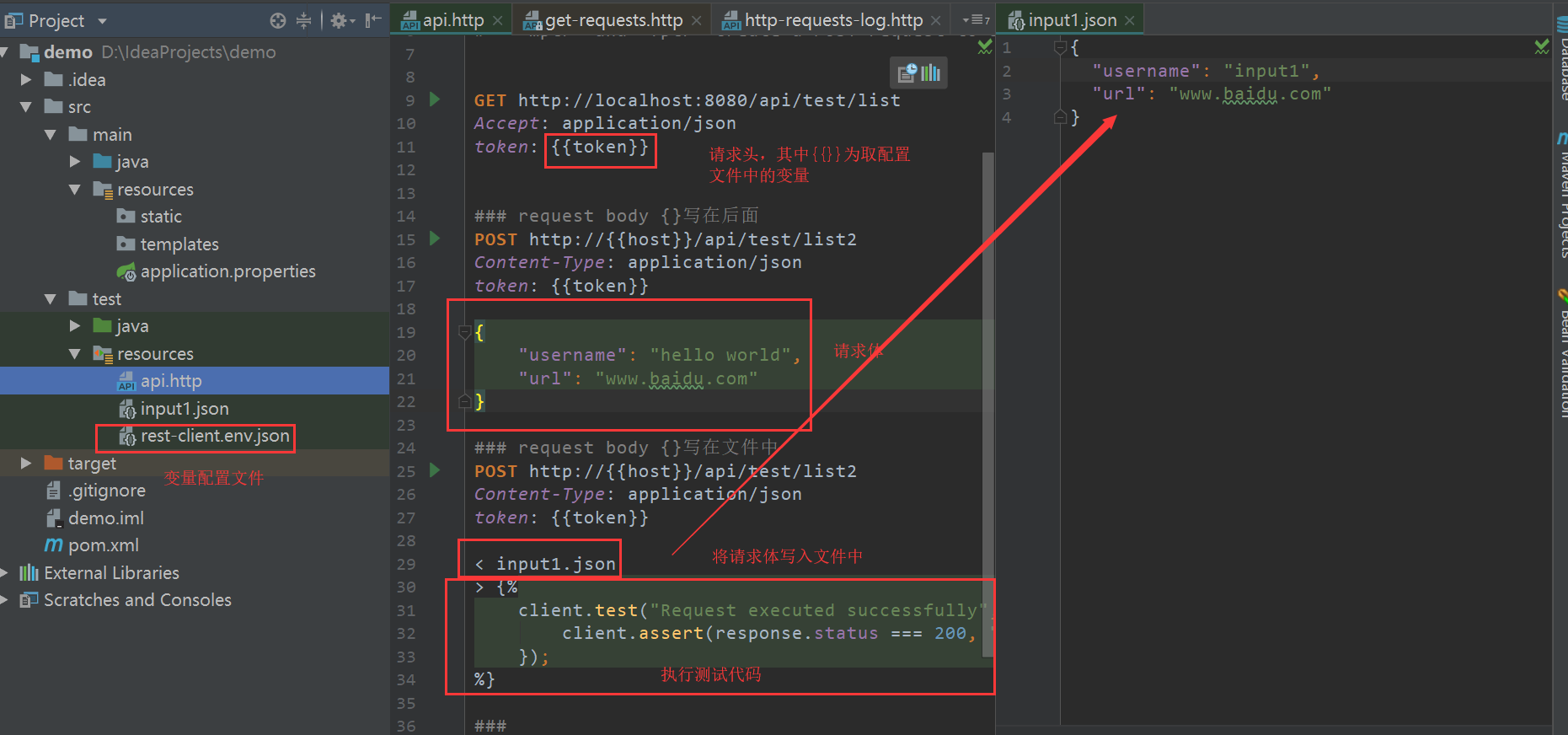
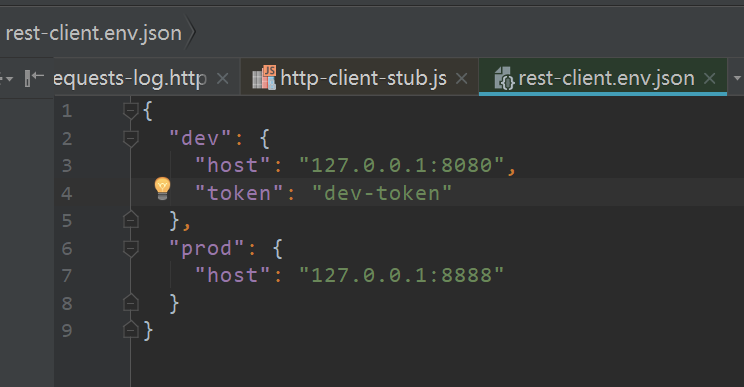
The front and back end separates the project, and the front and back end communicates through the api. If you use the free version of postman for API testing, because you can not save the test script to the file, it is not convenient for the front-end to view.
You can choose the paid version. You can also use the HTTP Client Editor that comes with IDEA to write test scripts. The main purpose of writing demo here is to facilitate query grammar.
HTTP request
### Get request with a header GET https://httpbin.org/ip Accept: application/json ### Get request with parameter GET https://httpbin.org/get?show_env=1 Accept: application/json ### Get request with environment variables GET {{host}}/get?show_env={{show_env}} Accept: application/json ###
POST request
### Send POST request with json body POST https://httpbin.org/post Content-Type: application/json { "id": 999, "value": "content" } ### Send POST request with body as parameters POST https://httpbin.org/post Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded id=999&value=content ### Send a form with the text and file fields POST https://httpbin.org/post Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=WebAppBoundary --WebAppBoundary Content-Disposition: form-data; name="element-name" Content-Type: text/plain Name --WebAppBoundary Content-Disposition: form-data; name="data"; filename="data.json" Content-Type: application/json < ./request-form-data.json --WebAppBoundary-- ###
Authentication request
### Basic authorization. GET https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd Authorization: Basic user passwd ### Basic authorization with variables. GET https://httpbin.org/basic-auth/user/passwd Authorization: Basic {{username}} {{password}} ### Digest authorization. GET https://httpbin.org/digest-auth/realm/user/passwd Authorization: Digest user passwd ### Digest authorization with variables. GET https://httpbin.org/digest-auth/realm/user/passwd Authorization: Digest {{username}} {{password}} ### Authorization by token, part 1. Retrieve and save token. POST https://httpbin.org/post Content-Type: application/json { "token": "my-secret-token" } > {% client.global.set("auth_token", response.body.json.token); %} ### Authorization by token, part 2. Use token to authorize. GET https://httpbin.org/headers Authorization: Bearer {{auth_token}} ###
Test response
### Successful test: check response status is 200 GET https://httpbin.org/status/200 > {% client.test("Request executed successfully", function() { client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200"); }); %} ### Failed test: check response status is 200 GET https://httpbin.org/status/404 > {% client.test("Request executed successfully", function() { client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200"); }); %} ### Check response status and content-type GET https://httpbin.org/get > {% client.test("Request executed successfully", function() { client.assert(response.status === 200, "Response status is not 200"); }); client.test("Response content-type is json", function() { var type = response.contentType.mimeType; client.assert(type === "application/json", "Expected 'application/json' but received '" + type + "'"); }); %} ### Check response body GET https://httpbin.org/get > {% client.test("Headers option exists", function() { client.assert(response.body.hasOwnProperty("headers"), "Cannot find 'headers' option in response"); }); %} ###
The above scripts are good demo s that cover grammar and can be run by clicking directly.