1, JSON server
- Official website document address
JSON server document
- Install JSON server
npm install -g json-server
- Create a database JSON file under the target root directory: db.json
{
"posts": [
{ "id": 1, "title": "json-server", "author": "typicode" }
],
"comments": [
{ "id": 1, "body": "some comment", "postId": 1 }
],
"profile": { "name": "typicode" }
}
- Start JSON server
Enter the following command in the current folder: JSON server db.json
2, Understanding and use of axios
1. What is Axios?
- The most popular ajax request library on the front end
- react/vue officials recommend using axios to send ajax requests
- file: https://github.com/axios/axios
2.axios features
- Asynchronous ajax request Library Based on xhr + promise
- Both browser side and node side can be used
- Support request / response interceptors
- Support request cancelled
- Request / response data conversion
- Batch send multiple requests
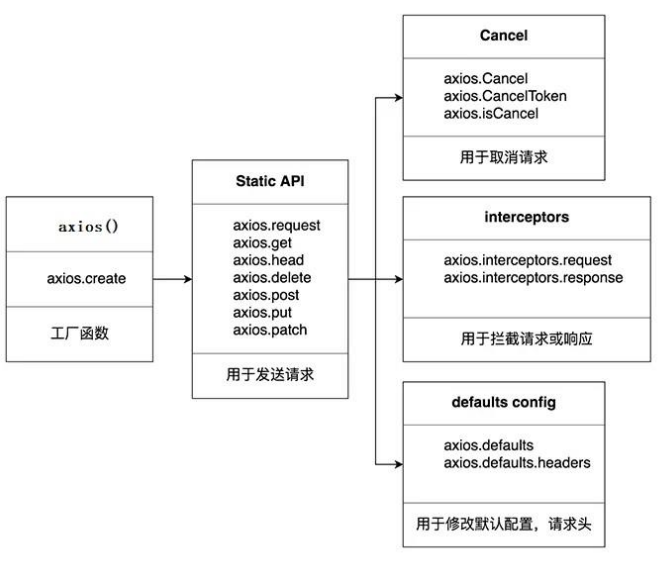
3. axios common syntax
- axios(config): a general / essential way to send any type of request
- axios(url[, config]): you can only specify the url to send a get request
- axios.request(config): equivalent to axios(config)
- axios.get(url[, config]): send get request
- axios.delete(url[, config]): Send a delete request
- axios.post(url[, data, config]): Send a post request
- axios.put(url[, data, config]): Send a put request
- axios.defaults.xxx: requested default global configuration
- axios.interceptors.request.use(): add request interceptor
- axios.interceptors.response.use(): add a response interceptor
- axios.create([config]): create a new Axios (it does not have the following functions)
- axios.Cancel(): error object used to create cancel request
- axios.CancelToken(): a token object used to create cancellation requests
- axios.isCancel(): is it an error to cancel the request
- axios.all(promises): used for batch execution of multiple asynchronous requests
- axios.spread(): used to specify the method of callback function to receive all successful data
4. Use of Axios - default configuration
1. Basic use
// Introduce bootstrap style
<link
crossorigin="anonymous"
href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/twitter-bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet"
/>
<div class="container">
<h2 class="page-header">Basic use</h2>
<button class="btn btn-primary">send out GET request</button>
<button class="btn btn-warning">send out POST request</button>
<button class="btn btn-success">send out PUT request</button>
<button class="btn btn-danger">send out DELETE request</button>
</div>
// Introducing axios
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/axios/0.21.1/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
//Get button
const btns = document.querySelectorAll('button')
//first
btns[0].onclick = function () {
//Send AJAX request
axios({
//Request type
method: 'GET',
//URL
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts/2'
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
//Add a new article
btns[1].onclick = function () {
//Send AJAX request
axios({
//Request type
method: 'POST',
//URL
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts',
//Set request body
data: {
title: 'it's a nice day today, It's quite sunny',
author: 'Zhang San'
}
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
//Update data
btns[2].onclick = function () {
//Send AJAX request
axios({
//Request type
method: 'PUT',
//URL
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts/3',
//Set request body
data: {
title: 'it's a nice day today, It's quite sunny',
author: 'Li Si'
}
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
//Delete data
btns[3].onclick = function () {
//Send AJAX request
axios({
//Request type
method: 'delete',
//URL
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts/3'
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
}
</script>
2. Default configuration
//Default configuration
axios.defaults.method = 'GET';//Set the default request type to GET
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://localhost:3000';// Set base URL
axios.defaults.params = {id:100};
axios.defaults.timeout = 3000;//
btns[0].onclick = function(){
axios({
url: '/posts'
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
})
}
5. Schematic diagram
6. Understanding and use of difficult grammar
1,axios.create(config)
-
Create a new axios according to the specified configuration, that is, each new axios has its own configuration
-
The new axios just doesn't have the method of canceling requests and sending requests in batches. All other syntax is the same
-
Why design this grammar?
