I. Preface
1,Skip-Thought-Vector Paper https://github.com/ryankiros/skip-thoughts
2. This article assumes that the reader already understands Skip-Gram-Vector and RNN related foundations.
3. Quick_thoughtful Papers: Lajanugen Logeswaran, Honglak Lee, An efficient framework for learning sentence representations. In ICLR, 2018.
Two, actual combat
1. Make clauses on data (remove short sentences), delete sentences with high frequency, participle
def fenju(data): sentence=[] for i in range(len(data)): try: m = re.findall('. ',data[i][0]) # print(m) if data[i][1] is not None and len(m)>0: if len(m)>1: content=data[i][0].split('. ') # print(content) for c in range(len(content)): if len(content[c])>10: sentence.append(content[c]+'. ') elif len(data[i][0])>10: sentence.append(data[i][0]) else: continue except: continue return sentence def _process_sentence_list(sentence_list, threshold=0.01): sentence_count = Counter(sentence_list) total_count = len(sentence_list) # Calculate sentence frequency sentence_freqs = {w: c / total_count for w, c in sentence_count.items()} # Remove sentences that appear too frequently sentence=[] for w in range(len(sentence_list)): if sentence_freqs[sentence_list[w]] < threshold: sentence.append(sentence_list[w]) else: continue return sentence def fenci(alltext, writefile, filename): if not os.path.exists(writefile): os.makedirs(writefile) sentence = [' '.join(jieba.lcut(''.join(text.split()))) for text in alltext] print(sentence) with open(os.path.join(writefile, filename), "w") as fw: fw.write("\n".join(sentence))
2. Build vocab and TFRecord files (see github code in detail)
3. Model input definition (train/eval/encode of three modes)
def build_inputs(self): if self.mode == "encode": encode_ids = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, (None, None), name="encode_ids") encode_mask = tf.placeholder(tf.int8, (None, None), name="encode_mask") else: # Prefetch serialized tf.Example protos. input_queue = input_ops.prefetch_input_data( self.reader, FLAGS.input_file_pattern, shuffle=FLAGS.shuffle_input_data, capacity=FLAGS.input_queue_capacity, num_reader_threads=FLAGS.num_input_reader_threads) print("input_queue",input_queue) # Deserialize a batch. serialized = input_queue.dequeue_many(FLAGS.batch_size) encode = input_ops.parse_example_batch(serialized) encode_ids = encode.ids encode_mask = encode.mask self.encode_ids = encode_ids self.encode_mask = encode_mask
Since every sentence in our batch is padding, in order to prevent the impact of padding on training, we need to pass the mask to RNN Network - the original length of each sentence (encode_mask).
4. embedding input sentences
def build_word_embeddings(self): rand_init = self.uniform_initializer self.word_embeddings = [] self.encode_emb = [] self.init = None for v in self.config.vocab_configs: if v.mode == 'fixed': if self.mode == "train": word_emb = tf.get_variable( name=v.name, shape=[v.size, v.dim], trainable=False) embedding_placeholder = tf.placeholder( tf.float32, [v.size, v.dim]) embedding_init = word_emb.assign(embedding_placeholder) rand = np.random.rand(1, v.dim) word_vecs = np.load(v.embs_file) load_vocab_size = word_vecs.shape[0] assert(load_vocab_size == v.size - 1) word_init = np.concatenate((rand, word_vecs), axis=0) self.init = (embedding_init, embedding_placeholder, word_init) else: word_emb = tf.get_variable( name=v.name, shape=[v.size, v.dim]) encode_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(word_emb, self.encode_ids) self.word_emb = word_emb self.encode_emb.extend([encode_emb, encode_emb])##### if v.mode == 'trained': for inout in ["", "_out"]: word_emb = tf.get_variable( name=v.name + inout, shape=[v.size, v.dim], initializer=rand_init) if self.mode == 'train': self.word_embeddings.append(word_emb) encode_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(word_emb, self.encode_ids) self.encode_emb.append(encode_emb) if v.mode == 'expand': for inout in ["", "_out"]: encode_emb = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, ( None, None, v.dim), v.name + inout) self.encode_emb.append(encode_emb) word_emb_dict = read_vocab_embs(v.vocab_file + inout + ".txt", v.embs_file + inout + ".npy") self.word_embeddings.append(word_emb_dict) if v.mode != 'expand' and self.mode == 'encode': word_emb_dict = read_vocab(v.vocab_file) self.word_embeddings.extend([word_emb_dict, word_emb_dict])
Convert every word in a sentence into a vector of vocab size length. The three modes of v.mode are fixed (using pre-training embedding)/train (training)/expand (expansion). The final output is in the form of [encode_emb, encode_emb], which is used to get the link between the upper and lower sentences.
