1, What is a class loader
class loader: responsible for loading. class files (stored physical files) into memory
Class loading time:
1. Create an instance (object) of the class
2. Call the method of the class
3. Access class variables of classes or interfaces, or assign values to such variables
4. Use reflection to force the creation of java.lang.class objects corresponding to a class or interface
5. Initialize a class
6. Directly use the java.exe command to run a main class
Load when you need it, don't load it
2, Class loader procedure
1. Load: obtain this class through registration + class name, prepare to transfer it with stream, load this class into memory, and create a class object after loading
2. Verification: whether the information in the file complies with the virtual machine specification and whether there are potential security risks
Preparation: initializing static variables
Parsing: if other classes are used in this class, you need to find the corresponding class
3. Initialization: static variable assignment and initialization of other resources
3, Classification of class loaders
Bootstrap classloader: the built-in classloader of the virtual machine
Platform loader: it is responsible for loading some special modules in JDK
System classloader: it is responsible for loading the class library specified on the user's class path
1. Parental delegation model
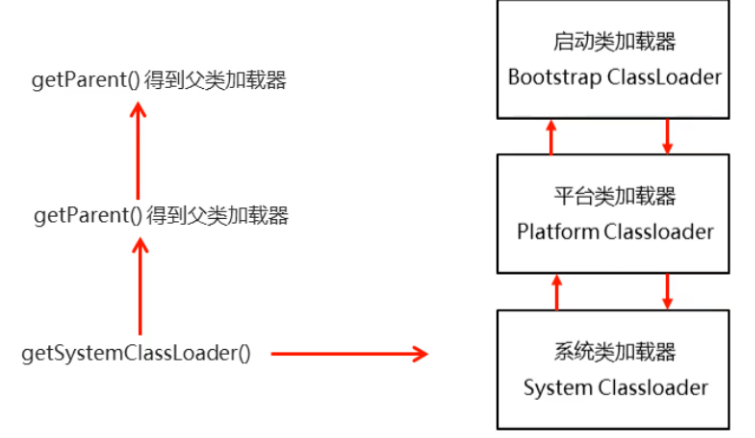
Obtain a system class loader through the getSystemClassLoader () method, and then obtain the parent class loader through the getParent () method
2. Common methods of class loader
| Method name | explain |
| public static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader(); | Get system loader |
| public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name); | Load a resource file |
public class ClassLoaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Class loader for system
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
//Class loader for platform
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
//Initiator class loader
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
//Printout
System.out.println("system class loader "+systemClassLoader);
System.out.println("Platform class loader"+parent);
System.out.println("Start class loader"+parent1);
}
}public class MethodDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
//Use the loader to load a specified file
//Parameters: path to file
//Return value: data in byte stream
InputStream is = systemClassLoader.getResourceAsStream("p.properties");
//Create properties collection
Properties pp = new Properties();
pp.load(is);
System.out.println(pp);
is.close();
}
}4, Overview of reflection
java reflection
In the running state, for any class, you can know that this class has many properties and methods;
For any object, you can call any of its properties and methods
This function of dynamically obtaining information and dynamically calling object methods is called the reflection mechanism of java language
Create objects with reflections
Reflection calls member variables, which can
Reflection calls member methods, which can
Ignore modifiers when calling properties and methods in other classes with reflection
Reflection is not dead, it's flexible
java launch mechanism:
Using reflection, you can get all the properties and methods in the class regardless of modifiers
First get the information in the configuration file, and then go to the information bin to find common objects and call methods
5, Get class object
Before calling a method in a class
Create an object of this class
Calling methods with objects
Reflection to call a method in a class
Created using class objects
Reflection method: creating objects
Reflection mode: calling method
1. Get the object of class
Class.forName("full class name");
class name. class;
Object. getClass();
public class ReflectDemo01 {
/*Three ways to get class objects*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. Method forName("full class name") in class
//Full class name = package name plus class name;
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect01.Student");
System.out.println(aClass);
//2. Get through the class attribute
Class<Student> studentClass = Student.class;
System.out.println(studentClass);
//3. Use the getclass method of the object to obtain the class object
//The getclass method is defined in the Object
Student stu = new Student();
Class<? extends Student> aClass1 = stu.getClass();
System.out.println(aClass1);
}
}6, Reflection acquisition construction method
The method used to get the constructor in the class
Constructor <? > [] getconstructors(); returns an array of all public constructor objects
Constructor <? > [] getdeclardeconstructors(); returns an array of all constructor objects
Constructor<T> Getconstructor (class <? >... Paramentertypes); returns a single public constructor object
Constructor<T> Getdeclardeconstructor (class <? >... Paramentertypes); returns a single constructor object
public class ReflectDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
// Get constructor object
//Get class object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect02.Student");
//Get the constructor object, which is all public constructors
Constructor<?>[] constructors = aClass.getConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor);
}
// Gets a constructor with parameters
// Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
// System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
}
}Methods used to create objects in the Constructor class
T newlnstance(Object...initargs): creates an object according to the specified construction method
public class ReflectDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// Get constructor object
//Get class object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect02.Student");
// method01(aClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = aClass.getConstructor();
Student o = (Student) constructor.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);
}
}If the privatized construction method is used, you need to cancel the check
public class ReflectDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//Get a private constructor and create an object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect02.Student");
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = aClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
/*Members decorated with private cannot be used directly
* If it is forcibly acquired and used by reflection, the check needs to be cancelled*/
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Student o = (Student) declaredConstructor.newInstance("zhangsan", 23);
