IO stream read / write operation decoration stream
First, brief
Decoration flow, also known as processing flow, is a typical decorator pattern.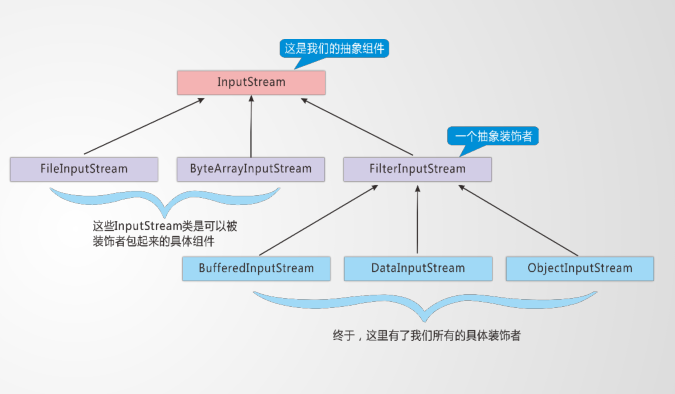
What is the decorator mode? You can find out through the following examples.
package IOstudy0304; /** * Analog coffee * 1.Abstract component: abstract object (interface or abstract parent class) to be decorated * 2.Specific components: objects to be decorated * 3.Abstract decoration class: contains references to abstract components and methods shared by decorators * 4.Specific decoration class: objects to be decorated * @author GP9 * */ public class DecorateTest02 { public static void main(String[] args){ Drink coffee=new Coffee(); Drink suger=new Suger(coffee); System.out.println(suger.info()+"--->"+suger.cost()); Drink milk=new Milk(coffee); System.out.println(milk.info()+"--->"+milk.cost()); milk=new Milk(suger); System.out.println(milk.info()+"--->"+milk.cost()); } } //Abstract component interface Drink{ double cost();//Cost String info();//Explain } //Specific components class Coffee implements Drink{ private String name="Original coffee"; @Override public double cost() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 10; } @Override public String info() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return name; } } //Abstract decoration class abstract class Decorate implements Drink{ //References to abstract components private Drink drink; public Decorate(Drink drink){ this.drink=drink; } @Override public double cost() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.drink.cost(); } @Override public String info() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return this.drink.info(); } } //Specific decoration class Milk extends Decorate{ public Milk(Drink drink){ super(drink); } @Override public double cost() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.cost()*4; } @Override public String info() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.info()+"Milk added"; } } //Specific decoration class Suger extends Decorate{ public Suger(Drink drink){ super(drink); } @Override public double cost() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.cost()*2; } @Override public String info() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return super.info()+"Sucrose added"; } }
2, Bufferedoutputstream & bufferedinputstream
The bottom layer of the buffer stream is still node stream, and the buffer size is 8k by default. When closing the stream, only the outer layer needs to be closed.
Example 1
import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; /* * Four steps: segment read file byte input stream and add buffer stream * 1,Create source * 2,Selection flow * 3,operation * 4,Release resources */ public class BufferedTest01 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Create source File src=new File("abc.txt"); //Selection flow InputStream is=null; try { is=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src)); //Operation (segment read) byte[] flush=new byte[1024];//Cache container int len=-1;//Receiving length while((len=is.read(flush))!=-1){ //Byte array - > to string String str=new String(flush,0,len); System.out.println(str); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //Release resources try { if(null!=is){ is.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
Example 2
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.OutputStream; /* *File byte output stream join buffer stream *1,Create source *2,Selection flow *3,operation *4,Release resources */ public class BufferedTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Create source File arc = new File("test.txt");//The file can not exist, it will help you create // 2. Select flow OutputStream os = null; // try { os =new BufferedOutputStream( new FileOutputStream(arc,true));//true append // 3, operation String msg = "i am so happy"; byte[] datas = msg.getBytes();// String - > to character array (encoding) os.write(datas, 0, datas.length); os.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 4. Release resources try { if (null != os) { os.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
3, Character buffer stream (bufferedwriter & BufferedReader)
Example 1
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; /* * Four steps: file character input stream join buffer stream * 1,Create source * 2,Selection flow * 3,operation * 4,Release resources */ public class BufferedTest03 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Create source File src=new File("abc.txt"); //Selection flow BufferedReader reader=null; try { reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src)); //Operation (read line by line) String line=null; while((line=reader.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //Release resources try { if(null!=reader){ reader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
Example 2
import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; /* *File character output stream joins buffer stream (only files can be processed) *1,Create source *2,Selection flow *3,operation *4,Release resources */ public class BufferedTest04 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. Create source File arc = new File("test.txt");//The file can not exist, it will help you create // 2. Select flow BufferedWriter writer = null; // try { writer = new BufferedWriter( new FileWriter(arc));//true append // 3, operation //Write a way /*String msg = "\ni am so happy,So I decided to eat more tonight "; char[] datas = msg.toCharArray();// String - > to character array writer.write(datas, 0, datas.length); writer.flush();*/ //Writing two /*String msg = "\ni am so happy,So I decided to eat more tonight "; writer.write(msg); writer.flush();*/ //Writing three writer.append("i am so happy"); writer.newLine(); writer.append("so More to eat tonight"); writer.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 4. Release resources try { if (null != writer) { writer.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4, Conversion stream (outputstreamwriter & inputstreamreader)
