mysql installation
- Uninstall the original mysql
#Check whether there is a built-in mariadb rpm -qa | grep -i mariadb #If yes, uninstall the built-in mariadb rpm -e --nodeps mariadb-libs
- Modify / tmp directory permissions
chmod -R 777 /tmp
- Check for dependencies
#The current package should exist [there are many virtual machines under normal circumstances] rpm -qa|grep libaio #Current package should exist rpm -qa|grep net-tools
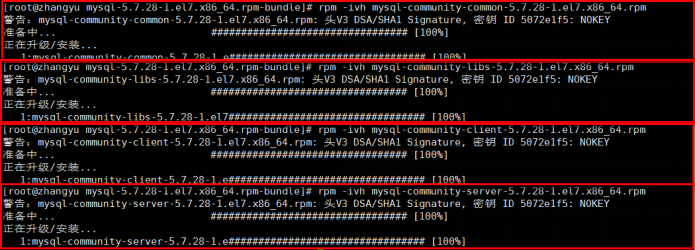
- Install the four rpm installation packages. The installation sequence must be as follows [I am currently installing in the / opt directory]
rpm -ivh mysql-community-common-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-libs-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-client-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-server-5.7.28-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
5. View mysql version
mysqladmin --version

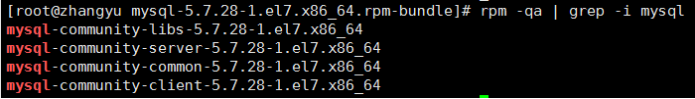
- Execute the rpm -qa|grep -i mysql command to check whether the installation is successful. You need to add - i without case sensitivity, otherwise you can't find it.
Directory structure after installation
--basedir /usr/bin Related command directory mysqladmin mysqldump Such command --datadir /var/lib/mysql/ mysql Storage path of database file --plugin-dir /usr/lib64/mysql/plugin mysql Plug in storage path --log-error /var/log/mysqld.log mysql Error log path --pid-file /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid process pid file --socket /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock For local connection unix s socket /usr/share/mysql Profile directory mysql Scripts and configuration files /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mysqld.service Scripts related to service startup and shutdown /etc/my.cnf mysql configuration file cat /etc/my.cnf
Service initialization
In order to ensure that the database directory and file owner are mysql login users, if you are running mysql service as root, you need to execute the following command to initialize:
mysqld --initialize --user=mysql
In addition, the -- initialize option is initialized in the "safe" mode by default. A password will be generated for the root user and marked as expired. You need to set a new password after logging in
View password: cat /var/log/mysqld.log
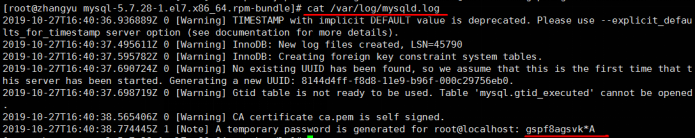
Sometimes when viewing the log, an error will be reported [there is no screenshot of the error, sorry]: delete the initialized data and reinitialize
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/*
Now check whether the mysql service is started. The following commands can be viewed by yourself
Start: systemctl start mysqld.service
Close: systemctl stop mysqld.service
Restart: systemctl restart mysqld.service
View status: systemctl status mysqld.service
View process: ps -ef | grep -i mysql
Check whether the service starts automatically: systemctl is enabled mysqld.service
Set service self startup: systemctl enable mysqld.service
Log in to mysql according to the temporary password. If you are currently logged in to mysql, please check whether the service is started
Enter the following command and press enter: mysql -u root -p
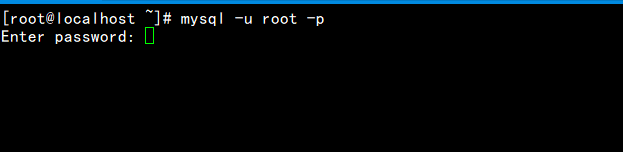
Enter temporary password
Change temporary password
#The root user sets the password to root ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'root';
Change the default character set for databases and data tables
First, take a look at the default character set of the database and data table
show variables like 'character%';
±-------------------------±---------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
±-------------------------±---------------------------+
| character_set_client | utf8 |
| character_set_connection | utf8 |
| character_set_database | utf8 |
| character_set_filesystem | binary |
| character_set_results | utf8 |
| character_set_server | utf8 |
| character_set_system | utf8 |
| character_sets_dir | /usr/share/mysql/charsets/ |
±-------------------------±---------------------------+
I have changed the default encoding of the database and data table
Modify character set: vim /etc/my.cnf
[client]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_general_ci
After modification, please restart mysql: systemctl restart mysqld