Brief introduction
matplotlib library is one of the libraries in Python data mining, which is mainly used for 2D drawing, simple 3D drawing and data visualization.
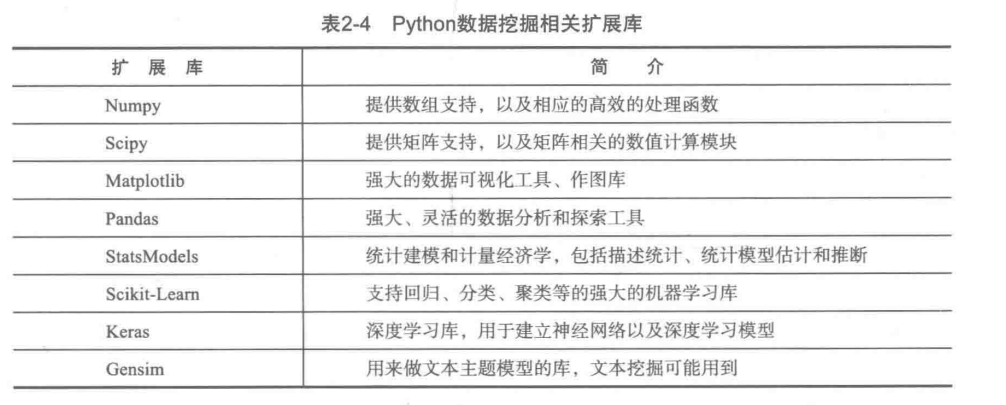
Python data mining related extension library
Simple use
(1) Draw a straight line
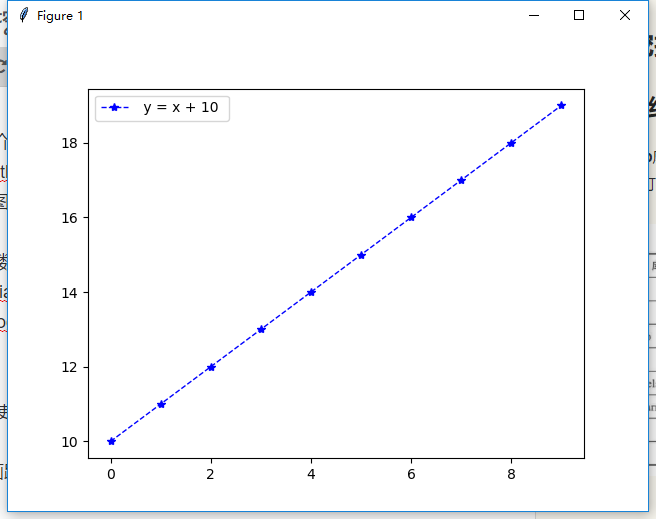
Line y=x+10
Code:
def print_line_draw(): """ //Draw straight lines :return: """ # Create a numpy array with a 1 interval between 0-10 x = np.arange(0, 10, 1) y = x + 10 # Drawing graphics plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', linestyle='--', marker='*', linewidth=1, label=' y = x + 10 ') # Save picture, dpi plt.savefig('first.png', dpi=50) # Show Legend plt.legend() # display graphics plt.show()
(2) Draw a pie chart
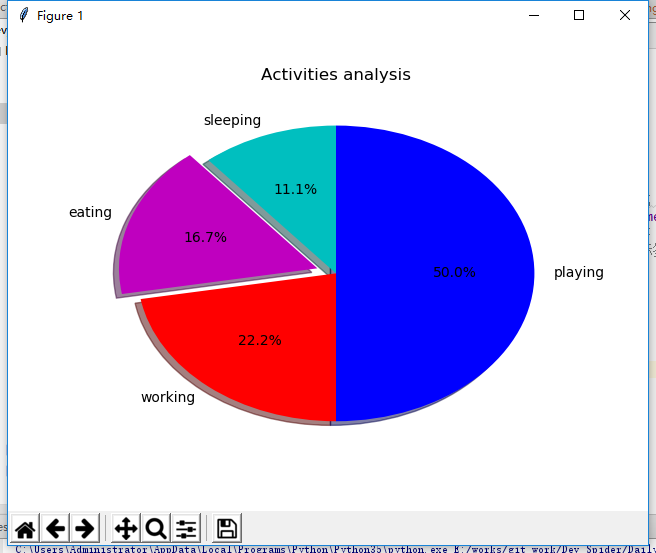
Pie chart
Code:
def print_pie_draw(): """ //Pie chart :return: """ # Specify the size (scale) of each slice slice = [2,3,4,9] # Specified tag activities =['sleeping','eating','working','playing'] # colour cols = ['c','m','r','b'] plt.pie(slice, labels=activities, colors=cols, startangle=90, #Start angle, default is 0 degrees, starting from the x-axis, 90 degrees starting from the y-axis shadow=True, explode=(0,0.1,0,0), # Pull out the second slice. If it's all 0, it doesn't pull out. The distance between the number here and the center of the circle autopct='%1.1f%%') # Show percentage plt.title('Activities analysis') # The first 0 of the parameter in expand represents the first slice, and the distance from the origin is 0 plt.show()
(3) Draw a scatter
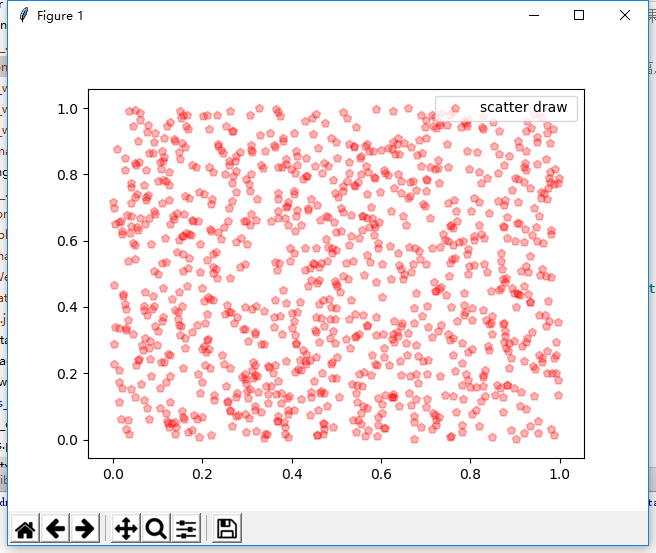
Scatter plot
Code:
def print_scatter_draw(): """ //Scatter plot :return: """ x = np.random.rand(1000) y = np.random.rand(len(x)) # Mapping plt.scatter(x,y,color='r',alpha=0.3,label='scatter draw ',marker='p') plt.legend() #plt.axis([0,2,0,2])# Set the range of coordinates plt.show()
(4) Draw a histogram
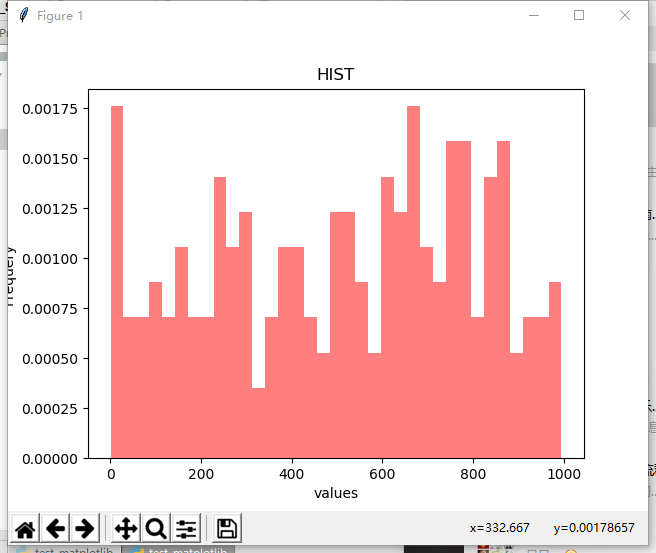
