Catalog
view resolver
View Parser: Add the page path section to the configuration file
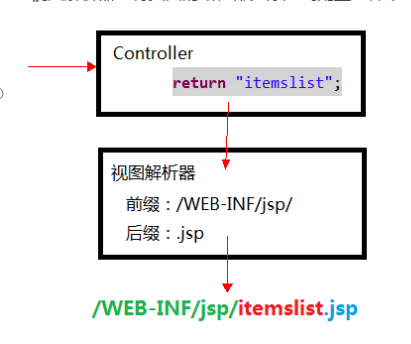
No View Parser
return "/WEB-INF/show01.jsp";
With View Parser
return "show01.jsp";
Configure View Resolver in Spring MVC Set prefix and suffix Put View Resolver in Spring container
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver(){
//Create View Parser
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
//Set prefix
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/");
//Set Suffix
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
Exception Handler
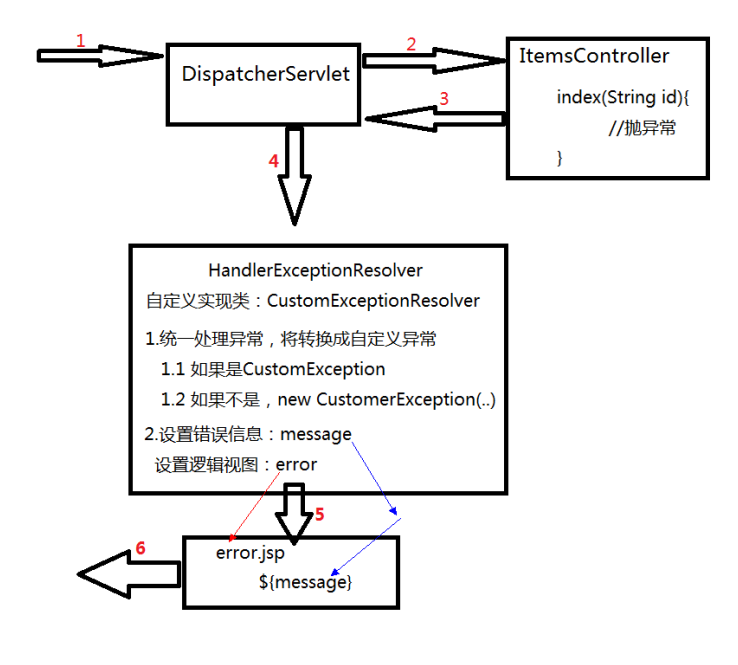
A global exception handler is provided in SpringMVC to unify the handling of exceptions in the system. Exceptions in Dao Service Controller are throws up in the general system. Finally, the global exception handling is unified by the front-end controller of SpringMVC.
Typically, you customize an exception and then parse it to determine which exception it belongs to and handle it if it is not a custom exception.
Error System Error Contact Administrator Exception
Step 1 Customize Exceptions
public class CustomException extends Exception{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8222256702797084775L;
public CustomException() {
}
public CustomException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public CustomException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public CustomException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public CustomException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}The second step defines the exception handler
Exception handler needs to implement HandlerExceptionResolver interface override method resolverException
@Component
public class CustomExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception ex) {
CustomException customException = null;
if(ex instanceof CustomException){
customException = (CustomException)ex;
}else{
customException = new CustomException("System error, please contact your administrator");
}
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("message",customException.getMessage());
modelAndView.setViewName("error");
return modelAndView;
}
}Step 3 Define the exception display interface
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
The following errors occurred in your operation: <br>
${message}
</body>
</html>Step 4 Test Procedure
@RequestMapping("index")
public String index(String id) throws CustomException {
if(id == null){
throw new CustomException("No, id parameter");
}
return "itemlist";
<a href = "${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/index.aticon">Exception Demo</a>Exception Processor Analysis
Interceptor
Summary
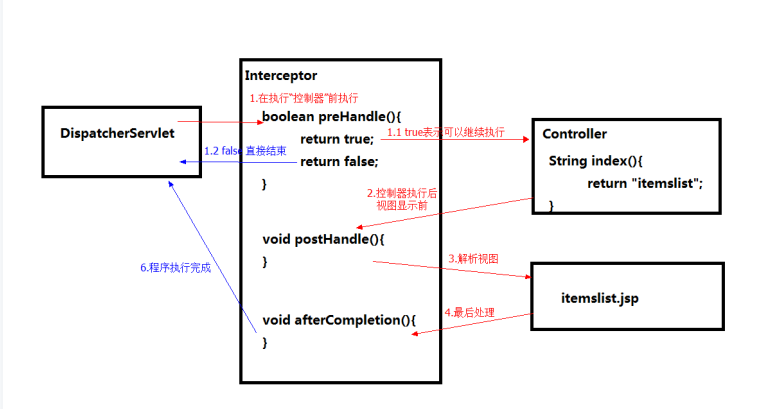
Interceptors in SpringMVC act like filters in Servlet s. Filter s are used to process the order of processors before and after
Interceptors need to implement interfaces: HandlerInterceptor
Analysis
Method
boolean preHandle(): Returns a boolean value Returns true Continue execution Returns false Direct End
void postHandle(): Executes before the view is displayed after the processor method has been executed
void afterCompletion(): executes after view resolution succeeds
Interceptor
The first step is to define an interceptor to implement the HandlerInterceptor interface
@Component
public class MyInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor1 Interceptor's preHandle");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor1 Interceptor's postHandle");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("MyInterceptor1 Interceptor's afterCompletion");
}
}Step 2 Configure Class Register Interceptor Set Interception Path
@Autowired
private MyInterceptor1 myInterceptor1;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
InterceptorRegistration interceptorRegistration = registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor1);
