access all member variables in Demo1 class through reflection, and output the name and type information of member variables.
package bao;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 demo=new Demo1();
Class demoC=demo.getClass();
//Get all member variables
Field[] declaredField=demoC.getDeclaredFields();
for(int i=0;i<declaredField.length;i++) {
Field field=declaredField[i];
System.out.println("The name is:"+field.getName()); //Get member variable name
Class fieldType=field.getType(); ///Get member variable type
System.out.println("Type:"+fieldType);
boolean isTurn=true;
while(isTurn) {
try {
isTurn=false;
System.out.println("The value before modification is:"+field.get(demo));
if(fieldType.equals(int.class)) { //Judge whether the type of member variable is int
System.out.println("Utilization method setInt()Modify the value of a member variable");
field.setInt(demo, 168); //Assign a value to a member variable of type int
}else if(fieldType.equals(float.class)){ //Judge whether the type of member variable is float type
System.out.println("Utilization method setFloat()Modify the value of a member variable");
field.setFloat(demo, 99.9F); //Assign a value to a member variable of type float
}else if(fieldType.equals(boolean.class)){ //Judge whether the type of member variable is boolean
System.out.println("Utilization method setBoolean()Modify the value of a member variable");
field.setBoolean(demo, true); //Assign a value to a boolean type member variable
}else {
System.out.println("Utilization method set()Modify the value of a member variable");
field.set(demo, "MWQ"); //You can assign values to various types of member variables
}
//Get member variable value
System.out.println("The modified value is:"+field.get(demo));
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("An exception is thrown when setting the value of a member variable,"+"Execute below setAccesssible()method!");
field.setAccessible(true); //Set to allow access
isTurn=true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/*Output results:
Name: i
Type: int
The value before modification is: 0
Modify the value of the member variable with the method setInt()
The modified value is 168
Name: f
Type: float
The value before modification is: 0.0
Modify the value of the member variable with the method setFloat()
The modified value is 99.9
Name: b
Type: boolean
The value before modification is: false
Use the method setBoolean() to modify the value of the member variable
The modified value is: true
Name: s
Type: class java.lang.String
An exception is thrown when setting the value of a member variable. Next, execute setaccessable() method!
The value before modification is null
Use the method set() to modify the value of the member variable
The modified value is MWQ
*/
3. Access method
Each Method object represents a Method, and the corresponding Method can be manipulated by using the Method object.
- getMethods()
- getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
- getDeclaredMethods()
- getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
Create Demo1 class and write four typical methods.
package bao;
public class Demo1{
static void staitcMethod() {
System.out.println("implement staitcMethod()method");
}
public int publicMethod(int i) {
System.out.println("implement publicMethod()method");
return i*100;
}
protected int protectedMethod(String s,int i)throws NumberFormatException {
System.out.println("implement protectedMethod()method");
return Integer.valueOf(s)+i;
}
private String privateMethod(String...strings) {
System.out.println("implement privateMethod()method");
StringBuffer stringBuffer=new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<stringBuffer.length();i++) {
stringBuffer.append(strings[i]);
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
Reflection accesses all methods in the Demm1 class and outputs information such as method name, entry parameter type, return value type, etc
package bao;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Demo1 demo = new Demo1();
Class demoC = demo.getClass();
// Get all methods
Method[] declaredMethods = demoC.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredMethods.length; i++) {
Method method = declaredMethods[i]; // traversal method
System.out.println("The name is:" + method.getName()); // Get method name
System.out.println("Allow variable number of parameters:" + method.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("The entry parameter types are as follows:");
// Get all parameter types
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
// Gets the return value type of the method
System.out.println("The return value type is:" + method.getReturnType());
System.out.println("The types of exceptions that may be thrown are:");
// Gets all the exception types that the method may throw
Class[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
boolean isTurn = true;
while (isTurn) {
try {
isTurn = false;
if("staitcMethod".equals(method.getName())) {
method.invoke(demo); // Execute methods without entry parameters
}else if("publicMethod".equals(method.getName())) {
System.out.println("The return value is:"+ method.invoke(demo, 168)); // Execution method
}else if("protectedMethod".equals(method.getName())) {
System.out.println("The return value is:"+ method.invoke(demo, "7", 5)); // Execution method
}else {
Object[] parameters = new Object[] { new String[] {"M", "W", "Q" } }; // Define a 2D array
System.out.println("The return value is:"+ method.invoke(demo, parameters));
}
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("Throw an exception when executing the method,"
+ "Execute below setAccessible()method!");
method.setAccessible(true); // Set to allow access
isTurn = true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/*Output results:
Name: publicMethod
Allow parameters with variable quantity: false
The entry parameter types are as follows:
int
The return value type is: int
The types of exceptions that may be thrown are:
Execute the publicMethod() method
Return value: 16800
Name: staitcMethod
Allow parameters with variable quantity: false
The entry parameter types are as follows:
The return value type is void
The types of exceptions that may be thrown are:
Execute the staitcMethod() method
Name: protectedMethod
Allow parameters with variable quantity: false
The entry parameter types are as follows:
class java.lang.String
int
The return value type is: int
The types of exceptions that may be thrown are:
class java.lang.NumberFormatException
Execute the protectedMethod() method
The return value is: 12
Name: privateMethod
Allow variable number of parameters: true
The entry parameter types are as follows:
class [Ljava.lang.String;
The return value type is: class java.lang.String
The types of exceptions that may be thrown are:
An exception is thrown when executing the method. Next, execute setAccessible() method!
