Adding fields to a table of ten million or more levels in MySQL has always been a headache. In this case, how to deal with it? This paper uses three common scenarios to illustrate the case.
1. Environmental preparation
Database version: 5.7.25-28 (Percona branch)
Server configuration: three centos 7 virtual machines with 2CPU 2G memory
Database architecture: 1 master-slave MHA architecture (in order to facilitate the demonstration of master-slave switching scenario, if GTID is enabled, then two nodes can be used). For the construction of MHA, please refer to this article MySQL highly available MHA cluster deployment
Prepare test table: create a 2kw record table. For quick creation methods, please refer to Quickly create a continuous number
This time, we slightly modified the stored procedure and added several more fields. The stored procedure is as follows:
DELIMITER $$ CREATE PROCEDURE `sp_createNum`(cnt INT ) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1; DROP TABLE if exists tb_add_columns; CREATE TABLE if not exists tb_add_columns(id int primary key,col1 int,col2 varchar(32)); INSERT INTO tb_add_columns(id,col1,col2) SELECT i as id ,i%7 as col1,md5(i) as col2; WHILE i < cnt DO BEGIN INSERT INTO tb_add_columns(id,col1,col2) SELECT id + i as id ,( id + i) %7 as col1,md5( id + i) as col2 FROM tb_add_columns WHERE id <=cnt - i ; SET i = i*2; END; END WHILE; END$$ DELIMITER ;
Call the stored procedure to complete the creation of test table and test data.
mysql> call sp_createNum(20000000);
2. Add fields directly
Usage scenario: when the system is not busy or the table has few accesses, such as meeting ONLINE DDL, it can be added directly.
Simulation scenario: create a test script, access a random record of the table every 10s, and then add fields to the table
The access script is as follows:
#!/bin/bash # gjc for i in {1..1000000000} # Access times 1000000000, adjust as needed do id=$RANDOM #Generate random number mysql -uroot -p'123456' --socket=/data/mysql3306/tmp/mysql.sock -e "select a.*,now() from testdb.tb_add_columns a where id = "$id # Access data sleep 10 # Pause for 10s done
Run script
sh test.sh
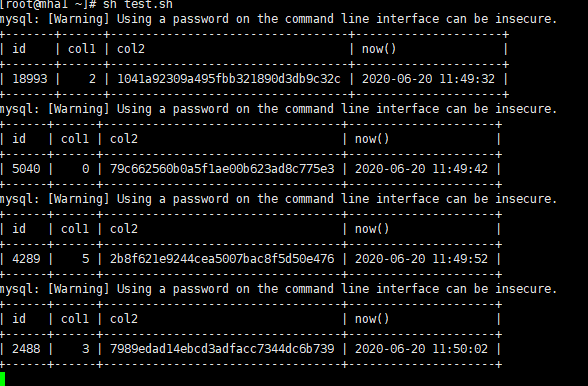
Add fields to table
mysql> alter table testdb.tb_add_columns add col3 int;
At this time, the access is normal.
