Objectives of this section
- Understand what a collection framework is
- Understand the meaning of learning set framework
- Master the relevant interfaces and common implementation classes of the collection framework
- Understand what to learn in the next stage
1. Introduction
Official course
The Java Collection Framework, also known as the container container, is a group defined under the java.util package
Interface interfaces and its implementation classes.
Its main performance is to place multiple elements in a unit for fast and convenient storage, store and retrieval of these elements
retrieve and manage manually, which is commonly known as add, delete, check and modify CRUD.
C: create, insert a record into the database;
R: read, query database records;
U: update to modify database records;
D: Delete to delete the database record.
For example, a deck of playing cards (a set of cards), a mailbox (a set of mail), an address book (a mapping relationship between a set of names and telephones), and so on.
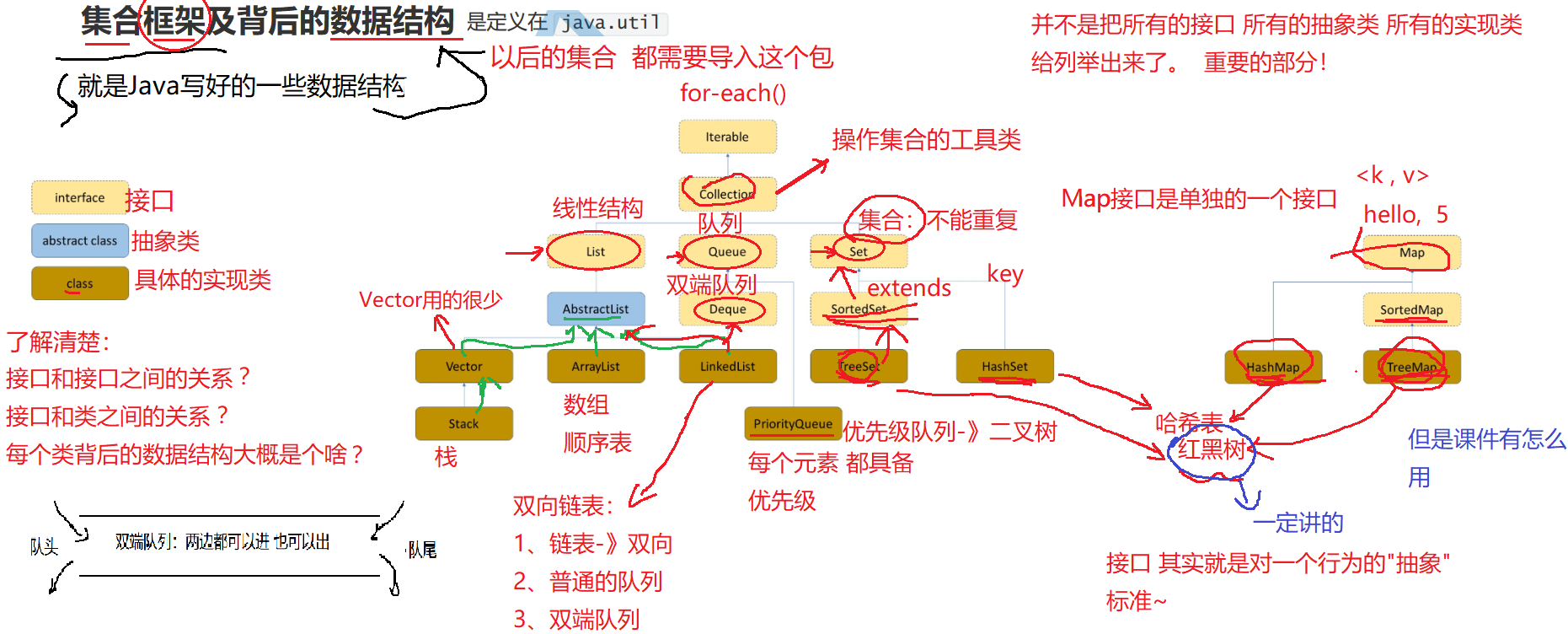
Overview of classes and interfaces
2. Significance of learning
2.1 advantages and functions of Java collection framework
- Using a mature collection framework helps us write efficient and stable code conveniently and quickly
- Learning the data structure knowledge behind it will help us understand the advantages, disadvantages and usage scenarios of each collection
2.2 written examination and interview questions
tencent-Java Background development experience 1. HashMap Do you understand? Let's introduce it. If an object is key When, hashCode and equals What should we pay attention to in the usage of method? 2. HashSet and HashMap What is the difference? 3. HashMap Is it thread safe? What does thread safety need?
Alibaba-Java Background development experience 1. ArrayList and LinkedList What is the difference? 2. Yes HashMap Is the concrete implementation of? 3. HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap Which is more efficient?
Today's headlines-Java Background development experience 1. Programming problem: judge whether a linked list is a palindrome linked list. 2. Redis of zset Type corresponds to java What is the general type of language? 3. hashCode What is it mainly used for?