interceptorRegistration.addPathPatterns("/**");
}Multiple Interceptor Configuration
Analysis
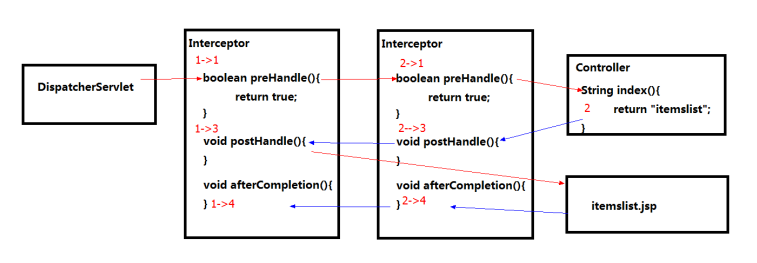
Configuration Class Registration Interceptor
@Autowired
private MyInterceptor1 myInterceptor1;
@Autowired
private MyInterceptor2 myInterceptor2;
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
InterceptorRegistration interceptorRegistration = registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor1);
interceptorRegistration.addPathPatterns("/**");
InterceptorRegistration interceptorRegistration2 = registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor2);
interceptorRegistration2.addPathPatterns("/**");
}Use scenarios
1. User Name Permission Check
2. Resolve garbles
3. Logging
File Upload
The first step defines the upload page
<form id="itemForm" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/user/upload.action" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
Full name:<input type="text" name="name"/> <br/>
Price:<input type="text" name="price"/> <br/>
Picture:<input type="file" name="picFile"/> <br/>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>Step 2 Controller
public String upload(String name, Double price, @RequestParam(required = false,value = "picFile") MultipartFile picFile) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Full name:" + name);
System.out.println("Price:" + price);
String originalFilename = picFile.getOriginalFilename();
System.out.println("Upload File Name:" + originalFilename);
File file = new File("F:\\Temp", originalFilename);
picFile.transferTo(file);
return "itemslist";
}Step 3 Configuration Profile Upload Parser
@Bean
public CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver(){
CommonsMultipartResolver multipartResolver = new CommonsMultipartResolver();
// Set the total size of all uploaded files to 10M
multipartResolver.setMaxInMemorySize(10*1024*1024);
// Set the size of a single file upload to 4M
multipartResolver.setMaxUploadSize(4*1024*1024);
multipartResolver.setDefaultEncoding("utf-8");
return multipartResolver;
}Import jar package or coordinates
Complete the upload using commons-fileupload to determine the import of the fileupload jar package
coordinate
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.2.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.3</version> </dependency>
MultipartFile object
String getOriginalFilename(): Get the file name of the long pass
transferTo(File file): Upload the file to the specified file
String getContentType(): Get the file MIME type
String getName(): Get the name of the file component in the form
JSON data interaction
@ RequestBody: Convert json, xml to Java objects
@RequestMapping("tj.action")
public void run1(@RequestBody String jsonStr){
System.out.println(jsonStr);
}@ ResponseBodey: Convert Java objects to json, xml
@RequestMapping("tj.action")
public @ResponseBody QVo getInfo(String name,Double price){
System.out.println("Receive Front End Data:" + name + " " + price);
QVo qVo = new QVo("lisiguang", 220.4);
return qVo;
}RESTful support
Summary
RESTful is a style of resource positioning and operation that is neither standard nor protocol but style
Resource Location requires URL s with no verbs, nouns with no parameters
URL Format http://blog.csdn.net/beat_the_world/article/details/45621673
Resource operations determine different requests through HTTP requests
get query resource post create new resource (or modify resource) put update resource delete delete delete resource
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{xxx}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
{xxx} is equivalent to a placeholder used to match parameters in a URL to get a path-matching resource through @PathVariable("xxx")
@RequestMapping("/viewItems/{id}")
public String viewItems(@PathVariable("id")String id, Model model){
model.addAttribute("id",id);
return "itemslist";
}