1. Download MariaDB database
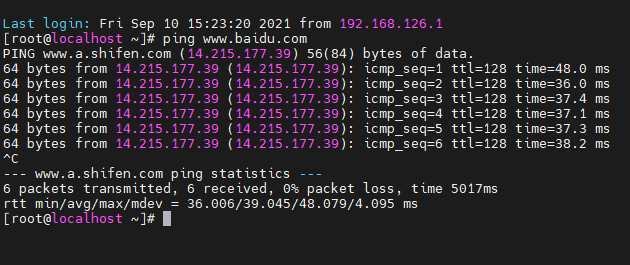
1.1 test: whether the current virtual machine can correctly link to the Internet.
ping www.baidu.com is used here for testing.
2. Installation method:
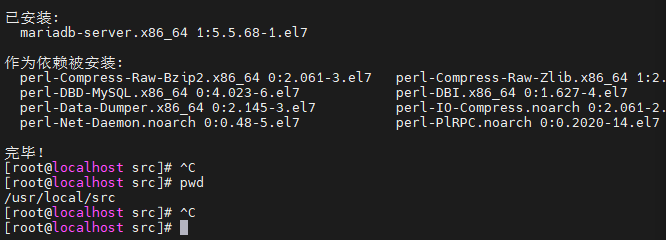
1. Command to install database:
yum install mariadb-server Install MariaDB database
yum clean all Empty installed files If the download fails, it will be executed later
Enter the / src directory and execute the command to install the database:
2. Method:
cd /usr/local/src
3. Results:
[root@localhost src]
3. Complete the installation
4. Database startup
4.1 relevant orders
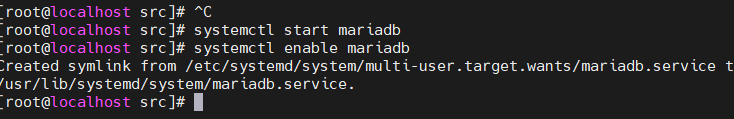
1. Start command [root@localhost src]# systemctl start mariadb 2. Restart command [root@localhost src]# systemctl restart mariadb 3. close command [root@localhost src]# systemctl stop mariadb 4. Set startup from [root@localhost src]# systemctl enable mariadb 5. Turn off from Startup [root@localhost src]# systemctl disable mariadb
4.2 set the database startup and self startup
5. Database initialization
5.1 initialization command
Note the path:
[root@localhost src]# mysql_secure_installation
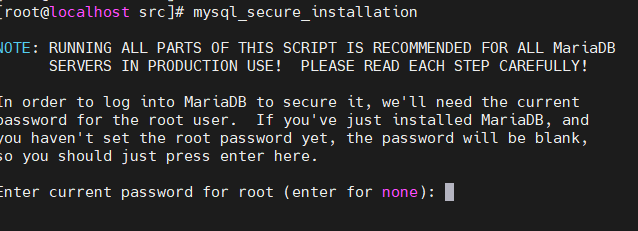
5.2 press Enter to continue and set the user and password

6. Test whether the database user name and password are valid
Enter the command: mysql -u root -p
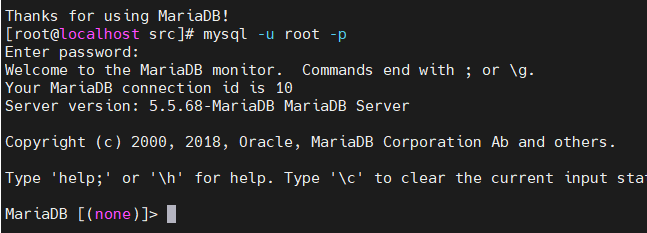
This brings in the database. The syntax is consistent with that used elsewhere. Pay attention to the semicolon.
7. Mysql database remote access configuration
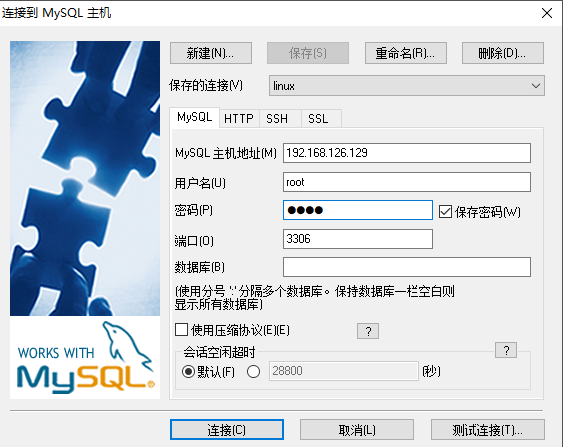
8. Description of linked database
explain:
1. If you need to remotely link the database, you must pass through the firewall
2. If the database is linked remotely, the database must have remote access permission, otherwise the link is rejected.
8.1 switching database mysql
The purpose is to query the host/root/password in the user table
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | mysql | | performance_schema | +--------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> use mysql; Reading table information for completion of table and column names You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A Database changed MariaDB [mysql]>
8.2 display tables in the database (user)
MariaDB [mysql]> show tables; +---------------------------+ | Tables_in_mysql |
8.3 modifying database tables
MariaDB [mysql]> select host,user,password from user; +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | host | user | password | +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | localhost | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | | 127.0.0.1 | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | | ::1 | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec) MariaDB [mysql]> update user set host="%" where host="localhost"; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0 MariaDB [mysql]> select host,user,password from user; +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | host | user | password | +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ | % | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | | 127.0.0.1 | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | | ::1 | root | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B | +-----------+------+-------------------------------------------+ 3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
8.4 refresh database permissions
MariaDB [mysql]> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
9. Configure Linux Firewall Policy
Under src directory
9.1 check firewall status
Command: firewall CMD -- state
[root@localhost src]# firewall-cmd --state running
9.2 firewall configuration
explain:
There is a profile in the firewall
Indicates how the firewall should operate when the Linux system starts
Requirement: tell the linux system that the firewall does not need to be started after boot
Command:
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl enable firewalld.service
[root@localhost src]# systemctl disable firewalld.service Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service. Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service. [root@localhost src]# systemctl enable firewalld.service Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/dbus-org.fedoraproject.FirewallD1.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service. Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/firewalld.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service.
9.3 manually turn off the firewall
Description: manually close the firewall through the command
1. systemctl stop firewalld.service
2. systemctl start firewalld.service
[root@localhost src]# systemctl stop firewalld.service [root@localhost src]# firewall-cmd --state not running
9.4 manually opening firewall ports
Note the catalog
[root@localhost /]# cd ~ [root@localhost ~]# firewall-cmd --query port 80/tcp
1. Check the open ports of the firewall
firewall-cmd --list-ports
2. Check whether the port is open
firewall-cmd --query-port 80/tcp
3. Turn on the firewall
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
4. Remove the port
firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=9090/tcp --permanent
5. Explanation of firewall operation
– zone # scope
– add port = 80 / TCP # add port in the format of port / communication protocol
– remove port = 80 / TCP # removes the port in the format of port / communication protocol
– permanent # takes effect permanently. If there is no such parameter, it will become invalid after restart
6. Restart the firewall
firewall-cmd --reload