rpm can realize fast and simple installation of programs (compared with compilation and installation), but rpm can't solve dependency by itself, so many tools come into being to solve dependency automatically, among which yum is one of them.
yum solution to dependency:
-
There must be a file server where all the rpm packages and the package related metadata (- qi, - qR) are placed. Metadata can be created using createrepo. And put it in the repodata directory.
This file server can use ftp, http, nfs protocol to transfer data, or file: / / (local service).
The client uses the yum program to install the package. During installation, query the file server, find the dependency from the file server, and install.
yum is a program. Check whether yum is installed on this computer:
# rpm -q yum yum-3.4.3-161.el7.centos.noarch
To view the profile used by the yum program:
/etc/yum.conf is the main configuration file, which references the directory / etc/yum.repos.d/, so *. repo under the directory / etc/yum.repos.d/ is also the configuration file of Yum. It provides the public configuration of all warehouses.
The configuration file is divided into many independent small configuration files.
/*. repo: under the directory of etc/yum.repos.d/provides configuration information for the pointing of the warehouse.
# rpm -qc yum /etc/logrotate.d/yum#log use /etc/yum.conf /etc/yum/version-groups.conf#version control
/etc/yum.conf content:
[main] cachedir=/var/cache/yum/$basearch/$releasever keepcache=0 debuglevel=2 logfile=/var/log/yum.log exactarch=1 obsoletes=1 gpgcheck=1 plugins=1 installonly_limit=5 bugtracker_url=http://bugs.centos.org/set_project.php?project_id=23&ref=http://bugs.centos.org/bug_report_page.php?category=yum distroverpkg=centos-release # This is the default, if you make this bigger yum won't see if the metadata # is newer on the remote and so you'll "gain" the bandwidth of not having to # download the new metadata and "pay" for it by yum not having correct # information. # It is esp. important, to have correct metadata, for distributions like # Fedora which don't keep old packages around. If you don't like this checking # interupting your command line usage, it's much better to have something # manually check the metadata once an hour (yum-updatesd will do this). # metadata_expire=90m # PUT YOUR REPOS HERE OR IN separate files named file.repo # in /etc/yum.repos.d
[main]: the main configuration, equivalent to the point entry of the program
cachedir: cache path
keepcache: whether to keep the cache
debuglevel: debug level
logfile: log file
Exact arch: whether to make exact match. If the OS is centos7, the rpm package found includes both centos6 and centos7. If the value here is 1, select centos7.
gpgcheck: check the integrity and source validity during installation. 1 checks
plugins: whether plug-ins are supported. The 1 is support.
Use whatis to see if there is man help.
# whatis yum.conf yum.conf (5) - Configuration file for yum(8).
Use: man 5 yum.conf to get detailed help from the yum.conf configuration file.
Definition of warehouse point
[repository id]: id of the warehouse
Name = name of the warehouse
-
baseurl=url://path/to/repository /: where is the warehouse and there can be multiple addresses, which one should be selected? Select according to failovermethod.
baseurl=url://server1/path/to/repository/
url://server2/path/to/repository/
url://server3/path/to/repository/
- failovermethod={roundrobin|priority}. The default is round robin, which means randomly selecting a url
- gpgcheck={1|0}: 1. The default is 1..
- enabled={1|0}: use this repo or not
- gpgkey=URL: public key
- enablegroups={1|0}: 1 uses the group function. The default is 1..
- const = the default value is 1000. If there are multiple matches, select cost.
There are several repo configuration files under / etc/yum.repos.d/ under centos7. Only the enabled repo in CentOS-Base.repo file is 1, that is, it can be used. The enabled repo in other configuration files is 0
# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/ CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-Base.repo_20191129 CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
View the contents of the configuration file: / etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.
[base] name=CentOS-$releasever - Base baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #released updates [updates] name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that may be useful [extras] name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages [centosplus] name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
Tips for specifying base URL: refers to the URL of the web page where repodata is located.
The value of the baseurl of the above updates is the URL of the address bar of the following page. The reason is that repodata is here.
