catalogue
1, Overview of arrays
◆ an array is an ordered collection of data of the same type
◆ array describes several data of the same type, which are arranged and combined in a certain order.
◆ each data is called an array element, and each array element can access them through a subscript
2, Array declaration creation
◆ array variables must be declared before using arrays in programs. The following is the syntax for declaring array variables:
Array type [] Array name// Preferred method
or
Array type Array name []// The effect is the same, but it is not the preferred method. It is written in C and C + +
◆ the Java language uses the new operator to create arrays. The syntax is as follows:
Array type [] Array name = new Array type[ Array length];
◆ the elements of the array are accessed through the index, and the array index starts from 0.
◆ get array length: Array name . length
package com.alic.array;
public class ArrayDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr;// Declare an array
arr = new int[5]; //Create an array and allocate five spaces to the array
//Export five spaces
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]); //The default value of int is 0
}
//Assign a value to an array
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 3;
arr[2] = 6;
arr[3] = 11;
arr[4] = 17;
//Print array
System.out.println(arr[0]);// 1
System.out.println(arr[1]);// 3
System.out.println(arr[2]);// 6
System.out.println(arr[3]);// 11
System.out.println(arr[4]);// 17
//Gets the length of the array
int arrLength =arr.length;
System.out.println(arrLength); //5
}
}
1. Array memory analysis
java Memory Analysis
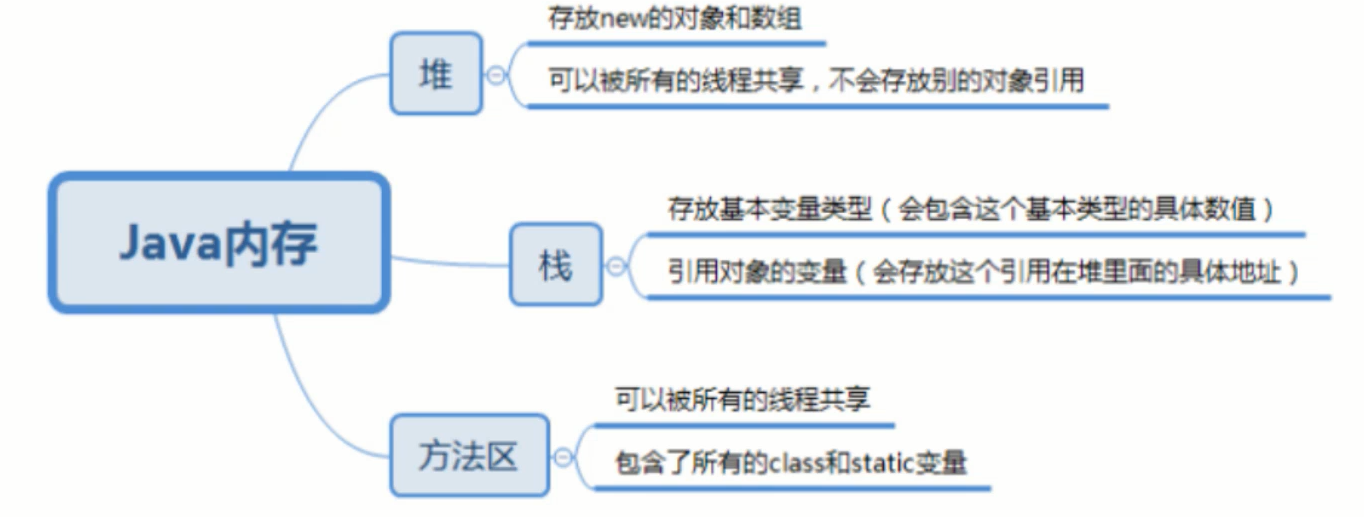
Write code, draw pictures and divide memory
2. Three initialization methods
-
initiate static
int[] a = {1,2,3};
int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3}
-
dynamic initialization
int[] a = new int[2];
a[0]=1;
a[1]=2;
Default initialization of arrays
-
Array is a reference type, and its elements are equivalent to the instance variables of the class. Therefore, once the array is allocated space, each element in it is implicitly initialized in the same way as the instance variables.
