Introduction to reflection
1, Introduction & overview
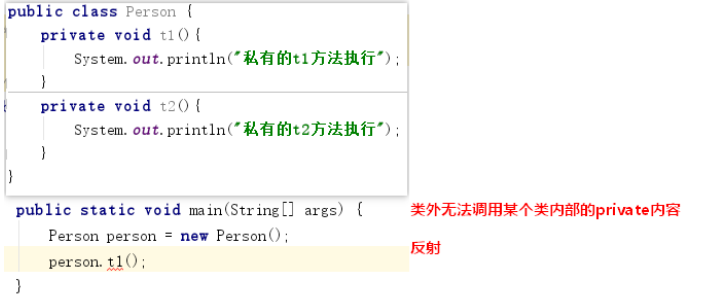
In order to have more flexible access to all the contents of the class (including private), we need reflection technology
Reflection: the act or characteristic of mapping a complete thing (the super power of any content in a single operation class)
Get member methods / member variables of a class
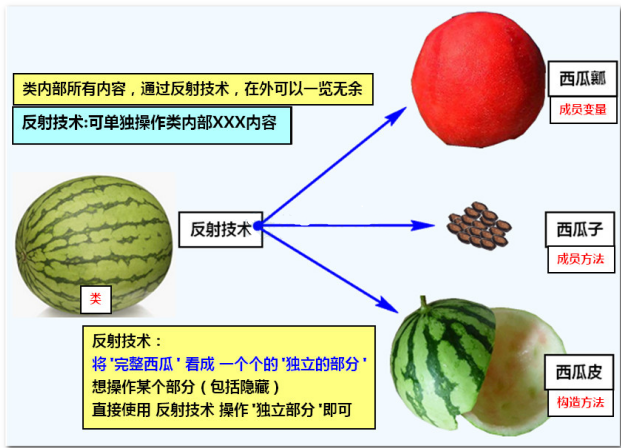
Flexible use of Java classes
2, Entry case 1: enforce private method
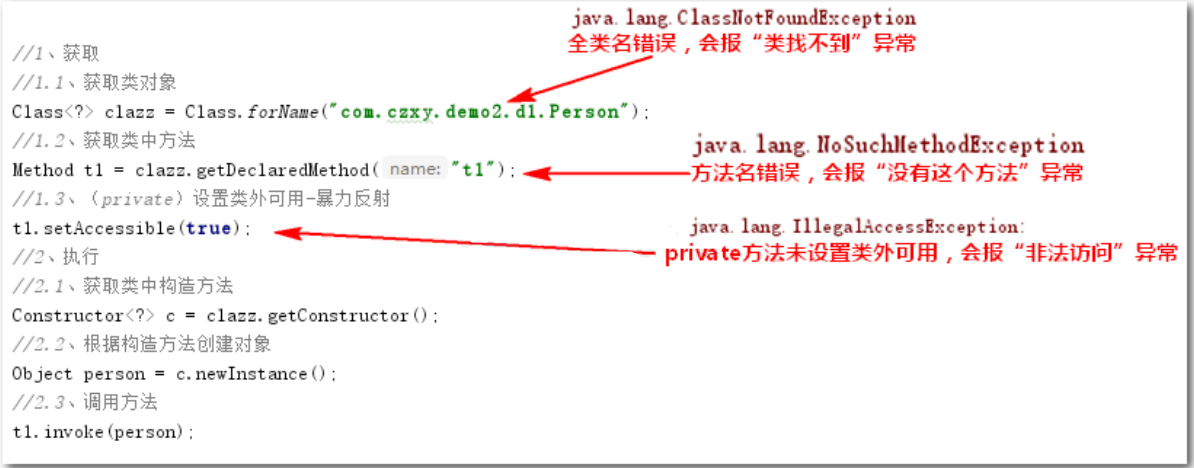
Code implementation: /* * Requirement: in the test class, call t1 method of Person class * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object (equivalent to getting the whole watermelon) Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Person"); //1.2. Obtaining method through class object (equivalent to extracting watermelon pulp from watermelon through super ability) Method t1 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("t1"); //1.3. Set available out of class t1.setAccessible(true); //2. Execution (equivalent to eating watermelon pulp) //2.1. Obtain the construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2. Create an object through the construction method (equivalent to Person person = new Person();) Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call method (equivalent to person.t1()) t1.invoke(person); }
matters needing attention:
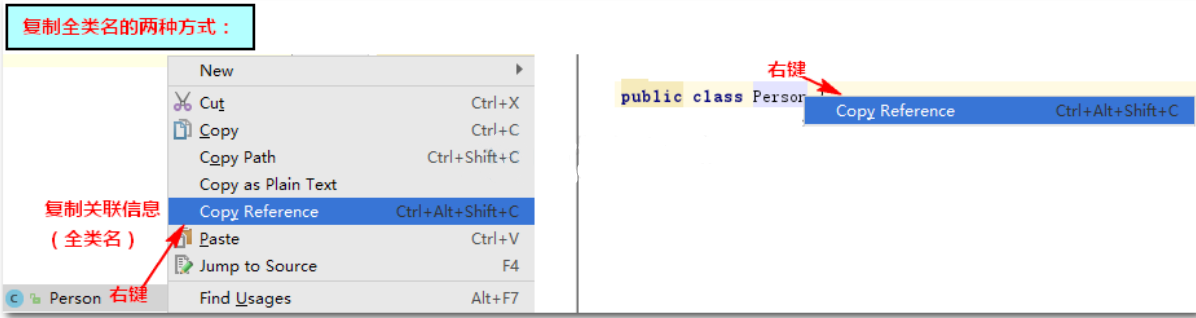
Skill: get full class name
Summary:
Reflection: get all member methods / member variables in a classReflection steps:1. Get1.1. Get class object (get all contents of this class)1.2. Obtain method through class object1.3. Set external availability (violent reflection, private)2, implementation2.1. Obtain the construction method through class object2.2. Create an object through the construction method (2.1 and 2.2 are equivalent to Person p = new Person())2.3 call method (equivalent to p. method ()) |
|---|
3, Entry case 2: enforce private method with parameters