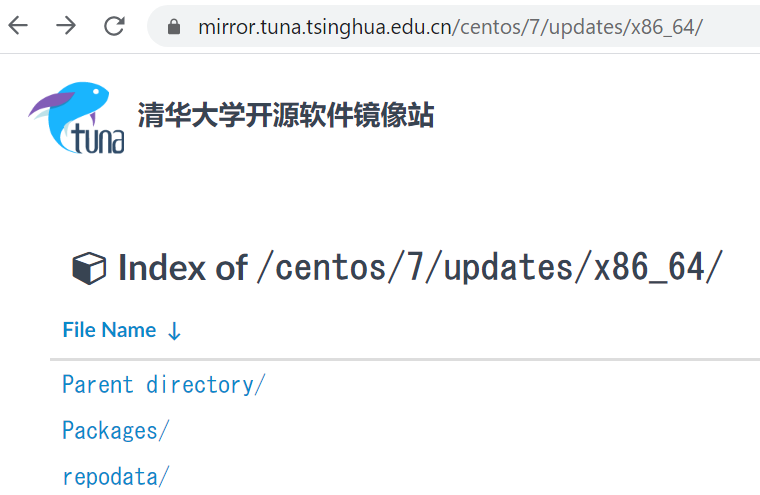
View repo list:
# yum repolist Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile repo id repo name status !base/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Base 10,097 !extras/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Extras 323 !updates/7/x86_64 CentOS-7 - Updates 1,446 repolist: 11,866
repo id:
repo name: is the value of name in the configuration file / etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
status: the number of rmp packets in this repo.
Introduction to yum command
yum [options][command] [package ...]
-
Display the repo list: repolist [all|enabled|disabled]
- All: show all
- Enabled: displays the available. Default value. That is, the repo with enabled=1 in the local repo configuration file will be displayed.
- disabled: displays unavailable. That is, the repo with enabled=0 in the local repo configuration file will be displayed.
# yum repolist all # yum repolist enabled # yum repolist disabled
-
Display which rpm packages are in the specified repo: yum list [all | glob_exp1] [glob_exp2] [etc.]
Show all packages:
# yum list
Glob? Exp can be used.
The third column of the display content: repoid in the repo configuration file
# yum list php* Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Available Packages php.x86_64 5.4.16-46.1.el7_7 updates php-bcmath.x86_64 5.4.16-46.1.el7_7 updates php-pear.noarch 1:1.9.4-21.el7 base php-pecl-memcache.x86_64 3.0.8-4.el7 base
Show packages not installed in repo: yum list available [glob_exp1] [...]
# yum list available
Show upgradeable packages in repo: yum list updates [glob_exp1] [...]
# yum list updates
Show installed packages: yum list installed [glob_exp1] [...]
- @anaconda: package installed when installing the system.
- Installed: later installed by myself.
# yum list installed zlib.x86_64 1.2.7-18.el7 @anaconda zsh.x86_64 5.0.2-33.el7 installed
Show packages in extra repo that have been installed: yum list extras [glob_exp1] [...]
# yum list extras
Display the installed packages, which are obsolete: Yum list distro extras [glob_exp1] [...]
# yum list distro-extras
-
Installation package: yum install package1 [package2
If there are multiple versions in repo, you can specify the version, for example, yum install gcc-4.8.5
You can also install the latest version without specifying the version: yum install gcc
-
Upgrade package: yum update [package1][package2] [...]
# yum update gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile No packages marked for update
-
Downgrade: downgrade package1 [package2] [...]
Similar: rpm -Uvh --oldpackage
-
Reinstall: reinstall package1 [package2] [...]
Similar: rpm -ivh --replacepkgs
Check which packages can be upgraded: Yum check update
-
Uninstall package: yum remove | erase package1 [package2] [...]
When the uninstalled package is dependent on other packages, other packages are also uninstalled
Uninstall cpp: since gcc depends on cpp, if you uninstall cpp, gcc will also be uninstalled.
-
View package information: yum info [glob_exp1] [...]
Similar to rpm -qi
# yum info gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Installed Packages Name : gcc Arch : x86_64 Version : 4.8.5 Release : 39.el7 Size : 37 M Repo : installed From repo : base Summary : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) URL : http://gcc.gnu.org License : GPLv3+ and GPLv3+ with exceptions and GPLv2+ with exceptions and LGPLv2+ and BSD Description : The gcc package contains the GNU Compiler Collection version 4.8. : You'll need this package in order to compile C code -
Check which package is provided by the program or file: yum provides | whatprovides feature1 [feature2]
Similar to rpm -qf file
# yum provides /usr/bin/gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile gcc-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) Repo : base Matched from: Filename : /usr/bin/gcc gcc-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 : Various compilers (C, C++, Objective-C, Java, ...) Repo : @base Matched from: Filename : /usr/bin/gcc
-
Clean [packages | metadata | expire cache | rpmdb | plugins | all]
When yum presses a file, it will cache the package and metadata file locally. When the installation is finished, yum will delete the package file, but not the metadata file.
Build cache: yum makecache [fast]
-
Search information with keywords: yum search string1 [string2] [...]
