1: Install toolkits wget, vim, and gcc
yum install -y wget
yum install -y vim-enhanced
yum install -y make cmake gcc gcc-c++ 2: Download nginx installation package
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz3: Install dependency package
yum install -y pcre pcre-devel
yum install -y zlib zlib-devel
yum install -y openssl openssl-devel4: Unzip nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz to / usr/local /
tar -zxvf nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz -C /usr/local/5: configure
Enter nginx-1.6.2 directory and execute. / configure command
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx6: Build install
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# make && make install7: Start nginx, and check whether nginx has started normally after starting. See the following information to indicate that nginx starts normally
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# ps -ef | grep nginx
root 24956 1 0 19:41 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nobody 24957 24956 0 19:41 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 24959 10533 0 19:41 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# If you want to turn off nginx, you can use the following command:
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stopIf you want to restart nginx hot, use the following command:
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload8: Configure firewall, the default port of nginx is 80
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
success
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv nginx-1.6.2]# 9: Test nginx
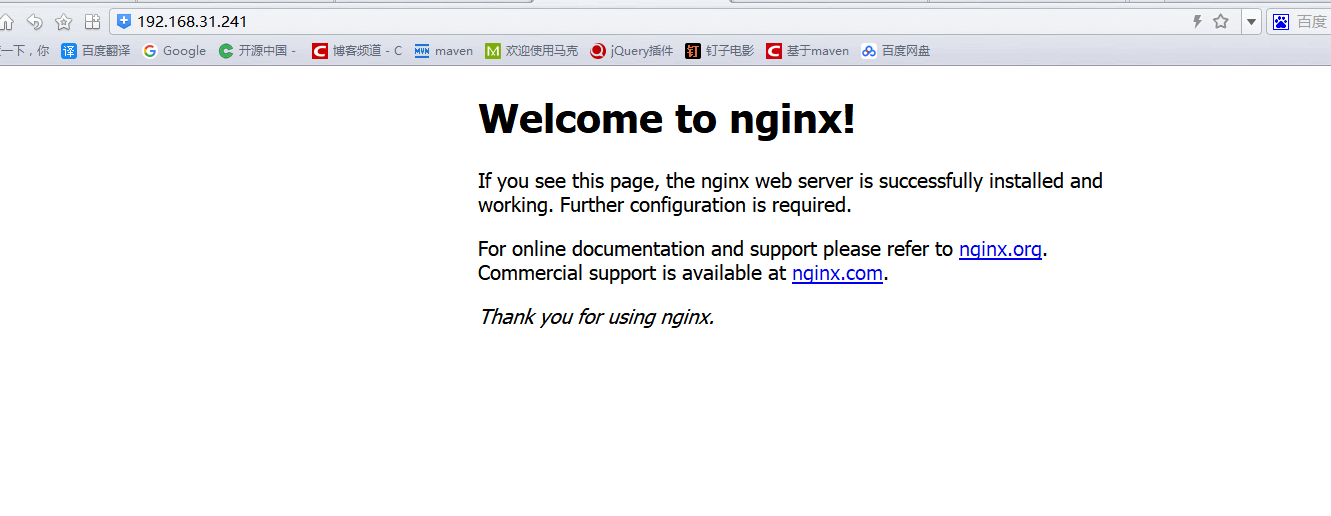
Access the nginx welcome page through the browser, and enter: http://192.168.31.241/ (port 80 is optional) or http://192.168.156.11:80/ , as shown in the following figure.
10: Learning nginx configuration
Enter the conf directory in the nginx directory, where there is a nginx.conf file, which is the most important configuration file of nginx
[root@MiWiFi-R3-srv conf]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.confThe entire contents of nginx.conf file are as follows (with annotation version):
#user nobody;
#Number of open processes < = number of CPUs
worker_processes 1;
#Error log save location
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#Process number save file
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#Maximum number of connections per process (maximum number of connections = number of connections x number of processes) how many links per worker are allowed to generate at the same time, 1024 by default
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
#File extension and file type mapping table
include mime.types;
#Default file type
default_type application/octet-stream;
#The output format of log file is similar to the global setting
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#Request log save location
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#Open send file
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
#Connection timeout
keepalive_timeout 65;
#Open gzip compression
#gzip on;
server {
#Listening port, 80 by default
listen 80;
#Monitor domain name
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#The nginx access log is placed under logs/host.access.log and uses the main format (you can also customize the format)
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#If there is no more specific location matching access path, access requests will be processed by the location.
location / {
#Root specifies that the root directory of nginx is / usr/local/nginx/html
root html;
#Access the file by default. On the welcome page, first go to the HTML directory to find index.html. If you can't find it, then go to index.htm
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
#The error page and its return address. If the error codes are 500, 502, 503 and 504, the 50.html error page will be returned.
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
#If "=" is followed by location, it means accurate matching
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
} Multiple servers can be added to the configuration file. The ports monitored by the server are different. You can have nginx proxy multiple ports as required. When accessing a port, you can specify to do something. I have added a server here. The listening port of this server is 1234. I specify the server name as test.com, that is, the domain name is test.com. When I visit 1234 port, I will automatically navigate to the page of / usr/local/nginx/tester/tester111.html, as shown below.
#user nobody;
#Number of open processes < = number of CPUs
worker_processes 1;
#Error log save location
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#Process number save file
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#Maximum number of connections per process (maximum number of connections = number of connections x number of processes) how many links per worker are allowed to generate at the same time, 1024 by default
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
#File extension and file type mapping table
include mime.types;
#Default file type
default_type application/octet-stream;
#The output format of log file is similar to the global setting
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#Request log save location
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#Open send file
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
#Connection timeout
keepalive_timeout 65;
#Open gzip compression
#gzip on;
server {
#Monitor port
listen 80;
#Monitor domain name
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#The nginx access log is placed under logs/host.access.log and uses the main format (you can also customize the format)
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#If there is no more specific location matching access path, access requests will be processed by the location.
location / {
#Root specifies that the root directory of nginx is / usr/local/nginx/html
root html;
#Access the file by default. On the welcome page, first go to the HTML directory to find index.html. If you can't find it, then go to index.htm
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
#The error page and its return address. If the error codes are 500, 502, 503 and 504, the 50.html error page will be returned.
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
#If "=" is followed by location, it means accurate matching
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
server {
listen 1234;
server_name test.com;
location / {
#Regular expression matching uri method: build a tester111.html under / usr/local/nginx/tester and then use regular matching
root tester;
index tester111.html;
}
}
}
}