Articles Catalogue
1. Installation of pymysql:
On the cmd command line, enter pip install pymysql installation, import pymysql import
2. The basic control function of pymysql:
| Method | describe |
|---|---|
| connect() | Connect to the database |
| cursor() | Create cursors that enable us to enter sql statements and execute them |
| execute() | Execute mysql to update individual data |
| commit() | Submit changes to the database |
| close() | Close the connection |
| fetchone() | Find and retrieve a piece of data |
| fetchall() | Get all the data |
| fetchmany(size) | Gets data for a specified number of bars |
connect Fillable Parameters:
- host: the address of the database
- User: database user name
- Password: database password
- db: Name of the database
- port: domain name
3. Addition of database data:
import pymysql #Connect to the database conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='pymysql_demo',port=3306) #Create a Cursor cursor=conn.cursor() #sql statement, user is the name of the table sql="insert into user (name,age) value(%s,%s)" #parameter name="li" age=23 #Pass in parameters to sql statements and execute them cursor.execute(sql,(name,age)) #Submit changes to the database conn.commit() #Close cursors and database connections cursor.close() conn.close()
Successful addition of a data to the database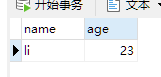
4. Delete the database data:
import pymysql #Connect to the database conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='pymysql_demo',port=3306) #Create a Cursor cursor=conn.cursor() #sql statement sql="delete from user where name=%s"#Delete all data with name #parameter name="li" #Execution statement cursor.execute(sql,name) #Submit amendments conn.commit() #Close cursors and connections cursor.close() conn.close()
This successfully deletes the data whose name is li
5. Modification of database data:
import pymysql conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='pymysql_demo',port=3306) cursor=.conn.cursor() #sql statements that modify data sql="update user set age=%s where name=%s"#The data that needs to be modified is placed behind the set #parameter name='li' age=20 cursor.execute(sql,(age,name))#The data location here must be the same as that of sql statements! conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
The age of li is changed from 23 to 20, which can also modify other data.
6. Batch addition of database data:
There's not much change compared with data addition, just more data added.
import pymysql conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='pymysql_demo',port=3306) cursor=conn.cursor() #sql statement, user is the name of the table sql="insert into user (name,age) values(%s,%s)" name1='wang' age1=25 name2='wu' age2=29 data=((name1,age1),(name2,age2)) #Excute becomes execute many cursor.executemany(sql,data) conn.commit() cursor.close() conn.close()
This adds two pieces of data
7. Query of database data (take out):
import pymysql conn=pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='123456',db='pymysql_demo',port=3306) cursor=conn.cursor() #sql statement sql="select * from user" cursor.execute(sql) value1=cursor.fetchone()#Find out a piece of data, pay attention! This data will not appear in the next fetch value2=cursor.fetchmany(2)#Take out two pieces of data value3=cursor.fetchall()#Get all the data out conn.commit() curspr.close() conn.close()
Note: The data retrieved will not appear in the next retrieve