Ugly histogram
Code:
def print_hist_draw(): """ //Draw histogram :return: """ x = np.random.randint(1,1000,200) axit = plt.gca() # Get the current drawing object #The number of bins histogram, the style of histtype histogram normalized histogram, display probability density (default false) axit.hist(x,bins=35,facecolor='r',normed=True,histtype='bar',alpha=0.5) axit.set_xlabel('values') # Label x axit.set_ylabel('Frequery') # Label y axit.set_title('HIST') plt.show()
(5) Simple trigonometric function
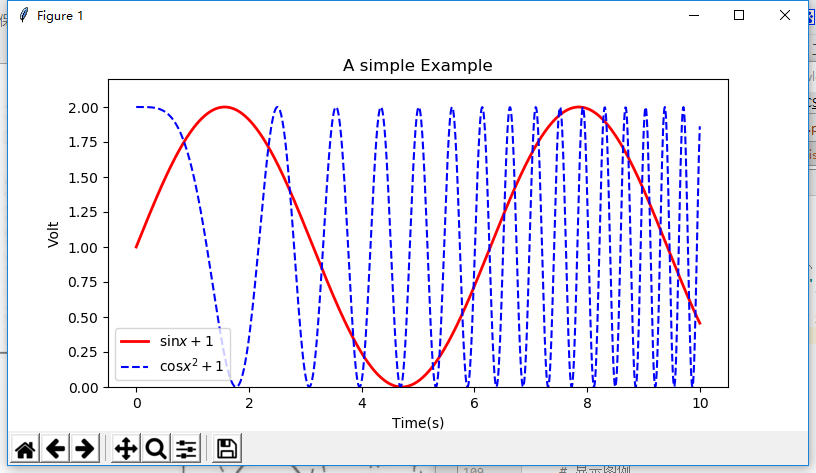
Trigonometric function diagram
Code:
def print_sinandcos_line(): x = np.linspace(0,10,1000) y = np.sin(x) +1 z = np.cos(x**2) +1 # Set image size plt.figure(figsize=(8,4)) # Drawing, setting label, line color, line size plt.plot(x,y,label='$\sin x +1$',color='red',linewidth=2) # Drawing, labeling, line type plt.plot(x,z,'b--',label='$\cos x^2+1$') # Set x-axis name plt.xlabel('Time(s)') # Set y-axis name plt.ylabel('Volt') # Set title plt.title('A simple Example') # Displayed y-axis range plt.ylim(0,2.2) # Show Legend plt.legend() # Display drawing results plt.show()
The above is a simple use of today's matplotlib function
All code
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/3/26 15:09 # @Author: snake cub # @Email : 643435675@QQ.com # @File : test_matplotlib.py import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np def print_line_draw(): """ //Draw straight lines :return: """ # Create a numpy array with a 1 interval between 0-10 x = np.arange(0, 10, 1) y = x + 10 # Drawing graphics plt.plot(x, y, color='blue', linestyle='--', marker='*', linewidth=1, label=' y = x + 10 ') # Save picture, dpi plt.savefig('first.png', dpi=50) # Show Legend plt.legend() # display graphics plt.show() def print_pie_draw(): """ //Pie chart :return: """ # Specify the size (scale) of each slice slice = [2,3,4,9] # Specified tag activities =['sleeping','eating','working','playing'] # colour