package com.alic.array;
public class ArrayDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//initiate static
//int[] a = {1,2,3};
int[] a = new int[]{4,5,66};
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
//dynamic initialization
int[] b = new int[2]; //Create an array to open up space
System.out.println(b[0]); // Default initialization 0
System.out.println(b[1]); // Default initialization 0
//Assign a value to an array
b[0] = 1;
b[1] = 2;
System.out.println(b[0]);// 1
System.out.println(b[1]);// 2
}
}3. Four basic characteristics of array
-
Its length is determined. Array - once created, its size cannot be changed.
-
Its elements must be of the same type and mixed types are not allowed.
-
The elements in the array can be any data type, including basic types and reference types.
-
Array variables are reference types. Arrays can also be regarded as objects. Each element in the array is equivalent to the member variables of the object. The array itself is an object. In Java, the object is in the heap. Therefore, whether the array saves the original type or other object types, the array object itself is in the heap.
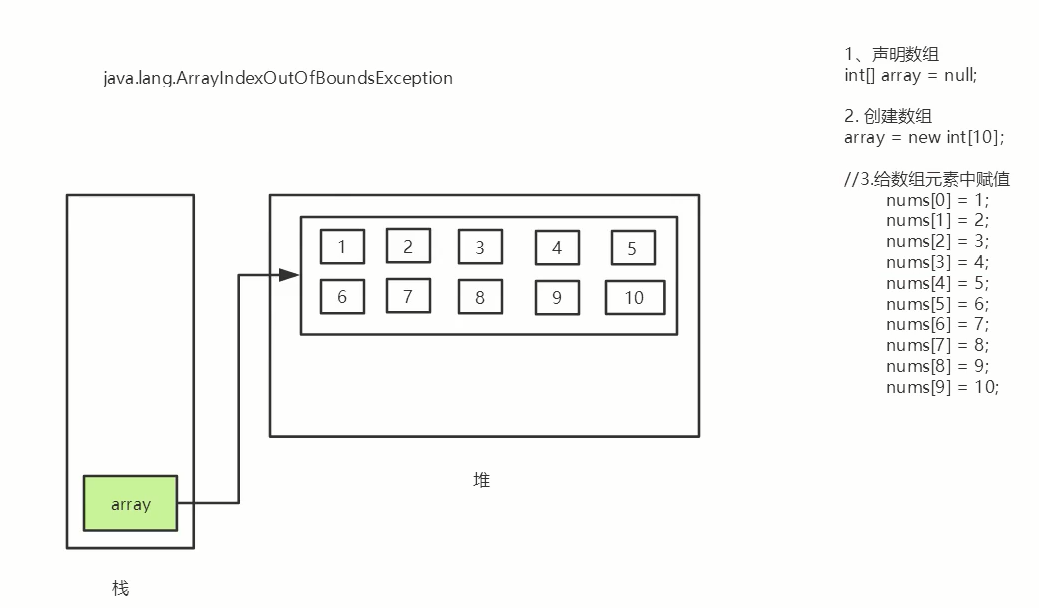
4. Array boundary
The legal range of the subscript: [0, length-1]. If it exceeds the range, an error will be reported;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[2] ;
System. out. println(a[2]);
}ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: array subscript out of bounds exception!
Summary:
-
An array is an ordered collection of the same data type (the data type can be any type)
-
Arrays are also objects. An array element is equivalent to a member variable of an object
-
The length of the array is fixed and immutable. If the boundary is exceeded, it will report: ArrayIndexOutofBounds
package com.alic.array;
/**
* Demonstrate array out of bounds
*/
public class ArrayDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Define an array
int[] arr = new int [2];// Index 0-1
System.out.println(arr[2]); // Index 2 has crossed the legal boundary. An error is reported!