Code implementation: /* * Requirement: in the test class, call t3 method of Person class with parameters * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Person"); //1.2. Get method through class object (method name: t3 parameter list: String int) Method t3 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("t3",String.class,int.class); //1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex) t3.setAccessible(true); //2. Execution (equivalent to eating watermelon pulp) //2.1. Obtain the construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2. Create an object through the construction method (equivalent to Person person = new Person();) Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call method (equivalent to person.t3("wisdom transfer", 1024)) t3.invoke(person,"Wisdom transmission",1024); }
matters needing attention:
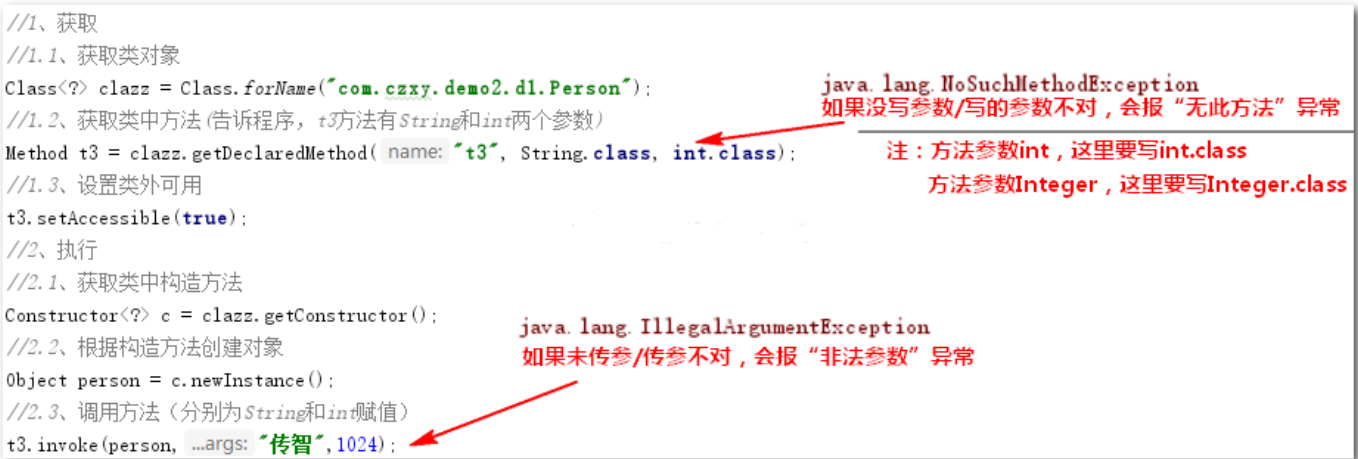
Summary: reflection with parameter method, acquisition method with parameter, execution method with parameter
4, Entry case 3: enforce private method with return value
Code implementation: /* * Requirement: in the test class, call t4 method of Person class with return value * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //1. Get //1.1. Get class object Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.czxy.demo1.Person"); //1.2. Obtain method through class object Method t3 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("t4"); //1.3. Setting out of class availability (violent reflex) t3.setAccessible(true); //2. Execution (equivalent to eating watermelon pulp) //2.1. Obtain the construction method through class object Constructor<?> c = clazz.getConstructor(); //2.2. Create an object through the construction method (equivalent to Person person = new Person();) Object person = c.newInstance(); //2.3. Call method (equivalent to String str = person.t4();) Object obj = t3.invoke(person); //Strong turn String str = (String) obj; System.out.println(str); }
Summary:
When the reflection band return value method is used, it will return the Object type after strong conversion
V. introduction summary
Reflection: get any member method / member variable in a class specifically.Format:Reflection performs private method steps: (even if 2.1 and 2.2 follow 1.1, it is also a way to write)1. Access1.1. Get class object1.2. Get methods in the class1.3. (private) set out of class availability violent reflection2. Implementation2.1. Get the construction method in the class2.2. Create objects according to the construction method2.3 calling method |
|---|
Please give yourself a compliment!
Make a little progress every day`~~~~~