System.out.println(o);
}
}Summary
Get calss object
Three methods - Class.forName("full class name")
Get the constructor object inside
getConstructor()
getDeclaredConstructor()
If it is public, create the object directly
newlnstance()
If it is not public, you need to cancel the check before creating the object
setAccessible (boolean) violent reflection
7, Reflection get member variable
1. Get Field object
File [] getfields(); returns an array of all public member variables
File [] getdeclaraedfields(); returns an array of all member variables
File [] getfield (string name); returns an array of single public member variables
File [] getdeclaraedfield (string name); returns an array of single member variables
public class ReflectDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
/*Field[] getFields(); Returns an array of all public member variable objects
* Field[] getDeclaredFields(); Returns an array of all member variable objects
* Field getField(String name); Returns a single public member variable object
* Field getDeclaredFields(); Returns a single member variable object*/
// method01();
// method02();
// method03();
// method04();
}
private static void method04() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getdeclaraedfields(); returns a single member variable object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("money");
System.out.println(name);
}
private static void method03() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
// Field getfield (string name); returns a single public member variable object
// The member variable you want to get must be real and public decorated
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
Field name = aClass.getField("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
private static void method02() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//Field [] getdeclaraedfields(); returns an array of all member variable objects
//1. Get the class object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
//2. Get Field object
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
//output
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(declaredField);
}
}
private static void method01() throws ClassNotFoundException {
// Field[] getFields(); returns an array of all public member variable objects
//1. Get the class object
Class aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
//2. Get Field object
Field[] fields = aClass.getFields();
//
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
}2. Assign or obtain values
void set(Object obj,Object value); assignment
Object get(Object obj); get value
public class ReflectDemo02 {
//Assign or get values to member variables
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// Void set (object obj, object value); assign value to the member of obj object
//Object get (object obj); returns the value of the field represented by the file on the specified object
// method01();
//1. Get Class object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
//2. Get the member variable Field object
Field money = aClass.getDeclaredField("money");
//3. Cancel the access check
money.setAccessible(true);
//4. Call the get method to get the value
//4.1 create an object
Student01 student = (Student01) aClass.newInstance();
//4.2 get the value of the member variable of the specified object
Object o = money.get(student);
//5. Printing
System.out.println(o);
}
private static void method01() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// Void set (object obj, object value); assign value to the member of obj object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student01");
Field name = aClass.getField("name");
//Assignment using set method
//Create object of Student class
Student01 student = (Student01) aClass.newInstance();
//You can assign a value to the specified object only if you have an object
name.set(student, "zhangsan");
System.out.println(student);
}
}8, Reflection get member method
1. Get member method
Method[] getMethods(); Returns all public member methods, including inherited methods
Method[] getDeclaredMethods(); Returns all member methods, excluding inherited methods
Method getMethod(String name,Class<?>...paramenterTypes); Returns a single public member method
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class<?>...paramenterTypes); Returns a single member method
//Get Method object
public class ReflectDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
/*Method[] getMethods();Returns an array of all public member method objects, including inherited
* Method[] getDeclaredMethods();Returns an array of all member method objects, excluding inherited
* Method getMethod(String name,Class<?>...parameterTypes);Returns a single public member method object
* Method getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class<?>...parameterTypes);Returns a single member method object
* */
// method01();
// method02();
// method03();
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student02");
Method show = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("show");
System.out.println(show);
}
private static void method03() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student02");
Method function01 = aClass.getMethod("function03",String.class);
System.out.println(function01);
}
private static void method02() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student02");
Method[] declaredMethods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println(declaredMethod);
}
}
private static void method01() throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student02");
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method);
}
}
}2. Operation method
Object invoke(Object obj,Object...args );
//Get the Method object and run it
public class ReflectDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
/*Object invoke(Object obj,Object...args);Operation method
* Parameter 1: call this method with obj object
* Parameter 2: transfer parameters of the calling method (if not, it will not be written)
* Return value: the return value of the method (if not, it will not be written)*/
//1. Get the class object
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.cheng.reflect03.Student02");
//2. Get the method object inside, function4
Method function04 = aClass.getMethod("function04", String.class);
//3. Run function4 method
//3.1 create a Student02 object as the caller of the method
Student02 o = (Student02) aClass.newInstance();
//3.2 operation method
Object fun = function04.invoke(o, "Zhang San");
//4. Print return value
System.out.println(fun);
}
}