(1) Requirements: the configuration required by some interfaces in the project is different from that required by other interfaces. How to deal with it
(2) Solution: create two new axios, each with its own unique configuration, which are applied to interface requests with different requirements
//Create instance object / getJoke
const duanzi = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://api.apiopen.top',
timeout: 2000
});
const onather = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://b.com',
timeout: 2000
});
//Here, the functions of duanzi and axios objects are almost the same
// duanzi({
// url: '/getJoke',
// }).then(response => {
// console.log(response);
// });
duanzi.get('/getJoke').then(response => {
console.log(response.data)
})
2. Interceptor function / ajax request / call order of callback function of request
- Note: calling axios() does not send ajax requests immediately, but requires a long process
- Process: request interceptor 2 = > request interceptor 1 = > send ajax request = > response interceptor 1 = > response interceptor 2 = > callback of request
- Note: this process is connected in series through promise. The request interceptor passes config and the response interceptor passes response
<script>
// Promise
// Set request interceptor config configuration object
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
console.log('Request interceptor succeeded - 1 number');
//Modify parameters in config
config.params = {
a: 100
};
return config;
}, function (error) {
console.log('Request interceptor failed - 1 number');
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.request.use(function (config) {
console.log('Request interceptor succeeded - 2 number');
//Modify parameters in config
config.timeout = 2000;
return config;
}, function (error) {
console.log('Request interceptor failed - 2 number');
return Promise.reject(error);
});
// Set response interceptor
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('Response interceptor success No. 1');
return response.data;
// return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('Response interceptor failed No. 1')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
axios.interceptors.response.use(function (response) {
console.log('Response interceptor success No. 2')
return response;
}, function (error) {
console.log('Response interceptor failed No. 2')
return Promise.reject(error);
});
//Send request
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts'
}).then(response => {
console.log('Results of successful processing of custom callback');
console.log(response);
});
</script>
3. Cancel request
- Basic process configuration cancelToken object
- Cache the cancel function used to cancel the request
- Call the cancel function at a later specific time to cancel the request
- Judge in the error callback that if the error is cancel, handle it accordingly
- To realize the function, click the button to cancel a request in progress,
<script>
//Get button
const btns = document.querySelectorAll('button');
//2. Declare global variables
let cancel = null;
//Send request
btns[0].onclick = function () {
//Check whether the last request has been completed
if (cancel !== null) {
//Cancel last request
cancel();
}
axios({
method: 'GET',
url: 'http://localhost:3000/posts',
//1. Add the properties of the configuration object
cancelToken: new axios.CancelToken(function (c) {
//3. Assign the value of c to cancel
cancel = c;
})
}).then(response => {
console.log(response);
//Initialize the value of cancel
cancel = null;
})
}
//Bind second event cancel request
btns[1].onclick = function () {cancel(); }
</script>
3, axios source code and analysis
1. Difficult problems of Axios
1. Directory structure
/ dist / # project output directory
/ lib / # project source directory
│ ♪ - / adapters / # define the requested adapter xhr, http
│ │♪ -- http.js # implements HTTP adapter (wrapping HTTP package)
│ │ └ - xhr.js # implement XHR adapter (wrap XHR object)
│ ♪ - / cancel / # define cancel function
│♪ - / core / # some core functions
│ │♪ - core main class of Axios.js # axios
│ │♪ -- dispatchRequest.js # is a function used to call the http request adapter method to send a request
│ │♪ - manager of InterceptorManager.js # interceptor
│ │ └ -- set.js # changes Promise status according to http response status
│♪ - / helpers / # some auxiliary methods
│♪ - axios.js # external exposure interface
│♪ - default configuration of defaults.js # axios
│ └ - utils.js # utility
package.json # project information
index.d.ts # configures the declaration file of TypeScript
└ - index.js # entry file
2. Relationship between Axios and Axios
- Syntactically, Axios is not an instance of Axios
- Functionally, Axios is an instance of Axios
- axios is the function returned by the Axios.prototype.request function bind()
- As an object, Axios has all methods on the Axios prototype object and all properties on the Axios object
3. What is the difference between instance and axios?
- Same:
(1) Is a function that can send any request: request(config)
(2) There are various methods for making specific requests: get()/post()/put()/delete()
(3) Both have default configuration and interceptor properties: defaults/interceptors - Different:
(1) The default configuration is likely to be different
(2) instance does not have some methods added after axios: create()/CancelToken()/all()
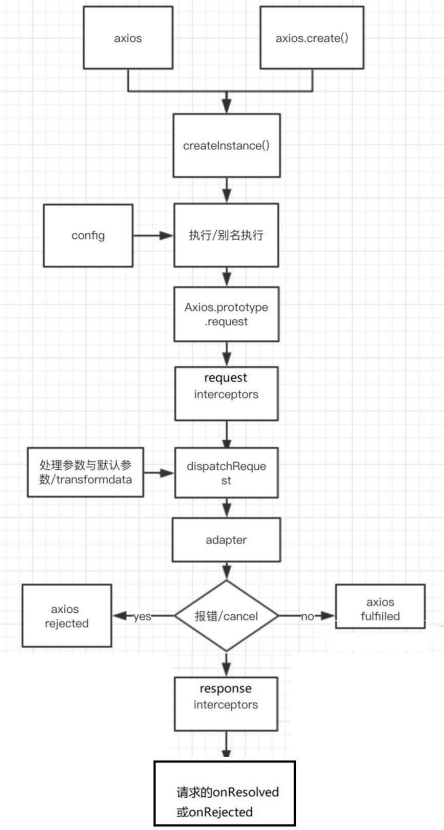
4. Overall process of Axios operation
-
Overall process:
request(config) ===> dispatchRequest(config) ===> xhrAdapter(config) -
request(config):
Connect the request interceptors / dispatchRequest() / response interceptors in series through the promise chain,
Return promise -
dispatchRequest(config):
Conversion request data = = = > the number of conversion responses after calling xhrAdapter() to send a request = = = > the request returns
Return promise according to -
xhrAdapter(config):
Create an XHR object, make corresponding settings according to config, send specific requests, and receive response data,
Return promise -
flow chart: