I/O multiplexing
I/O complex method: select poll epoll
effect:
- You can listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time,
Enables the server to process multiple file descriptors at the same time without introducing multiple processes.
Network programs need to use I/O multiplexing technology:
◼ The TCP server handles both listening sockets and connecting sockets.
◼ The server should process both TCP requests and UDP requests.
◼ The program processes multiple sockets at the same time.
◼ The client program handles both user input and network connections.
◼ The server should listen to multiple ports at the same time.
Although I/O multiplexing can listen to multiple file descriptors at the same time, it is blocked. And when
When multiple file descriptors are ready at the same time, if no additional measures are taken, the program can only process each file descriptor in sequence, which makes the server seem to work in serial. If you want to improve the ability of concurrent processing, you can use multithreading or multi process programming methods.
socket
socket read event generation:
The other side of socket communication closes the connection.
Listen for new link requests on the socket.
There is an unhandled error on the socket.
select system call
#include<sys/select.h>
select returns the number of file descriptors whose value is ready.
If no file descriptor is ready within the timeout, select returns 0.
If select fails, it returns - 1.
n> 0, n file descriptors are ready.
Handle three kinds of events: read event, write event, and exception event.
Set fd_set adds the descriptor to the collection. The total size defaults to 1024 bits.
int FD_ISSET(int fd, fd_set *fdset); // Test whether the bit FD of fdset is set.
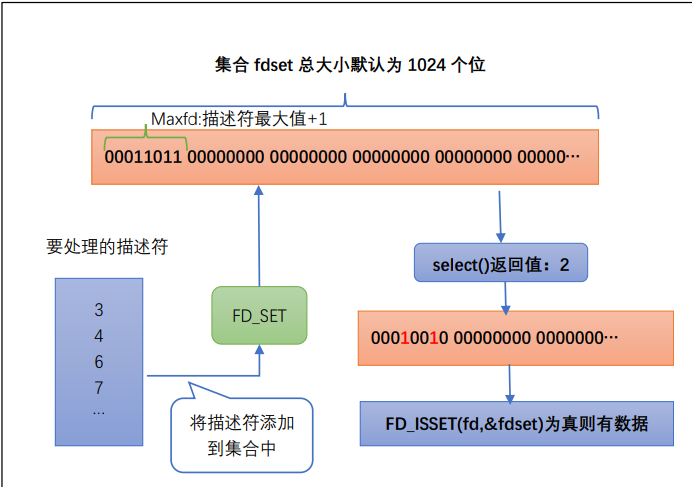
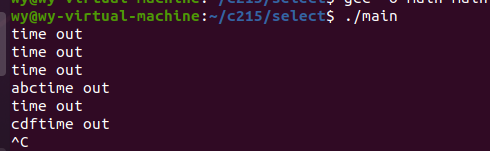
It is suitable for scenes with a small number of descriptors.
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<string.h>
3 #include<unistd.h>
4 #include<sys/select.h>
5 #include<sys/time.h>
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 int fd=0;// stdin 0; stdout 1; stderr 2 assigns the value of the keyboard descriptor to fd
10
11 fd_set fdset;//Define a collection to collect descriptors, which are detected by selet
12
13 while(1)//Cycle detection
14 {
15 struct timeval tv={5,0};//Set the timeout of 5 seconds
16 FD_ZERO(&fdset); //Clear each bit in the entire collection to 0
17 FD_SET(fd,&fdset);//Add a descriptor to the collection. There is only one descriptor if there are multiple descriptor loops
18
19 int n=select(fd+1,&fdset,NULL,NULL,&tv);//The maximum value of fd+1 descriptor + 1 only detects places with data
20 if(n==-1)
21 {
22 printf("select err\n");
23 break;
24 }
25 else if(n==0)
26 {
27 printf("time out\n");
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 if(FD_ISSET(fd,&fdset))//Detect whether there is data on the descriptor
32 {
33 char buff[128]={0};
34 read(fd,buff,127);
35 printf("read:%s\n",buff);
36 }
37 }
38 }
39
40 }
TCP
TCP server
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<unistd.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<sys/socket.h>
6 #include<netinet/in.h>
7 #include<arpa/inet.h>
8 #include<assert.h>
9 #include<sys/select.h>
10 #include<sys/time.h>
11
12 #define MAX 10
13 int socket_init();
14
15 void fds_init(int fds[])//Clear descriptor all to - 1
16 {
17 if(fds==NULL)
18 {
19 return;
20 }
21 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
22 {
23 fds[i]=-1;
24 }
25 }
26 void fds_add(int fd,int fds[])//Adds a descriptor to an idle collection
27 {
28 if(fds==NULL)
29 {
30 return;
31 }
32 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
33 {
34 if(fds[i]==-1)
35 {
36 fds[i]=fd;
37 break;
38 }
39 }
40 }
41 void fds_del(int fd,int fds[])//Remove descriptor from collection
42 {
43 if(fds==NULL)
44 {
45 return;
46 }
47 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
48 {
49 if(fds[i]==fd)
50 {
51 fds[i]=-1;
52 break;
53 }
54 }
55 }
56 int main()
57 {
58 int sockfd=socket_init();
59 assert(sockfd!=-1);
60 int fds[MAX];//Save descriptor in array
61
62 fds_init(fds);//The initialization array values are - 1, which means that the array is empty
63
64 fds_add(sockfd,fds);//Adds a listener socket to the array
65
66 fd_set fdset;//Set - > select
67
68 while(1)
69 {
70 FD_ZERO(&fdset);//Empty collection
71 int maxfd=-1;//Record descriptor maximum
72
73 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
74 {
75 if(fds[i]==-1)
76 {
77 continue;
78 }
79 FD_SET(fds[i],&fdset);//Adds a valid descriptor to the collection
80 if(maxfd<fds[i])
81 {
82 maxfd=fds[i];
83 }
84 }
85 struct timeval tv={5,0};//Timeout 5 seconds
86 int n=select(maxfd+1,&fdset,NULL,NULL,&tv);
87 if(n==-1)
88 {
89 continue;
90 }
91 else if(n==0)
92 {
93 printf("time out\n");
94 continue;
95 }
96 else
97 {
98 for(int i=0;i<MAX;i++)//Traverse all descriptors to find ready
99 {
100 if(fds[i]==-1)
101 {
102 continue;
103 }
104 if(FD_ISSET(fds[i],&fdset))
105 {
106 if(fds[i]==sockfd) //Listen for socket sub call accept
107 {
108 struct sockaddr_in caddr;
109 int len=sizeof(caddr);
110
111 int c=accept(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&caddr,&len);
112 if(c<0)
113 {
114 continue;
115 }
116 printf("accept c=%d\n",c);
117 fds_add(c,fds);
118 }
119 else //Connection socket sub call recv
120 {
121 char buff[128]={0};
122 int num=recv(fds[i],buff,127,0);
123 if(num<=0)
124 {
125 close(fds[i]);
126 fds_del(fds[i],fds);//Removes unused descriptors from the array
127 printf("cilent close\n");
128 continue;
129 }
130 printf("read:%s\n",buff);
131 send(fds[i],"ok",2,0);
132 }
133 }
134 }
135 }
136 }
137 }
138
139 int socket_init()
140 {
141 int sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
142 if(sockfd==-1)
143 {
144 return -1;
145 }
146
147 struct sockaddr_in saddr;
148 memset(&saddr,0,sizeof(saddr));
149 saddr.sin_family=AF_INET;
150 saddr.sin_port=htons(6000);
151 saddr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
152
153 int res=bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&saddr,sizeof(saddr));
154 if(res==-1)
155 {
156 return -1;
157 }
158
159 res=listen(sockfd,5);
160 if(res==-1)
161 {
162 return -1;
163 }
164 return sockfd;
165 }
TCP Client
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<unistd.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<assert.h>
6 #include<sys/socket.h>
7 #include<netinet/in.h>
8 #include<arpa/inet.h>
9
10 int main()
11 {
12 int sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);//Create socket
13 assert(sockfd!=-1);
14
15 //bind() / / can be bound, but generally not
16
17 struct sockaddr_in saddr;
18 memset(&saddr,0,sizeof(saddr));
19 saddr.sin_family=AF_INET;
20 saddr.sin_port=htons(6000);
21 saddr.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
22
23 int res=connect(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&saddr,sizeof(saddr));//Three handshakes
24 assert(res!=-1);
25 while(1)
26 {
27 char buff[128]={0};
28 printf("input:\n");
29 fgets(buff,128,stdin);
30
31 if(strncmp(buff,"end",3)==0)
32 {
33 break;
34 }
35 send(sockfd,buff,strlen(buff),0);
36
37 memset(buff,0,128);
38 recv(sockfd,buff,127,0);
39 printf("buff=%s\n",buff);
40 }
41 close(sockfd);
42 }
~
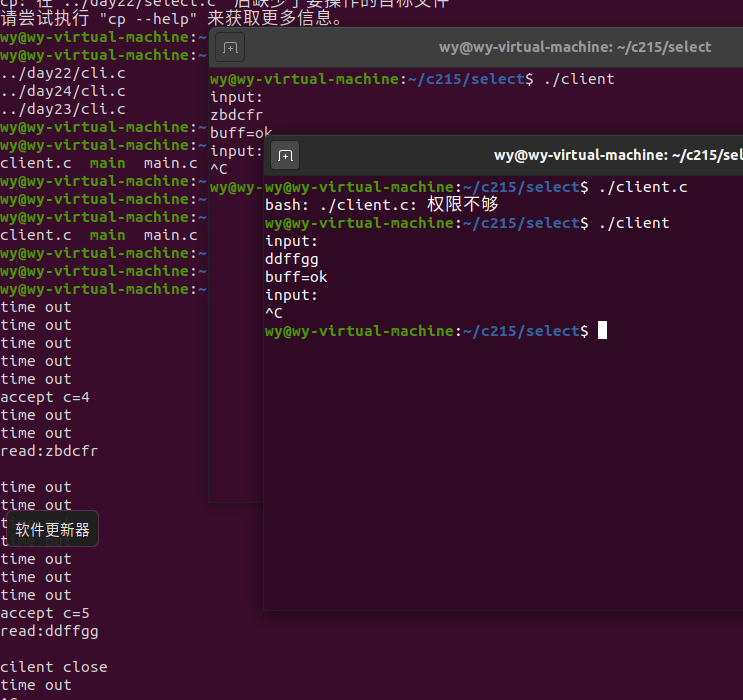
- Opposite close descriptor
- Send data to the other party
- Opposite link
select will return.