Some image processing operations with opencv are very simple and convenient, but for students who want to understand the details, it is best to write the generation of filter core and filter function. Understanding the change process of Gaussian function is of great help to our in-depth study of image processing.
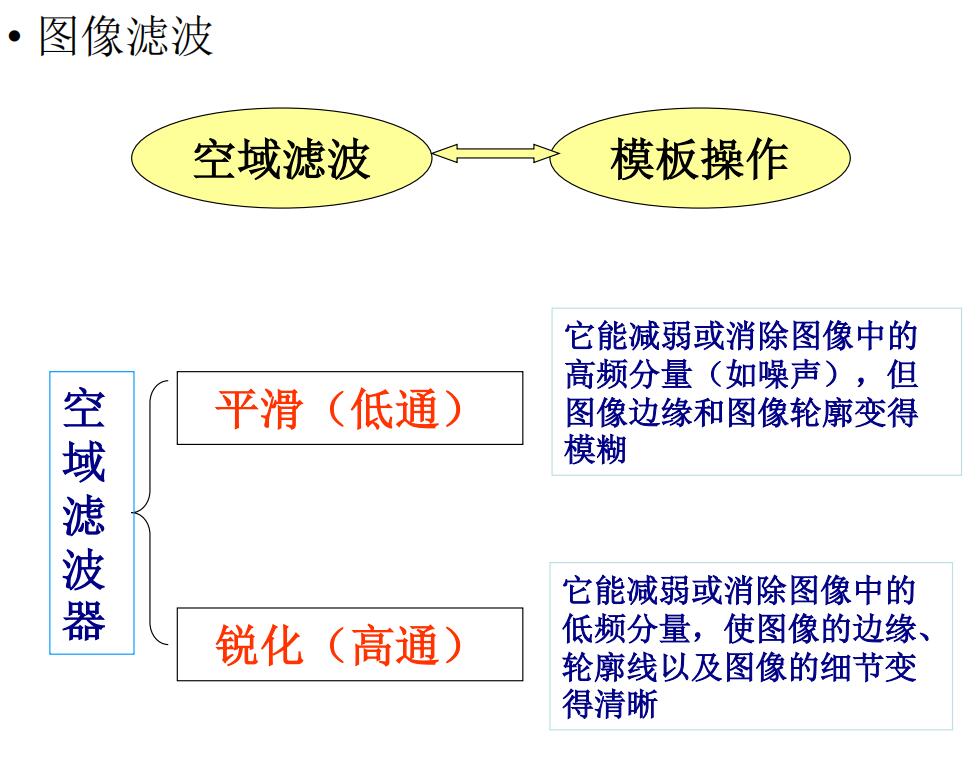
Function of image filtering
Generally speaking, it has two functions: smoothing (blurring the image edge and image contour) and sharpening (making the edge and contour details clear).
Fundamentals of Mathematics
Gaussian filtering is actually a spatial convolution done on the picture with the Gaussian filter kernel we generated. We can achieve different processing effects according to different filter kernels. The focus is to understand how to generate Gaussian kernel and the characteristics of Gaussian function.
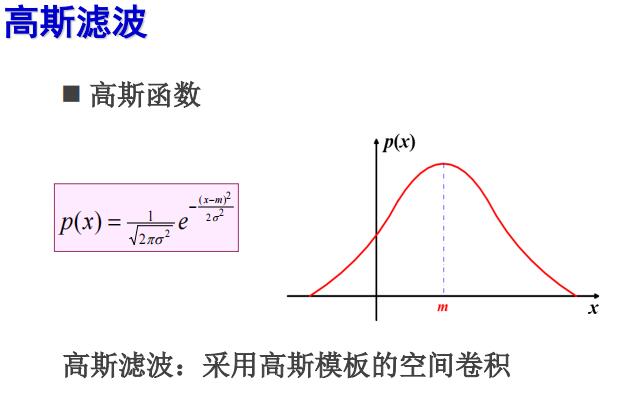
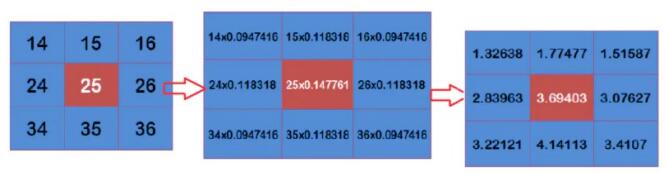
Next, use the code to explain how the filter core is generated. You can better understand it by comparing the above formula.