Searches the package name and the summary of the package for the specified keywords.
# yum search bash Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile ====================================================== N/S matched: bash ======================================================= bash-completion.noarch : Programmable completion for Bash bash-doc.x86_64 : Documentation files for bash libguestfs-bash-completion.noarch : Bash tab-completion scripts for libguestfs tools libvirt-bash-completion.x86_64 : Bash completion script pcp-pmda-bash.x86_64 : Performance Co-Pilot (PCP) metrics for the Bash shell bash.x86_64 : The GNU Bourne Again shell Name and summary matches only, use "search all" for everything.
-
Show the packages a package depends on: deplist package1 [package2] [...]
# yum deplist gcc Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile package: gcc.x86_64 4.8.5-39.el7 dependency: /bin/sh provider: bash.x86_64 4.2.46-33.el7 dependency: /sbin/install-info provider: info.x86_64 5.1-5.el7 ...
-
View the history of installation, update, and uninstall of yum: yum history without parameters is history list
history [info|list|packages-list|packages-info|summary|addon-info|redo|undo|rollback|new|sync|stats]
# yum history Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks ID | Login user | Date and time | Action(s) | Altered ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 | root <root> | 2020-02-15 23:00 | Install | 2 4 | root <root> | 2020-02-15 22:59 | Erase | 8 3 | root <root> | 2020-02-15 22:48 | Update | 11 < 2 | ys <ys> | 2019-11-29 17:38 | Install | 8 > 1 | System <unset> | 2019-11-29 16:44 | Install | 1458 history listThe above is the summary information. If you want to see the details of id 5, that is, which packages have been installed with id 5, then use:
# yum history info 5 Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Transaction ID : 5 Begin time : Sat Feb 15 23:00:14 2020 Begin rpmdb : 1459:fe9d7def2a5edd098cfe39ebe0732b67038170b5 End time : 23:00:19 2020 (5 seconds) End rpmdb : 1461:ed3657ce694e0e90ea8bf62a092f06422c81ac28 User : root <root> Return-Code : Success Command Line : install gcc Transaction performed with: Installed rpm-4.11.3-35.el7.x86_64 @anaconda Installed yum-3.4.3-161.el7.centos.noarch @anaconda Installed yum-plugin-fastestmirror-1.1.31-50.el7.noarch @anaconda Packages Altered: Dep-Install cpp-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 @base Install gcc-4.8.5-39.el7.x86_64 @base history infoTo view the yumdb size:
# yum history stats Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks File : //var/lib/yum/history/history-2020-02-16.sqlite Size : 23,552 Transactions: 0 history stats
-
Local installation / upgrade: the package you want to install is not available in yum repo. You can download an rpm package to install it. But why not use rpm? rpm can't solve the dependency, but Yum can. So even the local rpm package can be installed using yum, but the parameter is the rpm filename.
localinstall/localupdate is to be compatible with previous versions. You should use the intall/update parameter as the rpm filename.
- localinstall rpmfile1 [rpmfile2][...]
(maintained for legacy reasons only - use install)
- localupdate rpmfile1 [rpmfile2][...]
(maintained for legacy reasons only - use update)
-
Group install / update / uninstall / view
-
See which groups are available for installation:
# yum groups list Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Available Environment Groups: Minimal Install Compute Node Infrastructure Server File and Print Server Basic Web Server Virtualization Host Server with GUI GNOME Desktop KDE Plasma Workspaces Development and Creative Workstation Installed Groups: Development Tools Available Groups: Compatibility Libraries Console Internet Tools Graphical Administration Tools Legacy UNIX Compatibility Scientific Support Security Tools Smart Card Support System Administration Tools System Management Done
-
To see which packages are in a group:
# yum groups info Development\ Tools Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Group: Development Tools Group-Id: development Description: A basic development environment. Mandatory Packages: gcc =gcc-c++ gettext =libtool make Default Packages: byacc =gcc-gfortran swig =systemtap Optional Packages: ElectricFence ant babel bzrMandatory Packages: packages that must be installed
Default Packages: packages installed by default
Optional Packages: Optional Packages
-
Installation:
# yum groups install "Development Tools"
-
To update:
# yum groups update "Development Tools" Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile Maybe run: yum groups mark install (see man yum) No packages in any requested group available to install or updates
-
Delete:
# yum groups remove Development\ Tools
-
Take the CD as a repo
1. Mount the centos system installation disk to the / media directory.
2. Create the local.repo file
[base] name=local repo centos baseurl=file:///media/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=0
3. Then you can use the yum command normally.
QQ group of mutual learning in c/c + +: 877684253
