2018-03-12
An array is a fixed length container that contains data of the same type
1, Declare array:
int[] a; declares an array variable.
[] indicates that the variable is an array
int means that every element in the array is an integer
a is the variable name
However, just this statement will not create an array
Sometimes it is also written as int a []; there is no difference, that is, what kind of pleasant question do you think:
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { // Declare an array int[] a; } }
2, To create an array:
When creating an array, indicate the length of the array. new int[5]
Reference concept:
If the variable represents an array, such as a, we call a reference; different from the basic type: int c = 5; this is called assigning C to 5
Declare a reference int[] a
a = new int[5];
Let a point to the array.
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { //Declare a reference int[] a; //Create an array with a length of 5 and use the reference a Point to the array a = new int[5]; int[] b = new int[5]; //When declared, points to an array } }
3, Access array:
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a; a = new int[5]; a[0]= 1; //Subscript 0, representing the first number in the array a[1]= 2; a[2]= 3; a[3]= 4; a[4]= 5; } }
4, Array length:
The. Length property is used to access the length of an array
Array access subscript range is 0 to length - 1
Once the range is exceeded, an array subscript out of bounds exception will be generated
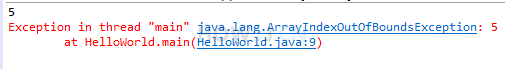
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a; a = new int[5]; System.out.println(a.length); //Print the length of the array a[4]=100; //Subscript 4, essentially "the fifth", is the last a[5]=101; //Subscript 5, essentially "6th", out of range ,Generate array subscript out of bounds exception } }
5, Initialize array:
1. Space allocation and assignment are carried out step by step:
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = new int[5]; //An array of length 5 was assigned, but no assignment was made //No assignment, then the default value will be used //Act as int Array of type, default is 0 System.out.println(a[0]); //Assignment a[0] = 100; a[1] = 101; a[2] = 103; a[3] = 120; a[4] = 140; } }
2. Allocate space and assign:
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { //Write method 1: assign space at the same time int[] a = new int[]{100,102,444,836,3236}; //Style 2: omitted new int[],Same effect int[] b = {100,102,444,836,3236}; //Style 3: allocate space and specify content at the same time //In this case, the length is 3 and the content is 5, which makes a contradiction //So if you specify the contents of the array, you cannot set the length of the array at the same time int[] c = new int[3]{100,102,444,836,3236}; } }