Execute the privateMethod() method
The return value is:
*/
2, Using the Annotation function
1. Define Annotation type
When defining an Annotation type, you also need to use the interface keyword used to define the interface, but you need to add an "@" symbol before the interface keyword, that is, the keyword defining the Annotation type is @ interface. The implied meaning of this keyword is that it inherits the java.lang.annotation.Annotation interface.
public @interface NoMemberAnnotation{
String value();
}
@interface: declare keywords.
NoMemberAnnotation: annotation name.
String: member type.
value: member name.

Define and use Annotation types
① Define Annotation type @ constructor_ The valid range of annotations is that the runtime loads annotations into the JVM.
package annotationbao;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) // Method for constructing
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // Load annotations into the JVM at run time
public @interface Constructor_Annotation{
String value() default "Default construction method"; // Define a String member with a default value
}
② Define an Annotation type @ field to annotate fields, methods, and parameters_ Method_ Parameter_ The valid range of annotations is that the runtime loads annotations into the JVM
package annotationbao;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER}) // For fields, methods, and parameters
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // Load annotations into the JVM at run time
public @interface Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation{
String descrblic(); // Define a String member with no default value
Class type() default void.class; // Define a Class member with a default value
}
③ Write a Record class and use the @ constructor of annotation type previously defined in this class_ Annotation and @ Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation annotates construction methods, fields, methods, and parameters.
package annotationbao;
public class Record {
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "number", type = int.class)
int id;
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "full name", type = String.class)
String name;
@Constructor_Annotation()
public Record() {
}
@Constructor_Annotation("Initialize constructor now")
public Record(
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "number", type = int.class)
int id,
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "full name", type = String.class)
String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "Get number", type = int.class)
public int getId() {
return id;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "Set number")
public void setId(
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "number", type = int.class)int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "Get name", type = String.class)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "Set name")
public void setName(
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "full name", type = String.class)String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
2. Access Annotation information
If @ Retention is set to RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME when defining the Annotation type, relevant Annotation information can be obtained through reflection when running the program, such as the Annotation information of construction methods, fields and methods.
Combine the above definitions and use the Annotation type to access the Annotation information in the Record class through reflection.
package annotationbao;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class Main_05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class recordC = null;
try {
recordC = Class.forName("Record");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("------ The construction method is described below ------");
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = recordC
.getDeclaredConstructors(); // Get all construction methods
for (int i = 0; i < declaredConstructors.length; i++) {
Constructor constructor = declaredConstructors[i]; // Traversal construction method
// See if there are comments of the specified type
if (constructor
.isAnnotationPresent(Constructor_Annotation.class)) {
// Gets a comment of the specified type
Constructor_Annotation ca = (Constructor_Annotation) constructor
.getAnnotation(Constructor_Annotation.class);
System.out.println(ca.value()); // Get comment information
}
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = constructor
.getParameterAnnotations(); // Get comments for parameters
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations.length; j++) {
// Gets the length of the specified parameter comment
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length;
if (length == 0) // If the length is 0, no comment is added for the parameter
System.out.println(" Not added Annotation Parameters of");
else
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
// Get comments for parameters
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation pa = (Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation) parameterAnnotations[j][k];
System.out.print(" " + pa.describe()); // Get parameter description
System.out.println(" " + pa.type()); // Get parameter type
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------- The fields are described below --------");
Field[] declaredFields = recordC.getDeclaredFields(); // Get all fields
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
Field field = declaredFields[i]; // Traversal field
// See if there are comments of the specified type
if (field
.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class)) {
// Gets a comment of the specified type
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation fa = field
.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class);
System.out.print(" " + fa.describe()); // Gets the description of the field
System.out.println(" " + fa.type()); // Gets the type of the field
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------- The method is described below --------");
Method[] methods = recordC.getDeclaredMethods(); // Get all methods
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method method = methods[i]; // traversal method
// See if there are comments of the specified type
if (method
.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class)) {
// Gets a comment of the specified type
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation ma = method
.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class);
System.out.println(ma.describe()); // Obtain a description of the method
System.out.println(ma.type()); // Gets the return value type of the method
}
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method
.getParameterAnnotations(); // Get comments for parameters
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations.length; j++) {
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length; // Gets the length of the specified parameter comment
if (length == 0) // If the length is 0, no comment is added for the parameter
System.out.println(" Not added Annotation Parameters of");
else
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
// Gets a comment of the specified type
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation pa = (Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation) parameterAnnotations[j][k];
System.out.print(" " + pa.describe()); // Get a description of the parameter
System.out.println(" " + pa.type()); // Gets the type of the parameter
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
/*Output results:
------ The construction method is described below------
Default construction method
Initialize constructor now
Number int
Name: class java.lang.String
-------- The fields are described below--------
Number int
Name: class java.lang.String
-------- The method is described below--------
Get name
class java.lang.String
Set name
void
Name: class java.lang.String
Get number
int
Set number
void
Number int
*/