5. Building encoder
encoder encode s sentences to get the final hidden state, where a single-layer LSTM network bidirectional LSTM bidirectional GRU can be used.
def _initialize_cell(self, num_units, cell_type="GRU"): if cell_type == "GRU": return tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(num_units=num_units) elif cell_type == "LSTM": return tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMCell(num_units=num_units) else: raise ValueError("Invalid cell type") def rnn(self, word_embs, mask, scope, encoder_dim, cell_type="GRU"): length = tf.to_int32(tf.reduce_sum(mask, 1), name="length") if self.config.bidir: if encoder_dim % 2: raise ValueError( "encoder_dim must be even when using a bidirectional encoder.") num_units = encoder_dim // 2 cell_fw = self._initialize_cell(num_units, cell_type=cell_type) cell_bw = self._initialize_cell(num_units, cell_type=cell_type) outputs, states = tf.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn( cell_fw=cell_fw, cell_bw=cell_bw, inputs=word_embs, sequence_length=length, dtype=tf.float32, scope=scope) if cell_type == "LSTM": states = [states[0][1], states[1][1]] state = tf.concat(states, 1) else: cell = self._initialize_cell(encoder_dim, cell_type=cell_type) outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn( cell=cell, inputs=word_embs, sequence_length=length, dtype=tf.float32, scope=scope) if cell_type == "LSTM": state = state[1] return state def build_encoder(self): """Builds the sentence encoder. Inputs: self.encode_emb self.encode_mask Outputs: self.thought_vectors Raises: ValueError: if config.bidirectional_encoder is True and config.encoder_dim is odd. """ names = ["", "_out"] self.thought_vectors = [] for i in range(2): with tf.variable_scope("encoder" + names[i]) as scope: if self.config.encoder == "gru": sent_rep = self.rnn(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask, scope, self.config.encoder_dim, cell_type="GRU") elif self.config.encoder == "lstm": sent_rep = self.rnn(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask, scope, self.config.encoder_dim, cell_type="LSTM") elif self.config.encoder == 'bow': sent_rep = self.bow(self.encode_emb[i], self.encode_mask) else: raise ValueError("Invalid encoder") thought_vectors = tf.identity(sent_rep, name="thought_vectors") self.thought_vectors.append(thought_vectors)
It can be seen that [encode_emb, encode_emb] is encoded, and [thought_vectors,thought_vectors]
6. Constructing Loss Function