OutputStreamWriter converts a character stream to a byte stream (encoding)
InputStreamReader converts byte stream to character stream (decode)
Example 1
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; /** * Conversion stream: InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter * 1.Manipulate a byte stream (plain text) as a character stream * 2.Specify character set * @author GP9 * */ public class ConvertTest { public static void main(String[] args){ //Operating System.in and System.out try(BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); BufferedWriter writer=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));){ //Loop to get the input of the keyboard (exit exit), and output this content String msg=""; while(!msg.equals("exit")){ msg=reader.readLine(); writer.write(msg); writer.newLine(); writer.flush();//force refresh } }catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("Abnormal operation"); } } }
Example 2
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.URL; /** * Conversion stream: InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter * 1.Manipulate a byte stream (plain text) as a character stream * 2.Specify character set * @author GP9 * */ public class ConvertTest02 { public static void main(String[] args){ //Download Baidu's source code by operating network stream try(BufferedReader reader= new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader( new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream(),"UTF-8"));){ //3. Operation (read) String msg; while((msg=reader.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(msg); } }catch(IOException e){ System.out.println("Abnormal operation"); } } }
5, Dataoutputstream & datainputstream
Not only can we keep the data, but also our data types; the reading order is consistent with the writing order.
Example
import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; /** * data stream * 1.Read after write * 2.Read in the same order as write out * DateOutputStream * DateInputStream * @author GP9 */ public class DateTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ ByteArrayOutputStream baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(baos)); //Operation data type + data dos.writeUTF("Code acrid tears, who can understand the taste"); dos.writeInt(18); dos.writeBoolean(false); dos.writeChar('l'); dos.flush(); byte[] datas=baos.toByteArray(); DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(datas))); String msg=dis.readUTF(); int age=dis.readInt(); boolean flag=dis.readBoolean(); char ch=dis.readChar(); System.out.println(msg); } }
6, Objectoutputstream & objectinputstream
Example
import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; /** * Object flow * 1.Read after write * 2.Read in the same order as write out * 3.Not all objects can be serialized * * ObjectOutputStream * ObjectInputStream * @author GP9 * */ public class ObjectTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ //Write out serialization ByteArrayOutputStream baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(baos)); //Operation data type + data oos.writeUTF("Code acrid tears, who can understand the taste"); oos.writeInt(18); oos.writeBoolean(false); oos.writeChar('l'); //object oos.writeObject("Another village"); Employee emp=new Employee("Jack Ma",66666); oos.writeObject(emp); oos.flush(); byte[] datas=baos.toByteArray(); //Read deserialization ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(datas))); //The order is consistent with the writing String msg=ois.readUTF(); int age=ois.readInt(); boolean flag=ois.readBoolean(); char ch=ois.readChar(); System.out.println(msg); //Data restore of objects Object str=ois.readObject(); Object employee=ois.readObject(); if(str instanceof String){ String strObj=(String)str; System.out.println(strObj); } if(employee instanceof Employee){ Employee employeeObj=(Employee)employee; System.out.println(employeeObj); } } } //JavaBeans encapsulate data class Employee implements Serializable{ private transient String name;//transient the data does not need to be serialized private double salary; public Employee(){ } public Employee(String name,double salary){ this.name=name; this.salary=salary; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void setSalary(double salary) { this.salary = salary; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]"; } }
7, Printstream
Example
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.FileDescriptor; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; /** * PrintStream * @author GP9 * */ public class PrintTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { //Print stream System.out PrintStream ps=System.out; ps.println("Printing flow"); ps.println(true); ps=new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("print.txt")),true); ps.println("Where there is no grass in the end of the world, why love a flower alone"); ps.println(false); ps.close(); //Redirect output System.setOut(ps); System.out.println("change"); //Redirect back to console System.setOut(new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor.out)),true)); System.out.println("hello"); } }