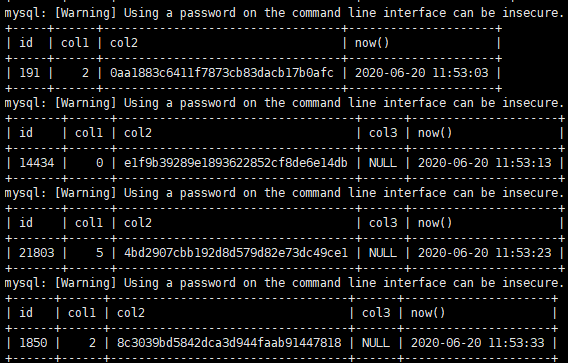
The scenario attached with ONLINE DDL is as follows. It is suggested that DBA s should be clear about it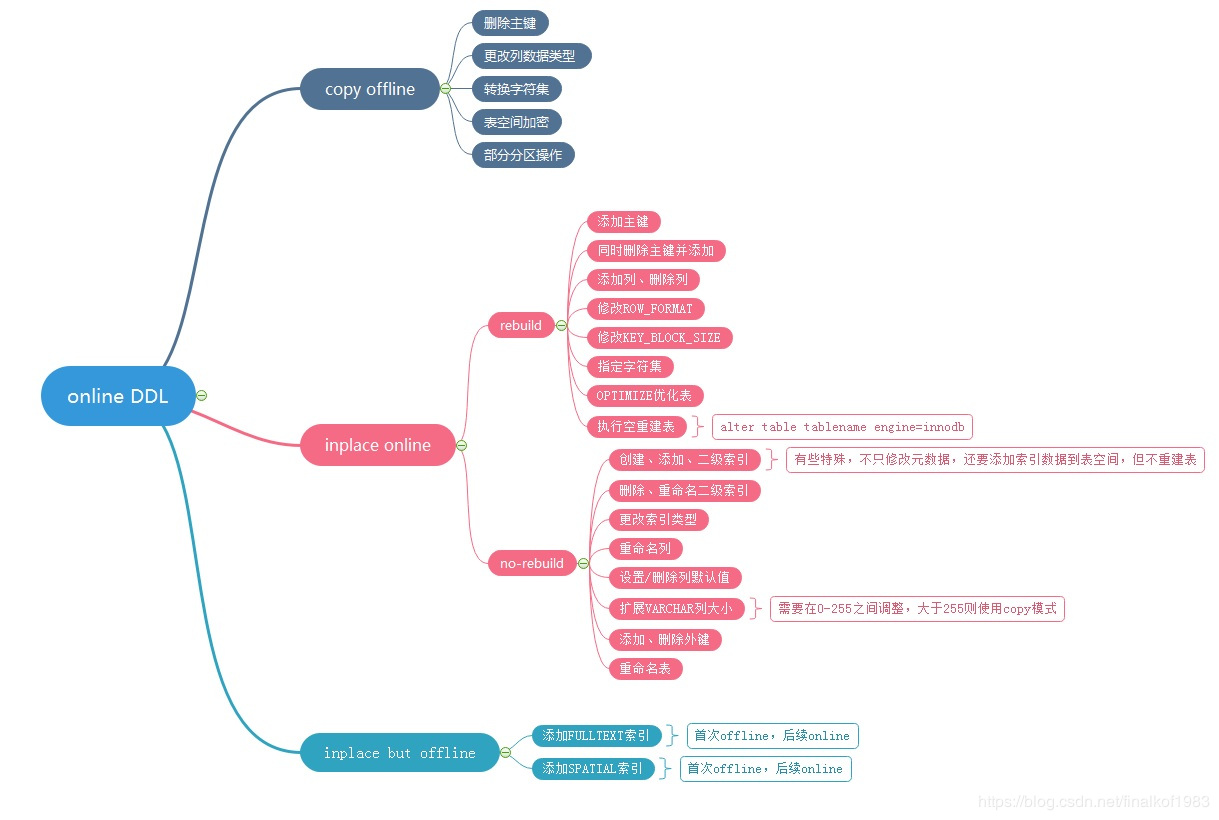
(image reproduced in https://blog.csdn.net/finalkof1983/article/details/88355314 )
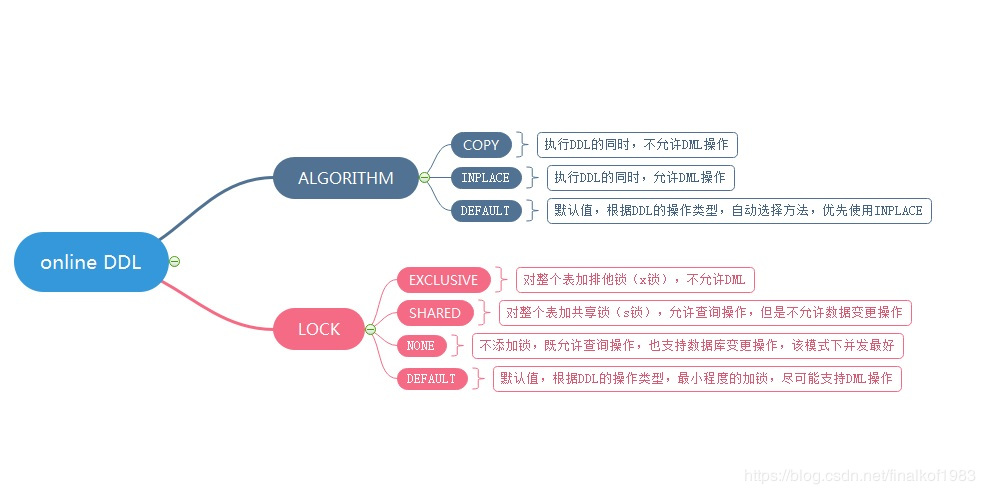
(image reproduced in https://blog.csdn.net/finalkof1983/article/details/88355314 )
3. Use tools to add online
Although the table can still be read and written when Online DDL adds fields, the tool Pt OSC or GH OST is used most for large table operations in production scenarios.
This paper mainly introduces Pt OSC (PT online schema change) to add fields. This command is the most frequently used one in Percona Toolkit
For the installation and main use of Percona Toolkit, please refer to Five minutes to learn how to install and use Percona Toolkit
Add field
root@mha1 ~]# pt-online-schema-change --alter "ADD COLUMN col4 int" h=localhost,P=3306,p=123456,u=root,D=testdb,t=tb_add_columns,S=/data/mysql3306/tmp/mysql.sock --charset=utf8mb4 --execute
The main process is as follows:
1> Cannot connect to A=utf8mb4,P=3306,S=/data/mysql3306/tmp/mysql.sock,h=192.168.28.132,p=...,u=root 1> Cannot connect to A=utf8mb4,P=3306,S=/data/mysql3306/tmp/mysql.sock,h=192.168.28.131,p=...,u=root No slaves found. See --recursion-method if host mha1 has slaves. # Because socket is used to connect to the database and the root remote connection account is not configured, this prompt will appear # A software update is available: Operation, tries, wait: analyze_table, 10, 1 copy_rows, 10, 0.25 create_triggers, 10, 1 drop_triggers, 10, 1 swap_tables, 10, 1 update_foreign_keys, 10, 1 Altering `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`... Creating new table... # Create an intermediate table named "_ Original table name_ new" Created new table testdb._tb_add_columns_new OK. Altering new table... # Modify the table, that is, add fields to the new table. Since the new table has no data, it will be added soon Altered `testdb`.