def gausskernel(size,k,sigma):
gausskernel = np.zeros((size,size),np.float32)
for i in range (size):
for j in range (size):
norm = math.pow(i-k,2) + pow(j-k,2)
gausskernel[i,j] = math.exp(-norm/(2*math.pow(sigma,2)))/2*math.pi*pow(sigma,2)
sum = np.sum(gausskernel)
kernel = gausskernel/sum
return kernel
The farther away from the center, the smaller the corresponding weight, so when using this filter to check image processing, we can dilute the details of the edge and achieve the smoothing effect we need.
Generated filter kernel

Then we do a convolution of filter kernel on our original image
Filtering effect
Note that if it is a color image, we should first split the image into three channels, and each channel should be Gaussian filtered, and then combined. If the gray image has only one channel, filter directly.
In addition, for color pictures, you can not split the image. We need to change the original 33 filter core to a 33 * 3 three-dimensional three-dimensional filter core, and then convolute it on the original image. Interested students can try it by themselves.
Input: a color image or gray image, generate Gaussian kernel and Gaussian filter, and output the processed image

Environment & source code
Environment: Python 3.6.13 + opencv Python 3.4.1.15 + vs Code
import math
import cv2
import numpy as np
def gausskernel(size,k,sigma):
gausskernel = np.zeros((size,size),np.float32)
for i in range (size):
for j in range (size):
norm = math.pow(i-k,2) + pow(j-k,2)
gausskernel[i,j] = math.exp(-norm/(2*math.pow(sigma,2)))/2*math.pi*pow(sigma,2)
sum = np.sum(gausskernel)
kernel = gausskernel/sum
return kernel
def mygaussFilter(img_gray,kernel):
h,w = img_gray.shape
k_h,k_w = kernel.shape
for i in range(int(k_h/2),h-int(k_h/2)):
for j in range(int(k_h/2),w-int(k_h/2)):
sum = 0
for k in range(0,k_h):
for l in range(0,k_h):
sum += img_gray[i-int(k_h/2)+k,j-int(k_h/2)+l]*kernel[k,l]
img_gray[i,j] = sum
return img_gray
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv2.imread("dog1.jpg")
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
img_g = img_gray.copy()
k=1
size = 2*k+1
kernel = gausskernel(size,k,1.5)
print(kernel)
img_B,img_G,img_R = cv2.split(img)
img_gauss_B = mygaussFilter(img_B,kernel)
img_gauss_G = mygaussFilter(img_G,kernel)
img_gauss_R = mygaussFilter(img_R,kernel)
img_gauss = cv2.merge([img_gauss_B,img_gauss_G,img_gauss_R])
img_comp = np.hstack((img,img_gauss))
cv2.imshow("gauss",img_comp)
cv2.waitKey(0)
conclusion
Gaussian filtering can make the image smooth. The main influencing factor is the variance when generating the filter core. The greater the variance, the more obvious the smoothing effect. However, there is a threshold. After exceeding the threshold, the image will become very blurred and lose the meaning of smoothing. If the variance is too small, there is no smoothing effect.
Therefore, for different images, we should select the appropriate variance according to the noise, the smoothness of the image and other factors in order to achieve the best effect.
The main factor affecting the program time is the size of the filter core. The improvement methods include changing the matrix operation to the column vector operation. In addition, the hardware can be improved, such as gpu with better performance to speed up the operation.