Introduction to MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL database, which is essentially different from relational databases such as MySQL in the form of data storage. The basic object stored in MongoDB is Document, so we call it a document database, and the collection of documents forms a Collection. In analogy to the concept of SQL, Collection corresponds to Table and Document corresponds to Row. Document uses a BSON (Binary JSON) structure to express it. JSON is familiar to everyone, as follows.
MongoDB application scenario
Game scenarios, using MongoDB to store game user information, user equipment, integrals, etc. are stored directly in the form of embedded documents for easy query and update.
Logistics scenario, using MongoDB to store order information, order status will be constantly updated during delivery, stored in the form of MongoDB embedded array, one query will be able to read out all changes to the order.
Social scenarios, using MongoDB to store user information and user's published circle of friends information, through geographic location index to achieve nearby people, places and other functions
In the Internet of Things scenario, MongoDB is used to store all accessed smart device information, as well as the log information reported by the device, and multi-dimensional analysis of these information is carried out.
Video live broadcasting, using MongoDB to store user information, gift information, etc.
MongoDB installation
MongoDB installation method is relatively simple, because the source installation is more troublesome, our intention is only to learn MongoDB and yum type of fool installation is more convenient to learn now, this paper uses yum installation method.
Tools:
VMware version number: 12.0.0
CentOS version: 7.0
Note: Version 3.4 MongoDB no longer provides commercial support for 32-bit platforms (Linux and Windows). This article installs version 3.4.
View your own Linux version:
uname –a
x86_64 represents 64-bit machines
i686 represents 32-bit machines
The entire MongoDB (Community Edition) contains the following software
# Contains the mongod daemon and associated configuration and init scripts mongodb-org-server # Contains the mongos daemon mongodb-org-mongos # Includes a mongo shell, which is a command-line client connected to mongodb, allowing users to enter nosql grammar management database directly mongodb-org-shell # MongoDB contains the following tools: data import, export, backup, recovery, etc. mongodb-org-tools
Create yum source files
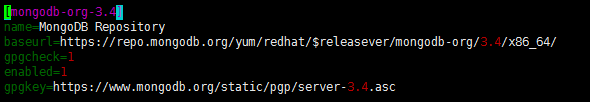
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.4.repo
Copy the following to the source file
[mongodb-org-3.4] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.4/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-3.4.asc
Start the yum command to start installation
yum install -y mongodb-org
If you use SELinux, you must configure SELinux to allow MongoDB to be started on a Red Hat Linux-based system (Red Hat Enterprise Linux or CentOS Linux)
vim /etc/selinux/config
Set the SELINUX value to disabled
Start Mongodb (default connection port for Mongodb server is 27017)
# Centos6 startup $ service mongod start # Centos7 Startup $ systemctl start mongod
Check whether to start
netstat -tlnup|grep mongod
Check to see if the port number 27017 is occupied
netstat -tlnup|grep 27017
Other Control Commands
# Stop Mongodb Service $ service mongod stop # Restart Mongodb $ service mongod restart
Set up boot start
chkconfig mongod on
Find the MongoDB client
find / -name mongo
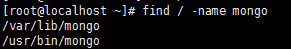
Connect client
/usr/bin/mongo
Enter the test command show dbs to see what the current database has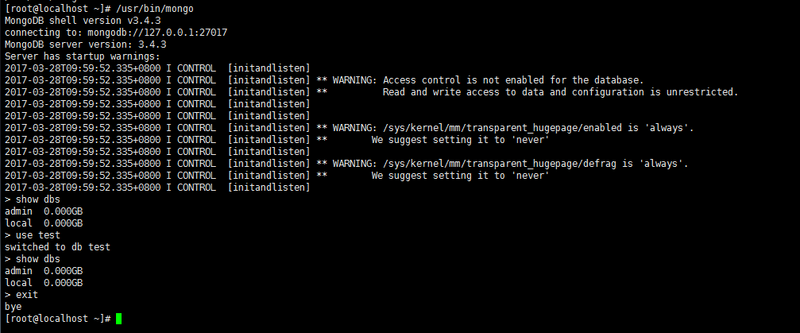
Stop the MongoDB server
You can use Ctrl + c or enter exit to exit the MongoDB interface.
Note: Warning will appear when entering the MongoDB interface
Server has startup warnings: 2017-03-30T06:40:26.039+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] 2017-03-30T06:40:26.039+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: Access control is not enabled for the database. 2017-03-30T06:40:26.039+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** Read and write access to data and configuration is unrestricted. 2017-03-30T06:40:26.039+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled is 'always'. 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** We suggest setting it to 'never' 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNING: /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag is 'always'. 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** We suggest setting it to 'never' 2017-03-30T06:40:26.040+0800 I CONTROL [initandlisten]
This is because MongoDB's security features, such as authorization and authentication, are not configured. Of course, it can be ignored just for learning, but the production environment must be configured.