`_tb_add_columns_new` OK. 2020-06-20T12:23:43 Creating triggers... # Create trigger, which is used to automatically synchronize data changes (add, modify, delete) in the original table to the new table during copying the original table to the new table 2020-06-20T12:23:43 Created triggers OK. 2020-06-20T12:23:43 Copying approximately 19920500 rows... # Copy data. The database volume is in the statistical information. It is not accurate Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 11% 03:50 remain # Copy data in batches (how much data is copied in each batch according to the table size). During the copying process, you can use show processlist to see the corresponding sql Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 22% 03:22 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 32% 03:10 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 42% 02:45 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 51% 02:21 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 62% 01:48 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 72% 01:21 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 81% 00:53 remain Copying `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`: 91% 00:24 remain 2020-06-20T12:28:40 Copied rows OK. # Copy data complete 2020-06-20T12:28:40 Analyzing new table... # Optimize new tables 2020-06-20T12:28:40 Swapping tables... # Exchange table name, change the original table to "_ Original table name_ old "and change the new table name to the original table name 2020-06-20T12:28:41 Swapped original and new tables OK. 2020-06-20T12:28:41 Dropping old table... # Delete the old table (or add parameters without deleting the old table) 2020-06-20T12:28:41 Dropped old table `testdb`.`_tb_add_columns_old` OK. 2020-06-20T12:28:41 Dropping triggers... # Delete trigger 2020-06-20T12:28:41 Dropped triggers OK. Successfully altered `testdb`.`tb_add_columns`. # complete
In the process of modification, reading and writing are not affected. You can write a program containing reading and writing
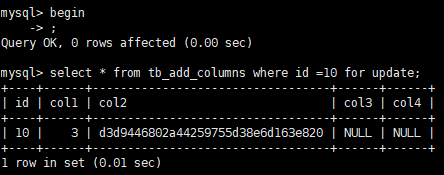
Note: whether you add fields directly or with Pt OSC, you need to obtain the metadata lock of the table before you can add it (including when Pt OSC creates triggers and exchanges table names at last). Therefore, if a table is a hot table, it cannot be added if it is read and written frequently or occupied by other sessions when it is added.