}
}3, Array usage
-
For each loop
-
Array as method input parameter
-
Array as return value
package com.alic.array;
public class ArrayDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Define an array
int[] arr = {1,3,4,7};
// Print array elements
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
System.out.println("==========================");
//for-each
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.print(i+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
//reversal
int[] arr1 = reverse(arr);
for (int i : arr1) {
System.out.print(i+"\t");
}
}
//Invert array
public static int [] reverse (int[] a){ //Array as method arguments
int[] result = new int[a.length];
for (int i = 0,j=result.length-1; i < a.length; i++,j--) {
result[j] = a[i];
}
return result; //Array as return value
}
}
}4, Multidimensional array
-
Multidimensional arrays can be regarded as arrays. For example, a two-dimensional array is a special one-dimensional array, and each element is a one-dimensional array.
-
Two dimensional array
int a[][] = new int[2][5];
Analysis: the above two-dimensional array a can be regarded as an array with two rows and five columns.
Thinking: the use of multidimensional arrays?
num[1] [0];
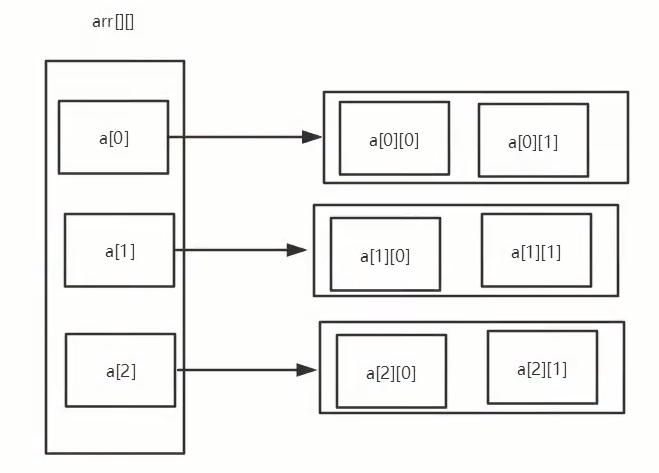
package com.alic.array;
/**
* Multidimensional array
*/
public class ArrayDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Define a one-dimensional array
int[] arr = {1,2,6,4};
// Define a 2D array
int[][] arr2 = {{1,2},{2,3},{7,7}};
//Define 3D array
int[][][] arr3 = {{{1,2},{1,2}},{{1,2},{1,2}},{{1,2},{1,2}}};
/*
Multidimensional array is the nesting of arrays. The understanding of two-dimensional array is to open up an array, and the elements of the array are arrays
*/
// arr = arr2; // Different types, unable to operate
//Print 2D array
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.print("{");
for (int j = 0; j < arr2[i].length; j++) {
if (j< arr2[i].length-1){
System.out.print(arr2[i][j]+",");
}
if (arr2[i].length-1 == j)System.out.print(arr2[i][j]);
}
System.out.println("}");
}
}
}5, Arrays tool class
◆ tool class of array: java.util.Arrays
◆ there are no methods for us to call array objects, but the API provides a tool class Arrays for us to use, so we can perform some basic operations on data objects.
◆ view JDK help documents
◆ all the methods in the Arrays class are static methods decorated with static. When using them, you can call them directly with the class name instead of using the object (Note: it is "no" instead of "no")
◆ it has the following common functions:
-
Assign a value to the array: through the fill method.
-
Sort the array: sort in ascending order through the sort method.
-
Compare arrays: use the equals method to compare whether the element values in the array are equal.
-
Find array elements: binary search can be performed on the sorted array through the binarySearch method.
package com.alic.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Arrays Array utility class
*/
public class ArrayDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[] {1,45,55,88,55};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); // [1, 45, 55, 88, 55]
//Sort the array in ascending order
Arrays.sort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //[1, 45, 55, 55, 88]
}
}Bubble sorting
-
Bubble sorting is undoubtedly one of the most famous sorting algorithms. There are eight sorting algorithms in total!
-
The bubbling code is still quite simple. The two-layer cycle, the number of bubbling rounds in the outer layer and the inner layer are compared in turn. Everyone in the Jianghu knows it
-
When we see nested loops, we should immediately conclude that the time complexity of this algorithm is O(n2).
◆ thinking: how to optimize?
package com.alic.array;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayDemo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Define an array
int[] arr = {22, 55, 78, 88, 20, 100};
int[] arr1 = sort(arr);
//Print the array elements. Here, use the tool class to print
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
}
// Bubble sorting
// 1. Compare two adjacent elements in the array. If the first number is larger than the second number, we will exchange their positions
// 2. Each comparison will produce a maximum or minimum number;
// 3. The next round can be sorted less - once!
// 4. Cycle successively until the end!
public static int[] sort(int[] array) {
int temp = 0;
//Outer circle, judge how many times we have to go;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
//The inner loop judges two numbers by price comparison. If the first number is larger than the second number, the position is exchanged
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[i+1]){
temp = array[j];
array[j]=array[i+1];
array[i+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
}Optimize partial code
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
//The inner loop judges two numbers by price comparison. If the first number is larger than the second number, the position is exchanged
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[i+1]){
temp = array[j];
array[j]=array[i+1];
array[i+1] = temp;
flag = false;
}
//If there is no sorting, return directly
if (flag){
break;
}
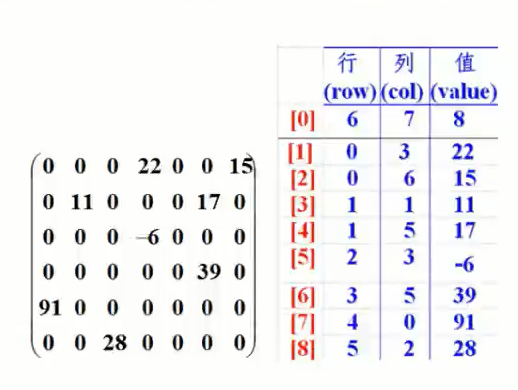
}6, Sparse array (Extended)
Take the bubble ascending order above as an example. Each traversal can find the maximum value and put it at the end of the array. The next traversal will exclude the maximum value and continue to sort the remaining elements until they are completely sorted

Requirements: in the preparation of Gobang games, there are functions of saving, exiting, continuing and hanging.
◆ analysis: because many values of the two-dimensional array are 0 by default, many meaningless data are recorded.
◆ solution: sparse array
Introduction to sparse array
-
When most elements in an array are 0 or an array with the same value, you can use a sparse array to save the array.
-
Sparse arrays are handled as follows:
◆ how many rows, columns and different values are there in the record array
◆ record the elements, rows, columns and values with different values in a small-scale array, so as to reduce the size of the program
-
As shown in the following figure: the original array is on the left and the sparse array is on the right
Code demonstration
package com.alic.array;
public class ArrayDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Play go 11 rows and 11 columns 1 is black chess and 2-digit white flag
//Define an array
int[][] arr = new int[11][11];
arr[1][2] = 1;
arr[2][3] = 2;
//Print array
for (int[] ints : arr) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
//===================================================
//Convert to sparse array
//Count the number of non-zero numbers
int sum =0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0) sum++;
}
}
//Define sparse array
int[][] arr1 = new int[sum+1][3];
//Record the information of the original array
arr1[0][0] = 11;
arr1[0][1] = 11;
arr1[0][2] = sum;
//Traverses the normal array and stores non-zero numbers in the sparse array
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0) {
count++;
arr1[count][0]=i;
arr1[count][1]=j;
arr1[count][2]=arr[i][j];
}
}
}
//Print sparse array
for (int[] ints : arr1) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
//=========================================
//Sparse array restore cars are like ordinary arrays
int[][] arr2 = new int[arr1[0][1]][arr1[0][1]];
for (int i = 1; i < arr1.length; i++) {
arr2[arr1[i][0]][arr1[i][1]] = arr1[i][2];
}
//Print array
for (int[] ints : arr2) {
for (int anInt : ints) {
System.out.print(anInt+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}