cols = ['c','m','r','b'] plt.pie(slice, labels=activities, colors=cols, startangle=90, #Start angle, default is 0 degrees, starting from the x-axis, 90 degrees starting from the y-axis shadow=True, explode=(0,0.1,0,0), # Pull out the second slice. If it's all 0, it doesn't pull out. The distance between the number here and the center of the circle autopct='%1.1f%%') # Show percentage plt.title('Activities analysis') # The first 0 of the parameter in expand represents the first slice, and the distance from the origin is 0 plt.show() def print_scatter_draw(): """ //Scatter plot :return: """ x = np.random.rand(1000) y = np.random.rand(len(x)) # Mapping plt.scatter(x,y,color='r',alpha=0.3,label='scatter draw ',marker='p') plt.legend() #plt.axis([0,2,0,2])# Set the range of coordinates plt.show() pass def print_hist_draw(): """ //Draw histogram :return: """ x = np.random.randint(1,1000,200) axit = plt.gca() # Get the current drawing object #The number of bins histogram, the style of histtype histogram normalized histogram, display probability density (default false) axit.hist(x,bins=35,facecolor='r',normed=True,histtype='bar',alpha=0.5) axit.set_xlabel('values') # Label x axit.set_ylabel('Frequery') # Label y axit.set_title('HIST') plt.show() pass def print_sinandcos_line(): x = np.linspace(0,10,1000) y = np.sin(x) +1 z = np.cos(x**2) +1 # Set image size plt.figure(figsize=(8,4)) # Drawing, setting label, line color, line size plt.plot(x,y,label='$\sin x +1$',color='red',linewidth=2) # Drawing, labeling, line type plt.plot(x,z,'b--',label='$\cos x^2+1$') # Set x-axis name plt.xlabel('Time(s)') # Set y-axis name plt.ylabel('Volt') # Set title plt.title('A simple Example') # Displayed y-axis range plt.ylim(0,2.2) # Show Legend plt.legend() # Display drawing results plt.show() pass if __name__ == '__main__': # print_line_draw() # print_pie_draw() # print_scatter_draw() # print_hist_draw() print_sinandcos_line()