For example: lock a record
Add fields with Pt OSC, and you will find that you are stuck in the step of creating trigger all the time
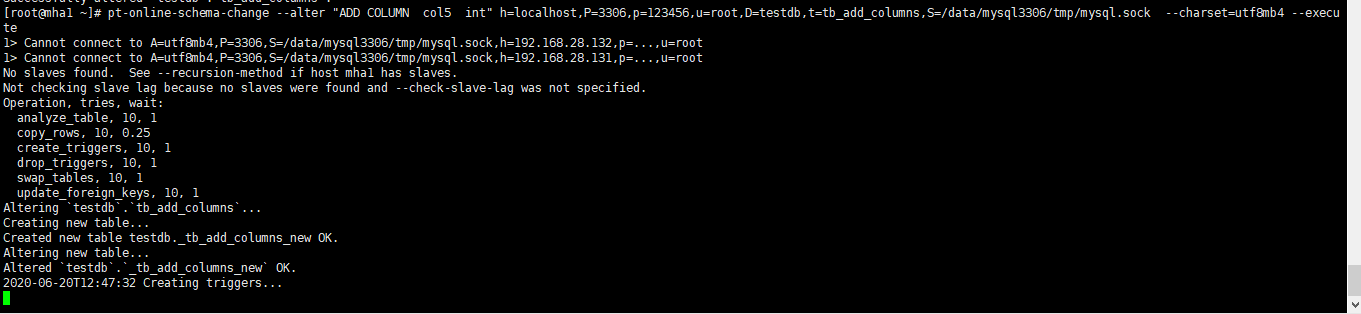
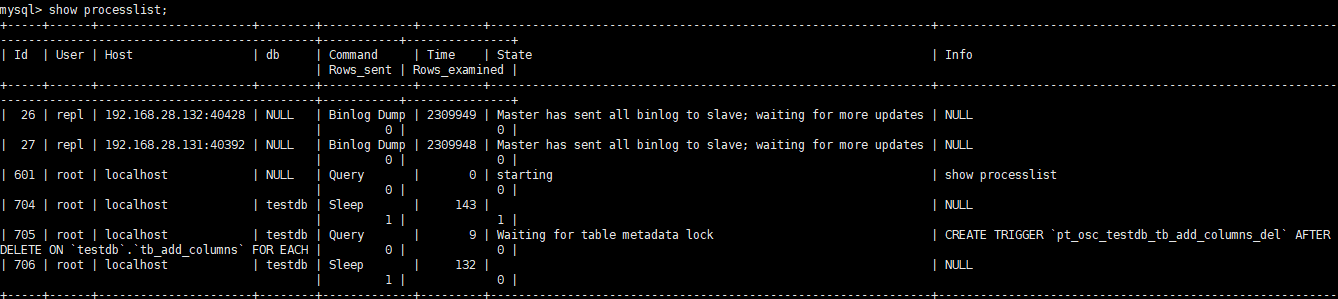
At this time, view the corresponding SQL and wait for metadata lock
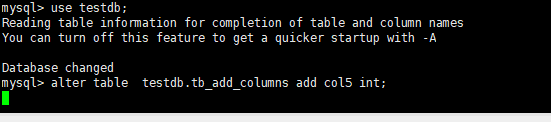
It's the same with adding directly, for example
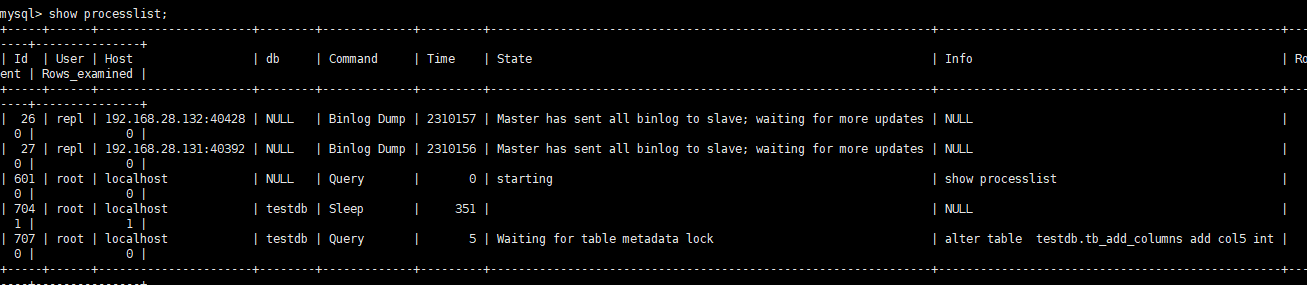
When the lock waiting is reached, an error will be reported to discard the added field
mysql> alter table testdb.tb_add_columns add col5 int; ERROR 1205 (HY000): Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
In this case, you need to wait for the system to be added when it is not busy, or use the subsequent master-slave switch after creating the slave library
4. Modify in the slave database first, and then switch between master and slave
Usage scenario: if a table in the above example has a large amount of data and is a hot table (read and write are particularly frequent), you can consider adding it to the slave database first, then switching between the master and slave, and then adding fields to several other nodes after switching.
First, add from the library (in this article, add from the alternative node)
mysql> alter table testdb.tb_add_columns add col5 int; Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 1.91 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
Switch between master and slave
Use MHA script to switch Online
masterha_master_switch --conf=/etc/masterha/app1.conf --master_state=alive --orig_master_is_new_slave --new_master_host=192.168.28.131 --new_master_port=3306
Add fields to other nodes after switching
/* Add 192.168.28.128 to the original master database */ mysql> alter table testdb.tb_add_columns add col5 int; Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 8.36 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 /* Another added 192.168.28.132 from the library */ mysql> alter table testdb.tb_add_columns add col5 int; Query OK, 0 rows affected (1 min 8.64 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
This completes the field addition.
5. Summary
There are three ways to add or modify fields in MySQL production environment. There are many precautions in actual use, so we need to summarize them.
- Add directly
If the reading and writing of the table is not frequent and the data volume is small (usually within 1G or a million), just add it directly (you can learn about online ddl)
- Use pt_osc add
If the table is large but the reading and writing is not too large, and you want to try not to affect the reading and writing of the original table, you can use percona tools to add, which is equivalent to creating a new table with added fields, then dropping the data of the original table to copy to the new table, and the data during the copying of historical data will also be synchronized to the new table, finally deleting the original table, renaming the new table to the name of the original table, and adding fields
- First add from library and then switch from master to slave
If a table has a large amount of data and is a hot table (read and write are particularly frequent), you can consider adding it to the slave database first, then switching between the master and slave, and then adding fields to several other nodes after switching