3. interfaces
3.1 basic relationship description
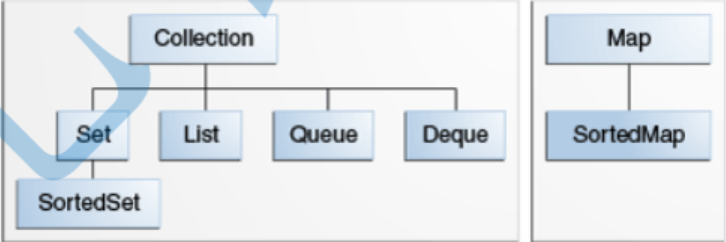
- Collection: used to store and manage a set of object objects, which are generally called element elements
- Set: the element cannot be repeated, which implies the semantics of find / search
- SortedSet: an ordered set of non repeatable elements
- List: linear structure
- Queue: queue
- Deque: Dual Ended queue
- Set: the element cannot be repeated, which implies the semantics of find / search
- Map: the key value pair implies search / search semantics
- SortedMap: an ordered set of key value pairs
3.2 Collection interface description
Collection official documentation
3.3 description of common methods of collection
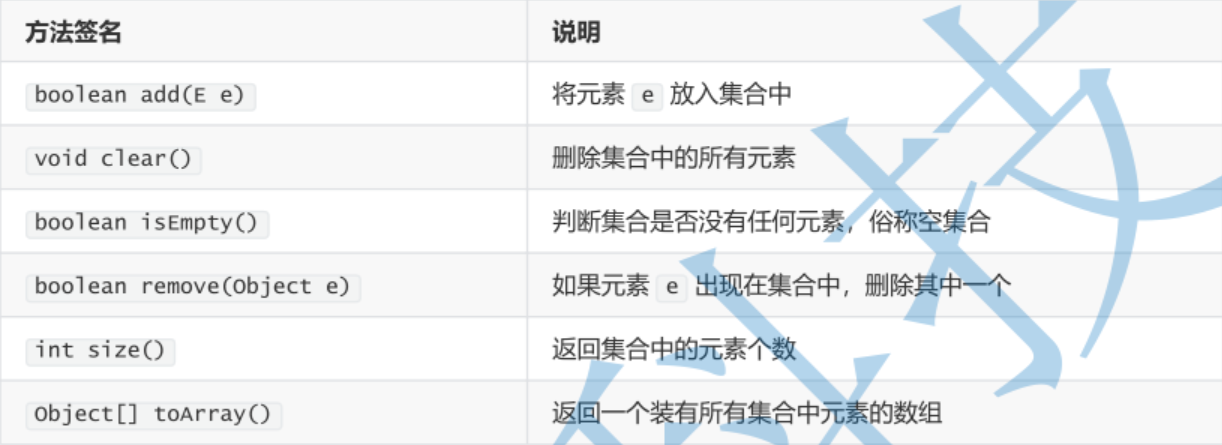
3.4 Collection example
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
list.add("I");
list.add("love");
list.add("Java");
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
Object[] array = list.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
list.remove("love");
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println(s);
}
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
}
}
Operation results:
0 true 3 false [I, love, Java] I love Java I Java 0 true
3.5 Map interface description
3.6 description of common methods of map

3.7 Map example
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println(map.get("author"));
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("author", "nameless"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("author"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue("nameless"));
map.put("author", "Lu Xun");
map.put("title", "A Madman's Diary");
map.put("Publication time", "1918 year");
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println(map.get("author"));
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("author", "nameless"));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("author"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue("nameless"));
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
System.out.println(entry.getValue());
}
}
}
Operation results:
0 true null nameless false false 3 false Lu Xun Lu Xun true false author Lu Xun Publication time 1918 year title A Madman's Diary
4. Implement classes
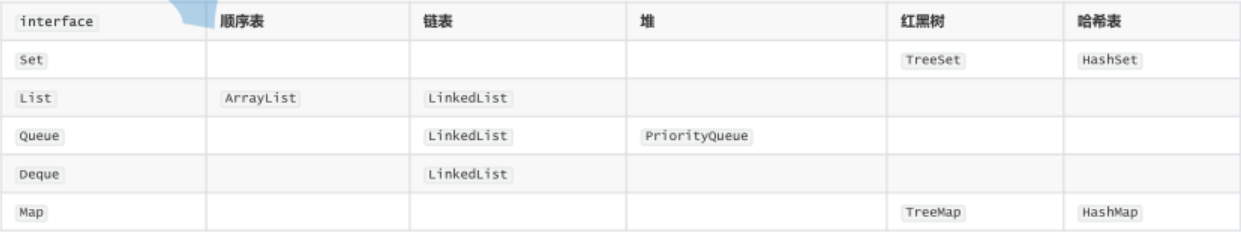
In addition, we will also learn Stack in java
5. Next stage
5.1 objectives
- Learn the basic use of the collection framework
- Learn basic data structure knowledge
- Learn seven comparison based sorting algorithms
- Learn relevant java knowledge points
5.2 knowledge points
-
Use of collection framework
- Collection
- List
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Stack
- Queue
- PriorityQueue
- Deque
- Set
- HashSet
- TreeSet
- Map
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- Collections
-
Theory and implementation of data structure
- Sequence table
- Linked list
- Stack
- queue
- Binary tree
- heap
-
Sorting algorithm
- Insert sort
- Shell Sort
- Select sort
- Heap sort
- Bubble sorting
- Quick sort
- Merge sort
-
Java syntax
- Generic generic
- autobox and autounbox
- equals method of Object
- Comparable and Comparator interfaces
Summary of key contents
The relationship between interfaces and in Java collection framework and its meaning
The relationship between interfaces and their corresponding common implementation classes in the Java collection framework
Main course contents of the next stage