def build_loss(self): """Builds the loss Tensor. Outputs: self.total_loss """ all_sen_embs = self.thought_vectors if FLAGS.dropout: mask_shp = [1, self.config.encoder_dim] bin_mask = tf.random_uniform(mask_shp) > FLAGS.dropout_rate bin_mask = tf.where(bin_mask, tf.ones(mask_shp), tf.zeros(mask_shp)) src = all_sen_embs[0] * bin_mask dst = all_sen_embs[1] * bin_mask scores = tf.matmul(src, dst, transpose_b=True) else: scores = tf.matmul(all_sen_embs[0], all_sen_embs[1], transpose_b=True)###study pre current post # Ignore source sentence scores = tf.matrix_set_diag(scores, np.zeros(FLAGS.batch_size)) # Targets targets_np = np.zeros((FLAGS.batch_size, FLAGS.batch_size)) ctxt_sent_pos = list(range(-FLAGS.context_size, FLAGS.context_size + 1)) ctxt_sent_pos.remove(0) for ctxt_pos in ctxt_sent_pos: targets_np += np.eye(FLAGS.batch_size, k=ctxt_pos) targets_np_sum = np.sum(targets_np, axis=1, keepdims=True) targets_np = targets_np/targets_np_sum targets = tf.constant(targets_np, dtype=tf.float32) # Forward and backward scores f_scores = scores[:-1] b_scores = scores[1:] losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( labels=targets, logits=scores) loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) tf.summary.scalar("losses/ent_loss", loss) self.total_loss = loss if self.mode == "eval": f_max = tf.to_int64(tf.argmax(f_scores, axis=1)) b_max = tf.to_int64(tf.argmax(b_scores, axis=1)) targets = range(FLAGS.batch_size - 1) targets = tf.constant(list(targets), dtype=tf.int64) fwd_targets = targets + 1 names_to_values, names_to_updates = tf.contrib.slim.metrics.aggregate_metric_map({ "Acc/Fwd Acc": tf.contrib.slim.metrics.streaming_accuracy(f_max, fwd_targets), "Acc/Bwd Acc": tf.contrib.slim.metrics.streaming_accuracy(b_max, targets) }) for name, value in names_to_values.items(): tf.summary.scalar(name, value) self.eval_op = names_to_updates.values()
The loss function is illustrated as follows:
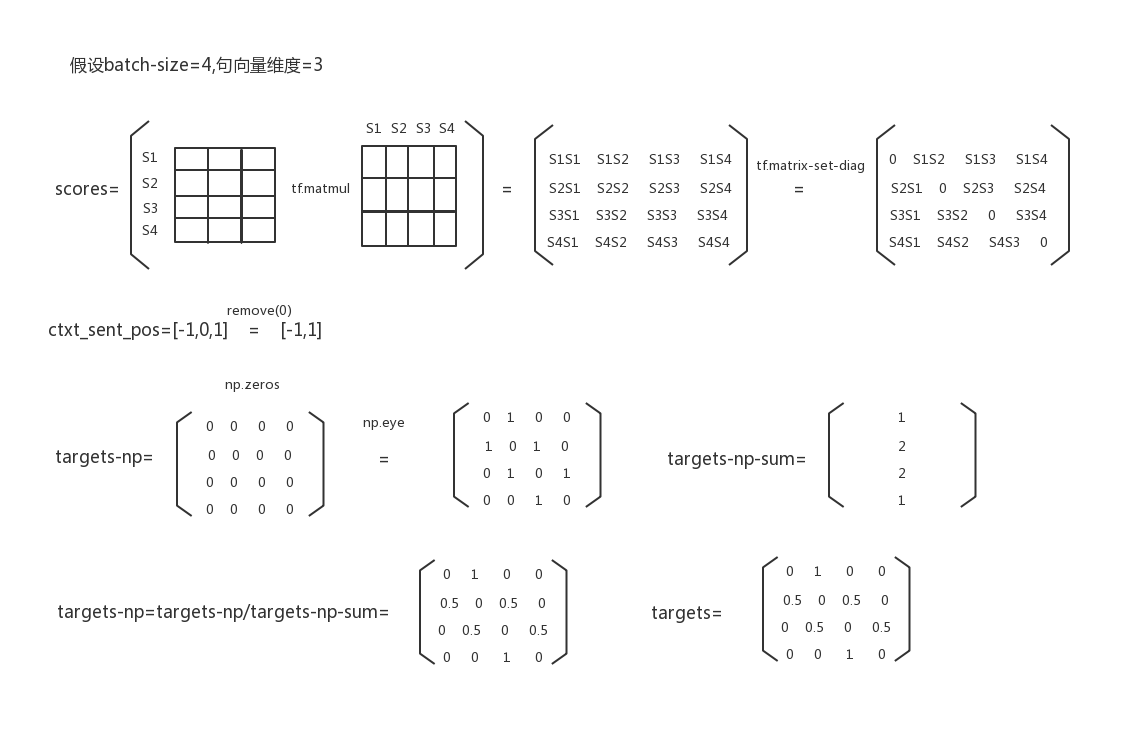
Using tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=targets, logits=scores) to carry out cross-entropy, we can see from targets that quick_thoughtful idea is to deduce the similarity of target sentences according to context. Personally, I don't think that I have learned the characteristics of target sentences. I use the sentence vector trained by quick_thoughtful to classify the target sentences into different categories, and the effect is not very good (quick_thoughtful evaluation). Examples include the emotional classification of movies.
Specific paper reproduction code https://github.com/lajanugen/S2V
Modify https://github.com/jinjia/Quick_Thought (Chinese)